Borland Software Corporation was a computer technology company founded in 1983 by Niels Jensen, Ole Henriksen, Mogens Glad, and Philippe Kahn. Its main business was the development and sale of software development and software deployment products. Borland was first headquartered in Scotts Valley, California, then in Cupertino, California, and then in Austin, Texas. In 2009, the company became a full subsidiary of the British firm Micro Focus International plc.

IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones. The term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, since IBM no longer sells personal computers after it sold its personal computer division in 2005 to Chinese technology company Lenovo. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "personal computer" generally, but rather an x86 computer capable of running the same software that a contemporary IBM PC could. The term was initially in contrast to the variety of home computer systems available in the early 1980s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore 64. Later, the term was primarily used in contrast to Apple's Macintosh computers.

The Lattice C Compiler was released in June 1982 by Lifeboat Associates and was the first C compiler for the IBM Personal Computer. The compiler sold for $500 and would run on PC DOS or MS-DOS. The first hardware requirements were given as 96KB of RAM and one floppy drives. It was ported to many other platforms, such as mainframes (MVS), minicomputers (VMS), workstations (UNIX), OS/2, the Commodore Amiga, Atari ST and the Sinclair QL.
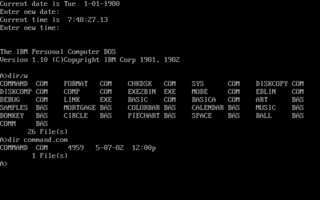
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM Personal Computer Disk Operating System, is a discontinued disk operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, its successors, and IBM PC compatibles. It was manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s. Developed by Microsoft, it was also sold by that company as MS-DOS. Both operating systems were identical or almost identical until 1993, when IBM began selling PC DOS 6.1 with new features. The collective shorthand for PC DOS and MS-DOS was DOS, which is also the generic term for disk operating system, and is shared with dozens of disk operating systems called DOS.

R:BASE is a relational database program for the PC created by Wayne Erickson in 1981. Erickson and his brother, Ron Erickson, incorporated the company, MicroRim, Inc. to sell the database, MicroRIM, on November 13, 1981.
Xara is an international software company founded in 1981, with an HQ in Berlin and development office in Hemel Hempstead, UK. It has developed software for a variety of computer platforms, in chronological order: the Acorn Atom, BBC Micro, Z88, Atari ST, Acorn Archimedes, Microsoft Windows, Linux, and more recently web browser-based services.

OrCAD Systems Corporation was a software company that made OrCAD, a proprietary software tool suite used primarily for electronic design automation (EDA). The software is used mainly by electronic design engineers and electronic technicians to create electronic schematics, and perform mixed-signal simulation and electronic prints for manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs). OrCAD was taken over by Cadence Design Systems in 1999 and was integrated with Cadence Allegro in 2005.
Interactive Systems Corporation was a US-based software company and the first vendor of the Unix operating system outside AT&T, operating from Santa Monica, California. It was founded in 1977 by Peter G. Weiner, a RAND Corporation researcher who had previously founded the Yale University computer science department and had been the Ph. D. advisor to Brian Kernighan, one of Unix's developers at AT&T. Weiner was joined by Heinz Lycklama, also a veteran of AT&T and previously the author of a Version 6 Unix port to the LSI-11 computer.
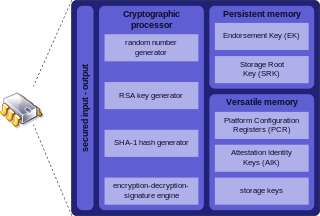
Trusted Platform Module is an international standard for a secure cryptoprocessor, a dedicated microcontroller designed to secure hardware through integrated cryptographic keys. The term can also refer to a chip conforming to the standard.
Hilgraeve is a software firm based in Monroe, Michigan, and is best known for its HyperTerminal Private Edition and HyperACCESS programs. In earlier years, HyperTerminal had been licensed for use by Microsoft in versions of Windows ranging from Windows 95 to Windows XP.
PVCS Version Manager is a software package by Serena Software Inc., for version control of source code files.
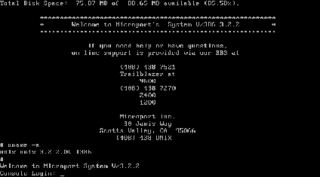
Microport Systems (1985–2002) was a software development group that pioneered a new approach towards software ports that dramatically reduced development costs and, consequently, the price charged for UNIX. Microport created the first ports of AT&T's UNIX System V for the IBM 286 and 386 personal computers, as well as IBM's PS/2 systems. Microport was critical to enabling the Free Software Foundation (FSF) to port its GNU C compiler (gcc) and associated utilities, onto the x86 architecture by donating a complete 386 development system to the Richard Stallman-led group. Microport also played a key role in Kevin Mitnick's first arrest, after he broke into the internal computer networks of both Microport and The Santa Cruz Operation.

NetObjects, Inc. is a software company founded in 1995 by Samir Arora, David Kleinberg, Clement Mok and Sal Arora. The company is best known for the development of NetObjects Fusion, a web design application for small and medium enterprises with designers who need complete control over page layout and a similar user interface as desktop publishing applications.
Central Point Software, Inc. was a leading software utilities maker for the PC market, supplying utilities software for the DOS and Microsoft Windows markets. It also made Apple II copy programs. Through a series of mergers, the company was ultimately acquired by Symantec in 1994.
Micro Focus International plc was a British multinational software and information technology business based in Newbury, Berkshire, England. The firm provided software and consultancy. The company was listed on the London Stock Exchange and the New York Stock Exchange until it was acquired by the Canadian software firm OpenText in January 2023.
This article presents a timeline of events in the history of 16-bit x86 DOS-family disk operating systems from 1980 to present. Non-x86 operating systems named "DOS" are not part of the scope of this timeline.
Synex Systems Corporation, a subsidiary of Synex International Inc. was formed in 1983 in an effort to develop software for the microcomputer market and was run by Synex International Vice President Murray Hendren until 1992. In 2002, Synex Systems was acquired by privately owned Lasata Software of Perth, Australia. In 2005, Lasata was acquired by UK based Systems Union. In 2007, Systems Union was acquired by privately held Infor Global Solutions, a U.S. company that specializes in enterprise software.
With operations in 11 countries, Serena Software Inc. is an American software company that provides IT management products to enterprises. Serena solutions offer a process orchestration approach and span the areas of development, DevOps and IT management.
Dimensions CM is a software change and configuration management product developed by Micro Focus. It includes revision control, change, build and release management capabilities.







