
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are highly carcinogenic chemical compounds, formerly used in industrial and consumer products, whose production was banned in the United States by the Toxic Substances Control Act in 1976 and internationally by the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants in 2001.
Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs), or simply dioxins, are a group of long-lived polyhalogenated organic compounds that are primarily anthropogenic, and contribute toxic, persistent organic pollution in the environment.
Polybrominated diphenyl ethers or PBDEs, are a class of organobromine compounds that are used as flame retardants. Like other brominated flame retardants, PBDEs have been used in a wide array of products, including building materials, electronics, furnishings, motor vehicles, airplanes, plastics, polyurethane foams, and textiles. They are structurally akin to polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and other polyhalogenated compounds, consisting of two halogenated aromatic rings. PBDEs are classified according to the average number of bromine atoms in the molecule. The health hazards of these chemicals have attracted increasing scrutiny, and they have been shown to reduce fertility in humans at levels found in households. Because of their toxicity and persistence, the industrial production of some PBDEs is restricted under the Stockholm Convention, a treaty to control and phase out major persistent organic pollutants (POPs).
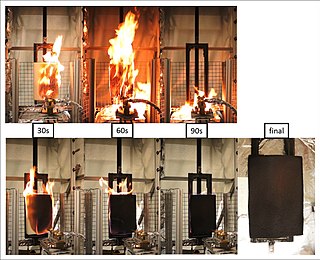
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and are intended to prevent or slow the further development of ignition by a variety of different physical and chemical methods. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive.
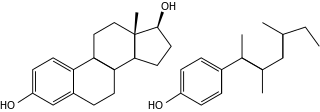
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine systems. These disruptions can cause cancerous tumors, birth defects, and other developmental disorders. Found in many household and industrial products, endocrine disruptors "interfere with the synthesis, secretion, transport, binding, action, or elimination of natural hormones in the body that are responsible for development, behavior, fertility, and maintenance of homeostasis ."
Halocarbon compounds are chemicals in which one or more carbon atoms are linked by covalent bonds with one or more halogen atoms resulting in the formation of organofluorine compounds, organochlorine compounds, organobromine compounds, and organoiodine compounds. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochlorides.
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds containing at least one covalently bonded atom of chlorine. The chloroalkane class includes common examples. The wide structural variety and divergent chemical properties of organochlorides lead to a broad range of names, applications, and properties. Organochlorine compounds have wide use in many applications, though some are of profound environmental concern, with TCDD being one of the most notorious.
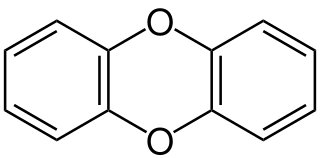
Dibenzo-1,4-dioxin, also dibenzodioxin or dibenzo-p-dioxin (dibenzo-para-dioxin), is a polycyclic heterocyclic organic compound in which two benzene rings are connected by a 1,4-dioxin ring. Its molecular formula is C12H8O2. The two oxygen atoms occupy opposite (para-) positions in the six-membered dioxin ring.

Persistent organic pollutants (POPs) are organic compounds that are resistant to degradation through chemical, biological, and photolytic processes. They are toxic chemicals that adversely affect human health and the environment around the world. Because they can be transported by wind and water, most POPs generated in one country can and do affect people and wildlife far from where they are used and released.
Brominated flame retardants (BFRs) are organobromine compounds that have an inhibitory effect on combustion chemistry and tend to reduce the flammability of products containing them. The brominated variety of commercialized chemical flame retardants comprise approximately 19.7% of the market. They are effective in plastics and textile applications like electronics, clothes and furniture.
Xenoestrogens are a type of xenohormone that imitates estrogen. They can be either synthetic or natural chemical compounds. Synthetic xenoestrogens include some widely used industrial compounds, such as PCBs, BPA, and phthalates, which have estrogenic effects on a living organism even though they differ chemically from the estrogenic substances produced internally by the endocrine system of any organism. Natural xenoestrogens include phytoestrogens which are plant-derived xenoestrogens. Because the primary route of exposure to these compounds is by consumption of phytoestrogenic plants, they are sometimes called "dietary estrogens". Mycoestrogens, estrogenic substances from fungi, are another type of xenoestrogen that are also considered mycotoxins.
Pentabromodiphenyl ether is a brominated flame retardant which belongs to the group of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Because of their toxicity and persistence, their industrial production is to be eliminated under the Stockholm Convention, a treaty to control and phase out major persistent organic pollutants (POP).

1,4-Dioxin (also referred as dioxin or p-dioxin) is a heterocyclic, organic, non-aromatic compound with the chemical formula C4H4O2. There is an isomeric form of 1,4-dioxin, 1,2-dioxin (or o-dioxin). 1,2-Dioxin is very unstable due to its peroxide-like characteristics.

Octachlorodibenzodioxin is one of polychlorinated dibenzodioxins (PCDDs).

Dioxins and dioxin-like compounds (DLCs) are a group of chemical compounds that are persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in the environment. They are mostly by-products of burning or various industrial processes or, in the case of dioxin-like PCBs and PBBs, unwanted minor components of intentionally produced mixtures.
Polychlorinated diphenyl ethers (PCDEs) are structurally similar to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), both which may be toxic polyhalogenated compounds and some PCDE congeners have been reported to cause toxic responses similar to those caused by some of the non-ortho-substituted PCBs, which are mediated by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR).
Toxic equivalency factor (TEF) expresses the toxicity of dioxins, furans and PCBs in terms of the most toxic form of dioxin, 2,3,7,8-TCDD. The toxicity of the individual congeners may vary by orders of magnitude.
Persistent, bioaccumulative and toxic substances (PBTs) are a class of compounds that have high resistance to degradation from abiotic and biotic factors, high mobility in the environment and high toxicity. Because of these factors PBTs have been observed to have a high order of bioaccumulation and biomagnification, very long retention times in various media, and widespread distribution across the globe. Most PBTs in the environment are either created through industry or are unintentional byproducts.

In chemistry, congeners are chemical substances "related to each other by origin, structure, or function".
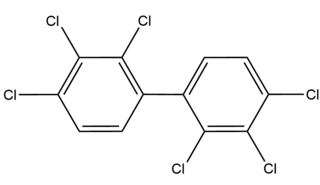
2,2',3,3',4,4'-Hexachlorobiphenyl is an organic chemical and belongs to a group of compounds called polychlorinated biphenyls. This group of organic compounds was used in transformers as dielectric fluids, until production was banned in 1979. While only being a part of this mixture, it is sometimes referred to as Aroclor 1260.








