IRIX is a discontinued operating system developed by Silicon Graphics (SGI) to run on the company's proprietary MIPS workstations and servers. It is based on UNIX System V with BSD extensions. In IRIX, SGI originated the XFS file system and the industry-standard OpenGL graphics system.

MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter, and "SQL", the abbreviation for Structured Query Language. A relational database organizes data into one or more data tables in which data types may be related to each other; these relations help structure the data. SQL is a language programmers use to create, modify and extract data from the relational database, as well as control user access to the database. In addition to relational databases and SQL, an RDBMS like MySQL works with an operating system to implement a relational database in a computer's storage system, manages users, allows for network access and facilitates testing database integrity and creation of backups.
Open Inventor, originally IRIS Inventor, is a C++ object oriented retained mode 3D graphics toolkit designed by SGI to provide a higher layer of programming for OpenGL. Its main goals are better programmer convenience and efficiency. Open Inventor exists as both proprietary software and free and open-source software, subject to the requirements of the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL), version 2.1.
GLX is an extension to the X Window System core protocol providing an interface between OpenGL and the X Window System as well as extensions to OpenGL itself. It enables programs wishing to use OpenGL to do so within a window provided by the X Window System. GLX distinguishes two "states": indirect state and direct state.
Nagios Core, formerly known as Nagios, is a free and open-source computer-software application that monitors systems, networks and infrastructure. Nagios offers monitoring and alerting services for servers, switches, applications and services. It alerts users when things go wrong and alerts them a second time when the problem has been resolved.
Linux Terminal Server Project (LTSP) is a free and open source terminal server for Linux that allows many people to simultaneously use the same computer. Applications run on the server with a terminal known as a thin client handling input and output. Generally, terminals are low-powered, lack a hard disk and are quieter and more reliable than desktop computers because they do not have any moving parts.

Kontact is a personal information manager and groupware software suite developed by KDE. It supports calendars, contacts, notes, to-do lists, news, and email. It offers a number of inter-changeable graphical UIs all built on top of a common core.
A Web Map Service (WMS) is a standard protocol developed by the Open Geospatial Consortium in 1999 for serving georeferenced map images over the Internet. These images are typically produced by a map server from data provided by a GIS database.

Vertica Systems is an analytic database management software company. Vertica was founded in 2005 by database researcher Michael Stonebraker and Andrew Palmer. Palmer was the founding CEO. Ralph Breslauer and Christopher P. Lynch served as later CEOs.

The open-core model is a business model for the monetization of commercially produced open-source software. Coined by Andrew Lampitt in 2008, the open-core model primarily involves offering a "core" or feature-limited version of a software product as free and open-source software, while offering "commercial" versions or add-ons as proprietary software.

ERPNext is a free and open-source integrated Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software developed by Frappe Technologies Pvt. Ltd. and is built on MariaDB database system using Frappe, a Python based server-side framework.
CopperEgg Corporation is a cloud computing systems management company based out of Austin, Texas. CopperEgg provides a family of Software as a Service (SaaS) based cloud monitoring services for public and private cloud environments. These services include server monitoring, website monitoring, and web application monitoring that track system and application performance, and alerts on and helps troubleshoot system and application issues. CRN Magazine included the company on its list of 10 hot new cloud startups to watch in 2011. In 2013, the company was recognized with the North America Frost & Sullivan Award for New Product Innovation within Cloud Monitoring Solutions. The company has strategic partnerships with companies such as Amazon AWS, advanced technical partner; Rackspace; SolarWinds; and Blitz IO.

icCube is a company founded in Switzerland that provides business intelligence (BI) software of the same name. The software can be fully embedded, can be hosted in a managed environment or installed in a customer's machine on premises.
OpenLMI provides a common management infrastructure for Linux systems. Available operations include configuration of various operating system parameters and services, hardware components configuration, and monitoring of system resources. Services provided by OpenLMI can be accessed both locally and remotely, using multiple programming languages and standardized APIs.

OpenIO offers object storage for a wide range of high-performance applications. OpenIO was founded in 2015 by Laurent Denel (CEO), Jean-François Smigielski (CTO) and five other co-founders; it has leveraged open source software, developed since 2006, based on a grid technology that enables dynamic behaviour and supports heterogenous hardware. In October 2017 OpenIO completed a $5 million funding round. In July 2020 OpenIO has been acquired by OVH.

Prometheus is a free software application used for event monitoring and alerting. It records real-time metrics in a time series database built using a HTTP pull model, with flexible queries and real-time alerting. The project is written in Go and licensed under the Apache 2 License, with source code available on GitHub, and is a graduated project of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation, along with Kubernetes and Envoy.

Element is a free and open-source software instant messaging client implementing the Matrix protocol.
Microsoft, a technology company historically known for its opposition to the open source software paradigm, turned to embrace the approach in the 2010s. From the 1970s through 2000s under CEOs Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer, Microsoft viewed the community creation and sharing of communal code, later to be known as free and open source software, as a threat to its business, and both executives spoke negatively against it. In the 2010s, as the industry turned towards cloud, embedded, and mobile computing—technologies powered by open source advances—CEO Satya Nadella led Microsoft towards open source adoption although Microsoft's traditional Windows business continued to grow throughout this period generating revenues of 26.8 billion in the third quarter of 2018, while Microsoft's Azure cloud revenues nearly doubled.
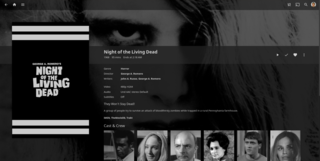
Jellyfin is a suite of multimedia applications designed to organize, manage, and share digital media files to networked devices. Jellyfin consists of a server application installed on a machine running Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux or in a Docker container, and another application running on a client device such as a smartphone, tablet, smart TV, streaming media player, game console or in a web browser. Jellyfin also can serve media to DLNA and Chromecast-enabled devices. It is a free and open-source software fork of Emby.










