Related Research Articles

Mopti is the fifth administrative region of Mali, covering 79,017 km2. Its capital is the city of Mopti. During the 2012 Northern Mali conflict, the frontier between Southern Mali which is controlled by the central government and the rebel-held North ran through Mopti Region.

Bandiagara is a small town and urban commune in the Mopti Region of Mali. The name translates roughly to "large eating bowl"—referring to the communal bowl meals are served in. Mainly on its Bandiagara Escarpment it has about 2,000 speakers of the vibrant Bangime language, an isolate used mainly as an anti-language; it has the highest point of the country.
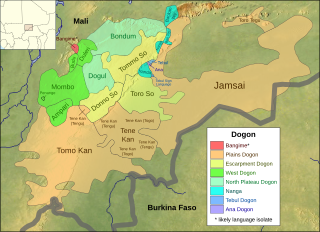
The Dogon languages are a small closely-related language family that is spoken by the Dogon people of Mali and may belong to the proposed Niger–Congo family. There are about 600,000 speakers of its dozen languages. They are tonal languages, and most, like Dogul, have two tones, but some, like Donno So, have three. Their basic word order is subject–object–verb.
Escarpment Dogon is a continuum of Dogon dialects of the Bandiagara Escarpment, including the standard language. There are three principal dialects:
Jamsay Dogon is one of the Dogon languages spoken in Mali, and the only one spoken in Burkina Faso apart from a few villages of Tomo Kan. It is one of the plains languages spoken in Dogon villages outside the Bandiagara Escarpment. It is a major language in Koro, at the south end of the escarpment, and stretches as far north as Douentza. It is not mutually intelligible with other Plains Dogon languages, but is widely known as the prestige variety due to its use as the language of radio broadcasts. Dialects are Domno tegu, Gono tegu, Bama tegu, and Guru tegu; their degree of mutual intelligibility has not been recorded. Domno is the standard dialect, and considered the purest; Guru (Koro) is the dialect of that town.
Jeffrey Heath is Professor of Historical Linguistics, Morphology, Arabic and Linguistic Anthropology at the University of Michigan, US. He is known particularly for his work in historical linguistics and for his extensive fieldwork.

Bangime is a language isolate spoken by 3,500 ethnic Dogon in seven villages in southern Mali, who call themselves the bàŋɡá–ndɛ̀. Bangande is the name of the ethnicity of this community and their population grows at a rate of 2.5% per year. The Bangande consider themselves to be Dogon, but other Dogon people insist they are not. Bangime is an endangered language classified as 6a - Vigorous by Ethnologue. Long known to be highly divergent from the (other) Dogon languages, it was first proposed as a possible isolate by Blench (2005). Research since then has confirmed that it appears to be unrelated to neighbouring languages. Heath and Hantgan have hypothesized that the cliffs surrounding the Bangande valley provided isolation of the language as well as safety for Bangande people. Even though Bangime is not related to Dogon languages, the Bangande still consider their language to be Dogon. Hantgan and List report that Bangime speakers seem unaware that it is not mutually intelligible with any Dogon language.
Sangha is a rural commune in the Cercle of Bandigara in the Mopti Region of Mali. The commune contains around 44 small villages and in the 2009 census had a population of 32,513. The administrative centre (chef-lieu) is the village of Sangha Ogol Leye, one of a cluster of at least 10 small villages at the top of the Bandiagara Escarpment.
Koro (Kɔ́rɔ́) is a town and commune and seat of the Cercle of Koro in the Mopti Region of Mali. At the 2009 Census, the commune had a population of 62,681.
Dinangourou is a village and commune of the Cercle of Koro in the Mopti Region of Mali. Jamsay Dogon is spoken in the village. A weekly Sunday market is hosted in the village. The local surname is Goro.
Dioungani is a village and commune of the Cercle of Koro in the Mopti Region of Mali. Jamsay Dogon is spoken in the commune.
Baboye or Baboy is a village and seat of the commune of Pignari in the Cercle of Bandiagara in the Mopti Region of southern-central Mali.
Dé is a village and seat of the commune of Diamnati in the Cercle of Bandiagara of the Mopti Region of southern-central Mali.
Déguéré is a village and seat of the commune of Bamba in the Cercle of Koro in the Mopti Region of southern-central Mali. The village sits on the edge of the Dogon Plateau.

Dogon country is a region of eastern Mali and northwestern Burkina Faso populated mainly by the Dogon people, a diverse ethnic group in West Africa with diverse languages. Like the term Serer country occupied by the Serer ethnic group, Dogon country is vast, and lies southwest of the Niger River belt. The region is composed of three zones: the plateau, the escarpment and the Seno-Gondo plain.
Budu Dogon or Bunoge, also known as Korandabo, is a recently discovered Dogon language spoken in Mali. It was first reported online. The plural suffix on nouns is closest to Kolum so, suggesting it should be classified as a West Dogon language.
Yanda Dogon is a Dogon language spoken in Mali. It is reported to be lexically similar to Nanga, which is only known from one report from 1953.
The Toro language, Tɔrɔ tegu 'Mountain speech', is a Dogon language spoken in Mali. It is closest to the prestige variety of Dogon, Jamsay tegu, though speakers deny they are related and understand little of it. Hochstetler report difficulties in comprehension between Tɔrɔ tegu and one of the western Plains Dogon languages, Tomo kan.
The Dogon dialects of the western plains below the Bandiagara Escarpment is Mali are mutually intelligible. They are sometimes called the Kan Dogon because they use the word kan for varieties of speech. The dialects are:
Chrotogonus senegalensis is a species of grasshopper in the family Pyrgomorphidae. It is found in the Sahel of Africa and in Central Africa.
References
- ↑ Heath, Jeffrey (September 2016). "A grammar of Penange (Dogon, Mali)". p. 2.
- ↑ Heath, Jeffrey (September 2016). "A grammar of Penange (Dogon, Mali)". p. 1.
