
Aleuts are the Indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleuts and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska and the Russian administrative division of Kamchatka Krai. This group is also known as the Unangax̂ in Unangam Tunuu, the Aleut language. There are 13 federally recognized Aleut tribes in the Aleut Region of Alaska. In 2000, Aleuts in Russia were recognized by government decree as a small-numbered Indigenous people.
Eskimo is an exonym that refers to two closely related Indigenous peoples: Inuit and the Yupik of eastern Siberia and Alaska. A related third group, the Aleut, who inhabit the Aleutian Islands, are generally excluded from the definition of Eskimo. The three groups share a relatively recent common ancestor, and speak related languages belonging to the family of Eskaleut languages.

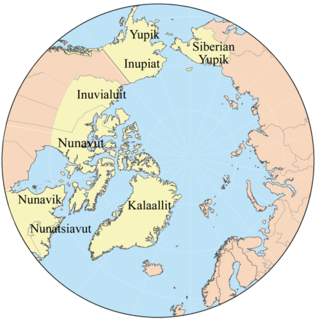
The Yupik are a group of Indigenous or Aboriginal peoples of western, southwestern, and southcentral Alaska and the Russian Far East. They are related to the Inuit and Iñupiat. Yupik peoples include the following:

A potlatch is a gift-giving feast practiced by Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast of Canada and the United States, among whom it is traditionally the primary governmental institution, legislative body, and economic system. This includes the Heiltsuk, Haida, Nuxalk, Tlingit, Makah, Tsimshian, Nuu-chah-nulth, Kwakwaka'wakw, and Coast Salish cultures. Potlatches are also a common feature of the peoples of the Interior and of the Subarctic adjoining the Northwest Coast, although mostly without the elaborate ritual and gift-giving economy of the coastal peoples.

The Eskaleut, Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages are a language family native to the northern portions of the North American continent, and a small part of northeastern Asia. Languages in the family are indigenous to parts of what are now the United States (Alaska); Canada including Nunavut, Northwest Territories, northern Quebec (Nunavik), and northern Labrador (Nunatsiavut); Greenland; and the Russian Far East. The language family is also known as Eskaleutian, Eskaleutic or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan.

Alaska Natives are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska and include Alaskan Creoles, Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and a number of Northern Athabaskan cultures. They are often defined by their language groups. Many Alaska Natives are enrolled in federally recognized Alaska Native tribal entities, who in turn belong to 13 Alaska Native Regional Corporations, who administer land and financial claims.

The Alutiiq people, also called by their ancestral name Sugpiaq, as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are one of eight groups of Alaska Natives that inhabit the southern-central coast of the region.

Nunivak Island is a permafrost-covered volcanic island lying about 30 miles (48 km) offshore from the delta of the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers in the US state of Alaska, at a latitude of about 60°N. The island is 1,631.97 square miles (4,226.8 km2) in area, making it the second-largest island in the Bering Sea and eighth-largest island in the United States. It is 76.2 kilometers (47.3 mi) long and 106 kilometers (66 mi) wide. It has a population of 191 persons as of the 2010 census, down from 210 in 2000. The island's entire population lives in the north coast city of Mekoryuk.

The history of Alaska dates back to the Upper Paleolithic period, when foraging groups crossed the Bering land bridge into what is now western Alaska. At the time of European contact by the Russian explorers, the area was populated by Alaska Native groups. The name "Alaska" derives from the Aleut word Alaxsxaq, meaning "mainland".

The Alaska Native Heritage Center is an educational and cultural institution for all Alaskans, located in Anchorage, Alaska. The center opened in 1999. The Alaska Native Heritage Center shares the heritage of Alaska's 11 major cultural groups. These 11 groups are the Athabaskan people, Eyak people, Tlingit people, Haida people, Tsimshian people, Unangax people (Aleut), Alutiiq people, Yup'ik, Cup'ik, Siberian Yupik, and Inupiaq.
Pamela Rae Huteson is an Alaska Native author and illustrator, from Prince of Wales Island in Southeast Alaska. She is both Tlingit and Haida, of the Shungkweidi Eagle moiety, from the Wolf House.
Cook Inlet Region, Inc. (CIRI) is one of thirteen Alaska Native regional corporations created under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act of 1971 (ANCSA) in settlement of aboriginal land claims. Cook Inlet Region, Inc. was incorporated in Alaska on June 8, 1972. Headquartered in Anchorage, Alaska, CIRI is a for-profit corporation, and is owned by more than 7,300 Alaska Native shareholders of Athabascan and Southeast Indian, Inupiat, Yup’ik, Alutiiq and Aleut descent.

