Related Research Articles
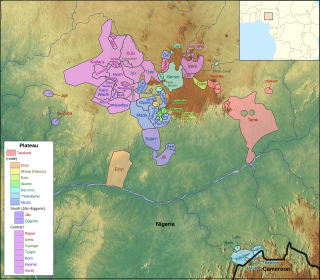
The forty or so Plateau languages are a tentative group of Benue–Congo languages spoken by 15 million people on the Jos Plateau Southern Kaduna, Nassarawa State and in adjacent areas in central Nigeria.

There are over 527 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language of Nigeria is English, the language of former colonial British Nigeria. As reported in 2003, Nigerian English and Nigerian Pidgin were spoken as a second language by 100 million people in Nigeria. Communication in the English language is much more popular in the country's urban communities than it is in the rural areas, due to globalization.
Nupe is a Volta–Niger language of the Nupoid branch primarily spoken by the Nupe people of the North Central region of Nigeria. Its geographical distribution stretches and maintains pre-eminence in Niger State as well as Kwara, Kogi, Lagos and the Federal Capital Territory.
Chakato is a West Chadic language spoken in Plateau State, Nigeria. It was identified by Roger Blench in 2016. It is spoken by about 500 people in one village, Dokan Tofa, which is located on the Jos-Shendam road in Plateau State. Blench (2017) suggests that Chakato may be related to spurious records of the Jorto language. Chakato speakers claim that their language is closely related to Goemai.
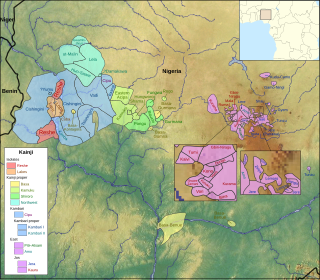
The Kainji languages are a group of about 60 related languages spoken in west-central Nigeria. They form part of the Central Nigerian (Platoid) branch of Benue–Congo.
Cipu (Cicipu), or Western Acipa, is a Kainji language spoken by about 20,000 people in northwest Nigeria. The people call themselves Acipu, and are called Acipawa in Hausa.
Basa-Gumna is an extinct Kainji language of Nigeria. It was spoken in Chanchaga, Niger state, and Nasarawa, near the Basa homeland. Speakers have shifted to Hausa.
u̠t-Ma’in or Fakai is a Northwest Kainji dialect continuum spoken by 36,000 people in the Fakai district of Nigeria. There are numerous rather divergent dialects:
The Shiroro languages, also known as the Pongu languages, form a branch of the Kainji languages of Nigeria. They are spoken near Shiroro Lake.
Adara, is a Plateau language of Nigeria. The name Adara is also used to refer to the ethnic group.
The Kamuku languages are a branch of the Kainji languages spoken by the Kamuku people of Niger State, western Nigeria, mostly in Mariga and Rafi LGAs.
Reshe is the most divergent of the Kainji languages of Nigeria. It is spoken on the northern and southern sides of Kainji Lake. It is spoken in Yauri LGA, Kebbi State, and in Borgu LGA, Niger State.
Bauchi is a cluster of Kainji languages spoken in Rafi, Nigeria LGA, Niger State, Nigeria.
Lopa consists of a pair of minor Kainji languages of Nigeria. Ethnic Lopa neighbouring the Busa language have shifted to that language.
Ura language, or Ura they also known as Ɓurawa (Ɓura), is a Kainji language of Niger State, Nigeria.
Rogo is a Kainji language of Nigeria. It is spoken around the town of Ucanja in the Rafi and Mariga Local Government Areas of Niger State, as well as the Birnin Gwari LGA of neighbouring Kaduna State.
Shama, or Shama-Sambuga after its two dialects, is a Kainji language of Nigeria.
Ziriya (Jiriya) and Sheni (Shaini) constitute a Kainji language of Nigeria. They are geographically but perhaps not linguistically distinct.
Yumu is a minor Kainji language of Nigeria. It is listed as a potential Kambari language by Roger Blench, however it does not have an Ethnologue nor Glottolog entry.

Tegina is a town in Rafi LGA, Niger State, Nigeria. Various Kainji languages are spoken in and around Tegina.
References
- ↑ Pongu at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- 1 2 3 Blench, Roger (2012). "The Kainji languages of northwestern and central Nigeria" (PDF). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.