Cabinda is an exclave and province of Angola, a status that has been disputed by several political organizations in the territory. The capital city is also called Cabinda, known locally as Tchiowa. The province is divided into four municipalities—Belize, Buco-Zau, Cabinda and Cacongo.

Bandundu is one of eleven former provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It bordered the provinces of Kinshasa and Bas-Congo to the west, Équateur to the north, and Kasai-Occidental to the east. The provincial capital is also called Bandundu.

The Kasai River is a tributary of the Congo River, located in Central Africa. The river begins in central Angola and flows to the east until it reaches the border between Angola and the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), where it turns north and serves as the border until it flows into the DRC. From Ilebo, between the confluences with Lulua river and Sankuru river, the Kasai river turns to a westerly direction. The lower stretch of the river from the confluence with Fimi river, is known as the Kwa(h) River, before it joins the Congo at Kwamouth northeast of Kinshasa. The Kasai basin consists mainly of equatorial rainforest areas, which provide an agricultural land in a region noted for its infertile, sandy soil. It is a tributary of Congo river and diamonds are found in this river. Around 60% of diamonds in Belgium go from Kasai river for cutting and shaping.

The Yaka are an African ethnic group found in southwestern Democratic Republic of the Congo, with Angola border to their west. They number about 300,000 and are related to the Suku people. They live in the forest and savanna region between the Kwango River and the Wamba River. They speak the Yaka language).

Hermenegildo de Brito Capelo was an officer in the Portuguese Navy and a Portuguese explorer, helping to chart territory between Angola and Mozambique in southern Central Africa that was unknown to Europeans in the 1870s and 1880s. Alongside Roberto Ivens, he is famous for being the first European to cross Central Africa from coast to coast between Angola and Mozambique.

A mission sui iuris, or in Latin missio sui iuris ; also spelled mission(s) sui juris), also known as an independent mission, is a rare type of Roman Catholic missionary pseudo-diocesan jurisdiction, ranking below an apostolic prefecture and an apostolic vicariate, in an area with very few Catholics, often desolate or remote.
The Archdiocese of Kinshasa is an archdiocese of the Roman Catholic Church in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its ecclesiastic territory includes the capital city of Kinshasa and surrounding districts. The archdiocese is the metropolitan see for the Ecclesiastical Province of Kinshasa. The current archbishop is Fridolin Ambongo Besungu.
The colonial history of Angola is usually considered to run from the appearance of the Portuguese under Diogo Cão in 1482 (Congo) or 1484 until the independence of Angola in November 1975. Settlement did not begin until Novais's establishment of São Paulo de Loanda (Luanda) in 1575, however, and the Portuguese government only formally incorporated Angola as a colony in 1655 or on May 12, 1886.
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Kikwit is a diocese located in the city of Kikwit in the Ecclesiastical province of Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Popokabaka is a diocese located in the city of Popokabaka in the Ecclesiastical province of Kinshasa in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The Roman Catholic Vicariate Apostolic of the Congo, the administrative region covering Catholic mission activity in the Congo area of Central Africa, was by the end of the nineteenth century already fragmented.
The Roman Catholic Apostolic Prefecture of Kwango was a mission territory in Central Africa set up at the end of the nineteenth century.

Portuguese Angola refers to Angola during the historic period when it was a territory under Portuguese rule in southwestern Africa. In the same context, it was known until 1951 as Portuguese West Africa.

Popokabaka Territory is a territory of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is located in the Kwango province. The territory is divided into three sectors: Yonso, Popokabaka and Lufuna. The Kwango River runs through the territory. The administrative center is the city of Popokabaka.

The Cuango or Kwango is a transboundary river of Angola and Democratic Republic of Congo. It is the largest left bank tributary of the Kasai River in the Congo River basin. It flows through Malanje town in Angola. The Kwango River basin has large resources of diamonds in the Chitamba-Lulo Kimberlite Cluster in Lunda Norte Province, discovered in the main river channel and on flats and terraces in its flood plains.

Kasongo Lunda is a town and seat of Kasongo Lunda Territory, in the Kwango Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The town lies near the border with Angola to the east, here defined by the Kwango River. As of 2012 the town was estimated to have a population of 23,820.

Kwango is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kwango, Kwilu, and Mai-Ndombe provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Bandundu province. Kwango was formed from the Kwango district whose town of Kenge was elevated to capital city of the new province.

Kasai District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, named after the Kasai River. It was formed around 1885 and went through several large changes in extent in the years that followed. The 1933 version of the district roughly corresponded to the former Kasai-Occidental province and the present Kasaï and Kasaï-Central provinces.

Kwango District was a district of the Congo Free State, Belgian Congo and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It went through various changes in extent. It roughly corresponded to the present provinces of Kwilu and Kwango.
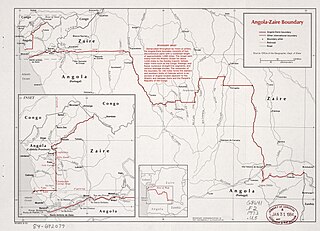
The Angola–Democratic Republic of the Congo border is 2,646 km in length and consists of two non-contiguous sections: a 225 km section along the border with Angola's province of Cabinda, running from the Atlantic Ocean to the tripoint with the Republic of Congo, and a much longer 2,421 km section running from the Atlantic to the tripoint with Zambia.