The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to chemistry:

In chemistry, many authors consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds, however, some authors consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. The definition of "organic" versus "inorganic", and whether some other carbon-containing compounds are organic or inorganic vary from author to author, and are topics of debate. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes and its derivatives are considered organic, but many others are considered inorganic, such as halides of carbon without carbon-hydrogen and carbon-carbon bonds, and certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen.
The Beilstein database is the largest database in the field of organic chemistry, in which compounds are uniquely identified by their Beilstein Registry Number. The database covers the scientific literature from 1771 to the present and contains experimentally validated information on millions of chemical reactions and substances from original scientific publications. The electronic database was created from Handbuch der Organischen Chemie, founded by Friedrich Konrad Beilstein in 1881, but has appeared online under a number of different names, including Crossfire Beilstein. Since 2009, the content has been maintained and distributed by Elsevier Information Systems in Frankfurt under the product name "Reaxys".
The Journal of the Chemical Society was a scientific journal established by the Chemical Society in 1849 as the Quarterly Journal of the Chemical Society. The first editor was Edmund Ronalds. The journal underwent several renamings, splits, and mergers throughout its history. In 1980, the Chemical Society merged with several other organizations into the Royal Society of Chemistry. The journal's continuity is found in Chemical Communications, Dalton Transactions, Faraday Transactions, and Perkin Transactions, all of which are published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
The National Academy of Sciences Award in Chemical Sciences is awarded for innovative research in the chemical sciences that in the broadest sense contributes to a better understanding of the natural sciences and to the benefit of humanity.

Ditellurium bromide is the inorganic compound with the formula Te2Br. It is one of the few stable lower bromides of tellurium. Unlike sulfur and selenium, tellurium forms families of polymeric subhalides where the halide/chalcogen ratio is less than 2.

The CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics is a comprehensive one-volume reference resource for science research. First published in 1914, it is currently in its 103rd edition, published in 2022. It is sometimes nicknamed the "Rubber Bible" or the "Rubber Book", as CRC originally stood for "Chemical Rubber Company".

Bismuth titanate or bismuth titanium oxide is a solid inorganic compound of bismuth, titanium and oxygen with the chemical formula of Bi12TiO20, Bi 4Ti3O12 or Bi2Ti2O7.

Pentamethyltantalum is a homoleptic organotantalum compound. It has a propensity to explode when it is melted. Its discovery was part of a sequence that lead to Richard R. Schrock's Nobel Prize discovery in olefin metathesis.
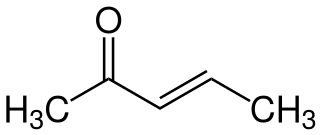
3-Penten-2-one is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH=CHCH3. It exists as (E) and (Z) stereoisomers. The compound is classified as an α,β-unsaturated ketone. It is a colorless volatile liquid with fruity to pungent odor.

Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and fluorine with the chemical formula YbF2.

Berkelium(III) iodide is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and iodine with the chemical formula BkI3.

Iodine dioxide is a binary inorganic compound of iodine and oxygen with the chemical formula IO
2. This compound is one of many iodine oxides.
Actinium oxyfluoride is an inorganic compound, with the chemical formula AcOF. It is radioactive. It crystallises in a calcium fluoride structure. It can be obtained by reacting actinium fluoride with ammonia and water:
Einsteinium fluoride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and fluorine with the chemical formula EsF3.
Einsteinium(II) chloride is a binary inorganic chemical compound of einsteinium and chlorine with the chemical formula EsCl2.

Tetrachloroethylene oxide, perchloroethylene oxide (PCEO) or tetrachlorooxirane, is the perchlorinated analogue of ethylene oxide and a proposed metabolite of tetrachloroethylene. It is a halogenated epoxide with the formula C2Cl4O. Tetrachloroethylene oxide is fairly stable, but rearranges to trichloroacetyl chloride at higher temperatures.