The Yupʼik or Yupiaq and Yupiit or Yupiat (pl), also Central Alaskan Yupʼik, Central Yupʼik, Alaskan Yupʼik, are an Indigenous people of western and southwestern Alaska ranging from southern Norton Sound southwards along the coast of the Bering Sea on the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta and along the northern coast of Bristol Bay as far east as Nushagak Bay and the northern Alaska Peninsula at Naknek River and Egegik Bay. They are also known as Cup'ik by the Chevak Cup'ik dialect-speaking people of Chevak and Cup'ig for the Nunivak Cup'ig dialect-speaking people of Nunivak Island.

The culture of the Tlingit, an Indigenous people from Alaska, British Columbia, and the Yukon, is multifaceted, a characteristic of Northwest Coast peoples with access to easily exploited rich resources. In Tlingit culture a heavy emphasis is placed upon family and kinship, and on a rich tradition of oratory. Wealth and economic power are important indicators of status, but so is generosity and proper behavior, all signs of "good breeding" and ties to aristocracy. Art and spirituality are incorporated in nearly all areas of Tlingit culture, with even everyday objects such as spoons and storage boxes decorated and imbued with spiritual power and historical associations.

Alaska Native cultures are rich and diverse, and their art forms are representations of their history, skills, tradition, adaptation, and nearly twenty thousand years of continuous life in some of the most remote places on earth. These art forms are largely unseen and unknown outside the state of Alaska, due to distance from the art markets of the world.

Shamanism among Alaska Natives was particularly important as it served to construct their special connection to their land, and a kinship with the animals with whom they share that land. Before the introduction of western culture and the religions that are now practiced in Alaska, there was a common spiritual connection made with the people to the land they occupied. The most common name for this connection is shamanism. Shamanism differs in every culture where it is practiced, in Alaska it is centered in the animals that are common in the area. Through the use of many myths, stories, and ceremonies these animals are personified and their spirits made tangible and in turn are deeply woven within the Native Alaska people today. It was through the shaman that the spirit world was connected to the natural world. A shaman in Alaska Native culture was a mediator, healer and the spirit worlds’ mouthpiece. Although shamanism is no longer popularly practiced, it was and continues to be the heart of the Native Alaskan people.
Alaska Natives are a group of indigenous people that live in the state of Alaska and trace their heritage back to the last two great migrations that occurred thousands of years ago. The Native community can be separated into six large tribes and a number of smaller tribes, including the Iñupiat, Yup'ik, Aleut, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and others. Even with just a small number of communities that make up the entire population, there were more than 300 different languages that the Natives used to communicate with one another.

The Alaskan Athabascans, Alaskan Athapascans or Dena are Alaska Native peoples of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. They are the original inhabitants of the interior of Alaska.

The Tanana Athabaskans, Tanana Athabascans or Tanana Athapaskans are an Alaskan Athabaskan peoples of the Athabaskan-speaking ethnolinguistic group. They are the original inhabitants of the Tanana River drainage basin in east-central Alaska Interior, United States and a little part lived in Yukon, Canada. Tanana River Athabaskan peoples are called in Lower Tanana and Koyukon language Ten Hʉt'ænæ, in Gwich'in language Tanan Gwich'in. In Alaska, where they are the oldest, there are three or four groups identified by the languages they speak. These are the Tanana proper or Lower Tanana and/or Middle Tanana, Tanacross or Tanana Crossing, and Upper Tanana. The Tanana Athabaskan culture is a hunter-gatherer culture and have a matrilineal system. Tanana Athabaskans were semi-nomadic and as living in semi-permanent settlements in the Tanana Valley lowlands. Traditional Athabaskan land use includes fall hunting of moose, caribou, Dall sheep, and small terrestrial animals, and also trapping. The Athabaskans did not have any formal tribal organization. Tanana Athabaskans were strictly territorial and used hunting and gathering practices in their semi-nomadic way of life and dispersed habitation patterns. Each small band of 20–40 people normally had a central winter camp with several seasonal hunting and fishing camps, and they moved cyclically, depending on the season and availability of resources.

Yup'ik clothing refers to the traditional Eskimo-style clothing worn by the Yupik people of southwestern Alaska.




















