
French Indochina, officially known as the Indochinese Union and after 1947 as the Indochinese Federation, was a grouping of French colonial territories in Mainland Southeast Asia until its end in 1954. It comprised Cambodia, Laos, the Chinese territory of Guangzhouwan, and the Vietnamese regions of Tonkin in the north, Annam in the centre, and Cochinchina in the south. The capital for most of its history (1902–1945) was Hanoi; Saigon was the capital from 1887 to 1902 and again from 1945 to 1954.
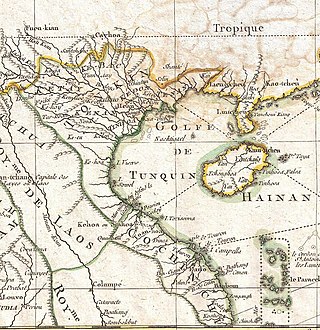
Tonkin, also spelled Tongkin, Tonquin or Tongking, is an exonym referring to the northern region of Vietnam. During the 17th and 18th centuries, this term referred to the domain Đàng Ngoài under Trịnh lords' control, including both the Northern and Thanh-Nghệ regions, north of the Gianh River. From 1884 to early 1945, this term was used for the French protectorate of Tonkin, composed of only the Northern region.

Annam, or Trung Kỳ (中圻), was a French protectorate encompassing the territory of the Empire of Đại Nam in Central Vietnam. Before the protectorate's establishment, the name Annam was used in the West to refer to Vietnam as a whole; Vietnamese people were referred to as Annamites. The protectorate of Annam became a part of French Indochina in 1887, along with two other Vietnamese regions, Cochinchina in the South and Tonkin in the North. The region had a dual system of French and Vietnamese administration. The government of the Nguyễn Dynasty still nominally ruled Annam and Tonkin as the Empire of Đại Nam, with the emperor residing in Huế. In 1948, the protectorate was merged in the Provisional Central Government of Vietnam, which was replaced the next year by the newly established State of Vietnam. The French legally maintained the protectorate until they formally signed over sovereignty to the Bảo Đại and the government of the State of Vietnam in 1950 after signing the Élysée Accords in 1949. The region was divided between communist North Vietnam and anti-communist South Vietnam under the terms of the Geneva Accord of 1954.
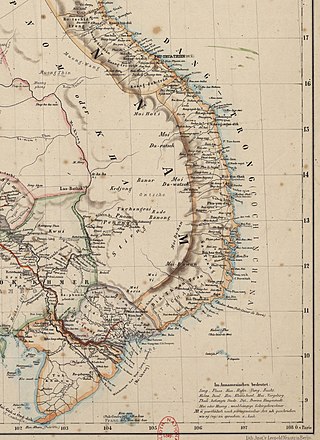
Cochinchina or Cochin-China is a historical exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer to the region south of the Gianh River.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Indochina.

During its time as a French colony, Obock issued its own postage stamps. At first the inhabitants used the general stamps of the French Colonies, but in 1892 they were overprinted with "OBOCK", as were stamped post cards. Later in the year some of these were also surcharged with values from 1 centime to 5 francs. By the end of the year, a supply of the omnibus Navigation and Commerce issues became available, inscribed OBOCK in red or blue.

The French post offices in Egypt were a system of post offices maintained by France in Egypt during the 19th century and the early years of the 20th century. They were primarily intended to facilitate commercial and trading interests that needed to communicate between France and points east.
Each "article" in this category is in fact a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries themselves are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.
Each "article" in this category is in fact a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries themselves are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.
Each "article" in this category is a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.
Each "article" in this category is a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.
Each "article" in this category is a collection of entries about several stamp issuers, presented in alphabetical order. The entries are formulated on the micro model and so provide summary information about all known issuers.

The piastre de commerce was the currency of French Indochina between 1885 and 1954. It was subdivided into 100 cents, each of 2~6 sapèques.

Between 1878 and 1885, the Cochinchina piastre was the currency of the French colony of Cochinchina. It was replaced by the French Indochinese piastre after the creation of a unified administration for Cochinchina and the other French protectorates and colonies in the Far East on 22 December 1885.

Auguste Jean-Marie Pavie was a French colonial civil servant, explorer and diplomat who was instrumental in establishing French control over Laos in the last two decades of the 19th century. After a long career in Cambodia and Cochinchina, Pavie became the first French vice-consul in Luang Prabang in 1886, eventually becoming the first Governor-General and plenipotentiary minister of the newly formed French colony of Laos.
French administration in Indochina began June 5, 1862, when the Treaty of Saigon ceded three provinces. By 1887 the French administered all of Indochina.
The postage stamps of Vietnam were issued by a variety of states and administrations. Stamps were first introduced by the French colonial administration. Stamps specifically for Vietnam were first issued in 1945. During the decades of conflict and partitioning, stamps were issued by mutually hostile governments. The reunification of Vietnam in 1976 brought about a unified postal service.

This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Laos.

Tonkin, or Bắc Kỳ, was a French protectorate encompassing modern Northern Vietnam. Like the French protectorate of Annam, Tonkin was still nominally ruled by the Nguyễn dynasty, but in 1886, the French separated Tonkin from the Nguyễn imperial court in Huế by establishing the office of "Viceroy". However, on 26 July 1897, the position of Viceroy was abolished, officially making the French resident-superior of Tonkin both the representative of the French colonial administration and the Nguyễn dynasty court in Huế, giving him the power to appoint local mandarins. In 1887, Tonkin became a part of the Union of Indochina.

The French conquest of Vietnam1 (1858–1885) was a series of military expeditions that pitted the Second French Empire, later the French Third Republic, against the Vietnamese empire of Đại Nam in the mid-late 19th century. Its end and results were victories for the French as they defeated the Vietnamese and their Chinese allies in 1885, the incorporation of Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia, and finally established French rules over constituent territories of French Indochina over Mainland Southeast Asia in 1887.















