Related Research Articles

Tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues or tumours of the haematopoietic and lymphoid malignancies are tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, lymph, and lymphatic system. Because these tissues are all intimately connected through both the circulatory system and the immune system, a disease affecting one will often affect the others as well, making myeloproliferation and lymphoproliferation closely related and often overlapping problems.

Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) is a form of cancer. It is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma involving aberrant T cells or null lymphocytes. The term anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL) encompasses at least four different clinical entities with the same name, which on histological examination share the presence of large pleomorphic cells that express CD30 and T-cell markers. Two types of ALCL present as systemic disease and are considered as aggressive lymphomas, while two types present as localized disease and may progress locally. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma is associated with various types of medical implants.

Cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a class of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, which is a type of cancer of the immune system. Unlike most non-Hodgkin lymphomas, CTCL is caused by a mutation of T cells. The cancerous T cells in the body initially migrate to the skin, causing various lesions to appear. These lesions change shape as the disease progresses, typically beginning as what appears to be a rash which can be very itchy and eventually forming plaques and tumors before spreading to other parts of the body.
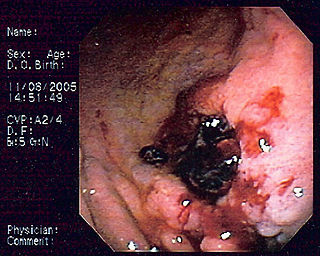
MALT lymphoma (MALToma) is a form of lymphoma involving the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT), frequently of the stomach, but virtually any mucosal site can be afflicted. It is a cancer originating from B cells in the marginal zone of the MALT, and is also called extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma.
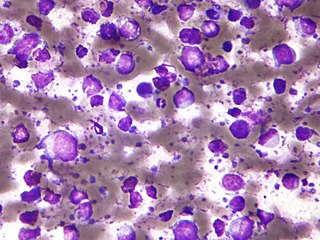
The B-cell lymphomas are types of lymphoma affecting B cells. Lymphomas are "blood cancers" in the lymph nodes. They develop more frequently in older adults and in immunocompromised individuals.

Intravascular lymphomas (IVL) are rare cancers in which malignant lymphocytes proliferate and accumulate within blood vessels. Almost all other tyes of lymphoma involve the proliferation and accumulation of malignant lymphocytes in lymph nodes, other parts of the lymphatic system, and various non-lymphatic organs but not in blood vessels.
Splenic marginal zone lymphoma (SMZL) is a type of cancer made up of B-cells that replace the normal architecture of the white pulp of the spleen. The neoplastic cells are both small lymphocytes and larger, transformed lymphoblasts, and they invade the mantle zone of splenic follicles and erode the marginal zone, ultimately invading the red pulp of the spleen. Frequently, the bone marrow and splenic hilar lymph nodes are involved along with the peripheral blood. The neoplastic cells circulating in the peripheral blood are termed villous lymphocytes due to their characteristic appearance.

Marginal zone B-cell lymphomas, also known as marginal zone lymphomas (MZLs), are a heterogeneous group of lymphomas that derive from the malignant transformation of marginal zone B-cells. Marginal zone B cells are innate lymphoid cells that normally function by rapidly mounting IgM antibody immune responses to antigens such as those presented by infectious agents and damaged tissues. They are lymphocytes of the B-cell line that originate and mature in secondary lymphoid follicles and then move to the marginal zones of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue, the spleen, or lymph nodes. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue is a diffuse system of small concentrations of lymphoid tissue found in various submucosal membrane sites of the body such as the gastrointestinal tract, mouth, nasal cavity, pharynx, thyroid gland, breast, lung, salivary glands, eye, skin and the human spleen.
CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, also known as primary cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma, is a cutaneous (skin) condition characterized by solitary or localized skin lesions that have a tendency to ulcerate.
Secondary cutaneous CD30+ large-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous condition that may arise in cases of mycosis fungoides, and in patients with lymphomatoid papulosis.
Non-mycosis fungoides CD30− cutaneous large T-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous condition that usually presents as solitary or generalized plaques, nodules, or tumors of short duration.
Pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a 5-year survival rate of 62%.
Lennert lymphoma is a systemic T-cell lymphoma that presents with cutaneous skin lesions roughly 10% of the time.
Cutaneous B-cell lymphomas constitute a group of diseases that occur less commonly than cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, and are characterized histologically by B-cells that appear similar to those normally found in germinal centers of lymph nodes. Conditions included in this group are:
Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphomas represent a heterogeneous group of diseases characterized by solitary or multiple dermal or subcutaneous nodules. Lymphomas included in this group are:
Plasmacytosis is a condition in which there is an unusually large proportion of plasma cells in tissues, exudates, or blood. Plasmacytosis may be divided into two types—cutaneous and systemic—both of which have identical skin findings.
Primary cutaneous follicle center lymphoma is a type of lymphoma. It was recognized as a distinct disease entity in the 2008 WHO classification. PCFCL had been previously conceived as a variant of follicular lymphoma (FL).

Umbralisib, sold under the brand name Ukoniq, is a medication for the treatment of marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) and follicular lymphoma (FL). It is taken by mouth.
Primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, leg type is a cutaneous lymphoma skin disease that occurs mostly in elderly females. In this disease, B-cells become malignant, accumulate in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue below the dermis to form red and violaceous skin nodules and tumors. These lesions typically occur on the lower extremities but in uncommon cases may develop on the skin at virtually any other site. In ~10% of cases, the disease presents with one or more skin lesions none of which are on the lower extremities; the disease in these cases is sometimes regarded as a variant of PCDLBL, LT termed primary cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, other (PCDLBC-O). PCDLBCL, LT is a subtype of the diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCL) and has been thought of as a cutaneous counterpart to them. Like most variants and subtypes of the DLBCL, PCDLBCL, LT is an aggressive malignancy. It has a 5-year overall survival rate of 40-55%, although the PCDLBCL-O variant has a better prognosis than cases in which the legs are involved.
References
- ↑ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ↑ Magro CM, Porcu P, Ahmad N, Klinger D, Crowson AN, Nuovo G (September 2004). "Cutaneous immunocytoma: a clinical, histologic, and phenotypic study of 11 cases". Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 12 (3): 216–24. doi:10.1097/00129039-200409000-00006. PMID 15551734. S2CID 2739996.