
MIDI is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. The specification originates in the paper Universal Synthesizer Interface published by Dave Smith and Chet Wood of Sequential Circuits at the 1981 Audio Engineering Society conference in New York City.

A sound card is an internal expansion card that provides input and output of audio signals to and from a computer under the control of computer programs. The term sound card is also applied to external audio interfaces used for professional audio applications.

Digital music technology encompasses digital instruments, computers, electronic effects units, software, or digital audio equipment by a performer, composer, sound engineer, DJ, or record producer to produce, perform or record music. The term refers to electronic devices, instruments, computer hardware, and software used in performance, playback, recording, composition, mixing, analysis, and editing of music.
A music sequencer is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open Sound Control (OSC), and possibly audio and automation data for DAWs and plug-ins.

MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by Microsoft and ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, then vice-president at Microsoft and director at ASCII Corporation. Microsoft and Nishi conceived the project as an attempt to create unified standards among various home computing system manufacturers of the period, in the same fashion as the VHS standard for home video tape machines. The first MSX computer sold to the public was a Mitsubishi ML-8000, released on October 21, 1983, thus marking its official release date.

Sound Blaster is a family of sound cards designed by Singaporean technology company Creative Technology. Sound Blaster sound cards were the de facto standard for consumer audio on the IBM PC compatible system platform, until the widespread transition to Microsoft Windows 95, which standardized the programming interface at application level, and the evolution in PC design led to onboard audio electronics, which commoditized PC audio functionality. By 1995, Sound Blaster cards had sold over 15 million units worldwide and accounted for seven out of ten sound card sales.

A sampler is an electronic or digital musical instrument which uses sound recordings of real instrument sounds, excerpts from recorded songs or found sounds. The samples are loaded or recorded by the user or by a manufacturer. These sounds are then played back by means of the sampler program itself, a MIDI keyboard, sequencer or another triggering device to perform or compose music. Because these samples are usually stored in digital memory, the information can be quickly accessed. A single sample may often be pitch-shifted to different pitches to produce musical scales and chords.

A digital audio workstation (DAW) is an electronic device or application software used for recording, editing and producing audio files. DAWs come in a wide variety of configurations from a single software program on a laptop, to an integrated stand-alone unit, all the way to a highly complex configuration of numerous components controlled by a central computer. Regardless of configuration, modern DAWs have a central interface that allows the user to alter and mix multiple recordings and tracks into a final produced piece.
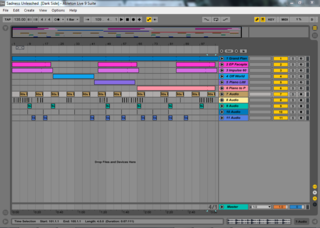
Ableton Live is a digital audio workstation for macOS and Windows developed by the German company Ableton. In contrast to many other software sequencers, Ableton Live is designed to be an instrument for live performances as well as a tool for composing, recording, arranging, mixing, and mastering. It is also used by DJs, as it offers a suite of controls for beatmatching, crossfading, and other different effects used by turntablists, and was one of the first music applications to automatically beatmatch songs. Live is available in three editions: Intro, Standard, and Suite.

The Korg Triton is a music workstation synthesizer, featuring digital sampling and sequencing, released in 1999. It uses Korg's HI Synthesis tone generator and was eventually available in several model variants with numerous upgrade options. The Triton became renowned as a benchmark of keyboard technology, and has been widely featured in music videos and live concerts. At the NAMM 2007, Korg announced the Korg M3 as its successor.

The Gravis UltraSound or GUS is a sound card for the IBM PC compatible system platform, made by Canada-based Advanced Gravis Computer Technology Ltd. It was very popular in the demoscene during the 1990s.

The MPU-401, where MPU stands for MIDI Processing Unit, is an important but now obsolete interface for connecting MIDI-equipped electronic music hardware to personal computers. It was designed by Roland Corporation, which also co-authored the MIDI standard.
Doepfer Musikelektronik GmbH is a German manufacturer of audio hardware, mostly synthesizer modules, based in Gräfelfing, Upper Bavaria and founded by Dieter Döpfer. The product range covers analog modular systems, MIDI controllers, MIDI hardware sequencers, MIDI-to-CV/Gate/Sync Interfaces, MIDI master keyboards and special MIDI equipment.

The Soundscape ELITE was Ensoniq's high-end ISA PC sound card offering. It offers the highest MIDI quality of any PC sound card Ensoniq produced. The board is an evolution of the company's previous Soundscape S-2000. The Soundscape ELITE was launched in March 1995.

The Sound Blaster AWE32 is an ISA sound card from Creative Technology. It is an expansion board for PCs and is part of the Sound Blaster family of products. The Sound Blaster AWE32, introduced in March 1994, was a near full-length ISA sound card, measuring 14 inches (356 mm) in length, due to the number of features included.

LMMS is a digital audio workstation application program. It allows music to be produced by arranging samples, synthesizing sounds, playing on a MIDI keyboard, and combining the features of trackers and sequencers. It supports the Linux Audio Developer's Simple Plugin API (LADSPA), LV2 and Virtual Studio Technology (VST) plug-ins. It is free and open source software, written in Qt and released under GPL-2.0-or-later.
Moonsound is the name of a sound card released for the MSX home-computer system at the Tilburg Computer Fair in 1995. It was designed by electronic engineer Henrik Gilvad and produced by Sunrise Swiss on a semi-hobby basis.

The Yamaha Y8950 is a sound chip, produced in 1984. It is also known as MSX-Audio as it was designed for inclusion in an expansion cartridge for the MSX personal computer.

Yamaha CX5M is an MSX-system compatible computer that expands upon the normal features expected from these systems with a built-in eight-voice FM synthesizer module, introduced in 1984 by Yamaha Corporation.















