
Populus is a genus of 25–30 species of deciduous flowering plants in the family Salicaceae, native to most of the Northern Hemisphere. English names variously applied to different species include poplar, aspen, and cottonwood.

Vitis vinifera, the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of Vitis vinifera grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production.
A glucoside is a glycoside that is chemically derived from glucose. Glucosides are common in plants, but rare in animals. Glucose is produced when a glucoside is hydrolysed by purely chemical means, or decomposed by fermentation or enzymes.

Ferulic acid is a hydroxycinnamic acid, is an organic compound and a polyphenol with the formula (CH3O)HOC6H3CH=CHCO2H. The name is derived from the genus Ferula, referring to the giant fennel (Ferula communis). Classified as a phenolic phytochemical, ferulic acid is an amber colored solid. Esters of ferulic acid are found in plant cell walls, covalently bonded to hemicellulose such as arabinoxylans.

Rutin, also called rutoside, quercetin-3-O-rutinoside and sophorin, is the glycoside combining the flavonol quercetin and the disaccharide rutinose. It is a flavonoid found in a wide variety of plants, including citrus.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart gave the name Anthokyan to a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color for the first time in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.

The phenolic content in wine refers to the phenolic compounds—natural phenol and polyphenols—in wine, which include a large group of several hundred chemical compounds that affect the taste, color and mouthfeel of wine. These compounds include phenolic acids, stilbenoids, flavonols, dihydroflavonols, anthocyanins, flavanol monomers (catechins) and flavanol polymers (proanthocyanidins). This large group of natural phenols can be broadly separated into two categories, flavonoids and non-flavonoids. Flavonoids include the anthocyanins and tannins which contribute to the color and mouthfeel of the wine. The non-flavonoids include the stilbenoids such as resveratrol and phenolic acids such as benzoic, caffeic and cinnamic acids.

Dandelion 'coffee' is a tisane made from the root of the dandelion plant. The roasted dandelion root pieces and the beverage have some resemblance to coffee in appearance and taste, and it is thus commonly considered a coffee substitute. Dandelion root is used for both medicinal and culinary purposes and is thought to be a detoxifying herb.

Cucurbitacin is a class of biochemical compounds that some plants – notably members of the pumpkin and gourd family, Cucurbitaceae – produce and which function as a defence against herbivores. Cucurbitacins are chemically classified as triterpenes, formally derived from cucurbitane, a triterpene hydrocarbon – specifically, from the unsaturated variant cucurbit-5-ene, or 19(10→9β)-abeo-10α-lanost-5-ene. They often occur as glycosides.

Isorhamnetin is an O-methylated flavon-ol from the class of flavonoids. A common food source of this 3'-methoxylated derivative of quercetin and its glucoside conjugates are pungent yellow or red onions, in which it is a minor pigment, quercetin-3,4'-diglucoside and quercetin-4'-glucoside and the aglycone quercetin being the major pigments. Pears, olive oil, wine and tomato sauce are rich in isorhamnetin. Others sources include the spice, herbal medicinal and psychoactive Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida), which is described as accumulating isorhamnetin and its 7-O-glucoside derivate. Nopal is also a good source of isorhamnetin, which can be extracted by supercritical fluid extraction assisted by enzymes.
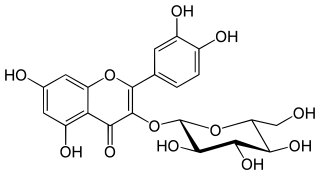
Isoquercetin, isoquercitrin or isotrifoliin is a flavonoid, a type of chemical compound. It is the 3-O-glucoside of quercetin. Isoquercitrin can be isolated from various plant species including Mangifera indica (mango) and Rheum nobile. It is also present in the leaves of Annona squamosa, Camellia sinensis (tea). and Vestia foetida

Apigeninidin is a chemical compound belonging to the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins and that can be found in the Patagonian plant Ephedra frustillata and in the soybean. Apigeninidin is one of the principal pigments found in sorghum. Extremely high level of apigeninidin (49 mg/g) has been documented in sorghum leaf sheath. Like all anthocyanidins it exists in a variety of tautomers depending on pH and hydration, several of these bare the distinctive pyrylium core.

Purple corn or purple maize is group of flint maize varieties originating in South America, descended from a common ancestral variety termed "kʼculli" in Quechua. It is most commonly grown in the Andes of Peru, Bolivia and Ecuador.

Oenin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of malvidin. It is one of the red pigments found in the skin of purple grapes and in wine.

Chrysanthemin is an anthocyanin. It is the 3-glucoside of cyanidin.
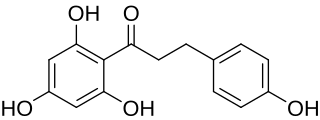
Phloretin is a dihydrochalcone, a type of natural phenol. It can be found in apple tree leaves and the Manchurian apricot.
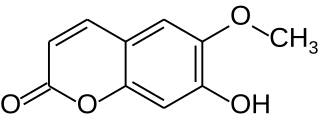
Scopoletin is a coumarin found in the root of plants in the genus Scopolia such as Scopolia carniolica and Scopolia japonica, in chicory, in Artemisia scoparia, in the roots and leaves of stinging nettle, in the passion flower, in Brunfelsia, in Viburnum prunifolium, in Solanum nigrum, in Datura metel, in Mallotus resinosus, or and in Kleinhovia hospita. It can also be found in fenugreek, vinegar, some whiskies or in dandelion coffee. A similar coumarin is scoparone. Scopoletin is highly fluorescent when dissolved in DMSO or water and is regularly used as a fluorimetric assay for the detection of hydrogen peroxide in conjunction with horseradish peroxidase. When oxidized, its fluorescence is strongly suppressed.

Ginkgotoxin (4'-O-methylpyridoxine) is a neurotoxin naturally occurring in Ginkgo biloba. It is an antivitamin structurally related to vitamin B6 (pyridoxine). It has the capacity to induce epileptic seizures.
Purple sweet potato color (PSPC) is a natural anthocyanin food coloring obtained from the sweet potato. Some cultivars, like the Ayamurasaki, released in Japan in 1995, are specially developed to have a higher anthocyanin content.

Prunus leveilleana is a native of Korea and Japan. It generally has autumnal leaves of reddish-brown or crimson red colour. It has flowers of bright yellow-white colors.


















