Related Research Articles

A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous.

Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder characterized by mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males with FXS is under 55, while about two thirds of affected females are intellectually disabled. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common, and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females.

Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and other consequences that may arise from expression of deleterious recessive traits resulting from incestuous sexual relationships and consanguinity. Animals avoid inbreeding only rarely.
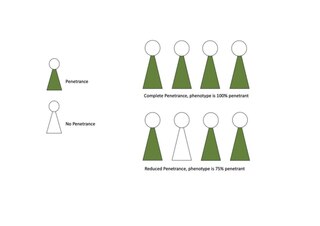
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant of a gene (genotype) that also expresses an associated trait (phenotype). In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is the proportion of individuals with the mutation that exhibit clinical symptoms among all individuals with such mutation. For example: If a mutation in the gene responsible for a particular autosomal dominant disorder has 75% penetrance, then 75% of those with the mutation will go on to develop the disease, showing its phenotype, whereas 25% will not.

A family tree, also called a genealogy or a pedigree chart, is a chart representing family relationships in a conventional tree structure. More detailed family trees, used in medicine and social work, are known as genograms.

Fabry disease, also known as Anderson–Fabry disease, is a rare genetic disease that can affect many parts of the body, including the kidneys, heart, brain, and skin. Fabry disease is one of a group of conditions known as lysosomal storage diseases. The genetic mutation that causes Fabry disease interferes with the function of an enzyme that processes biomolecules known as sphingolipids, leading to these substances building up in the walls of blood vessels and other organs. It is inherited in an X-linked manner.

A pedigree chart is a diagram that shows the occurrence and appearance of phenotypes of a particular gene or organism and its ancestors from one generation to the next, most commonly humans, show dogs, and race horses.

Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency also known as OTC deficiency is the most common urea cycle disorder in humans. Ornithine transcarbamylase, the defective enzyme in this disorder, is the final enzyme in the proximal portion of the urea cycle, responsible for converting carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline. OTC deficiency is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, meaning males are more commonly affected than females.

Coffin–Lowry syndrome is a genetic disorder that is X-linked dominant and which causes severe mental problems sometimes associated with abnormalities of growth, cardiac abnormalities, kyphoscoliosis, as well as auditory and visual abnormalities.
Human genetics is the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings. Human genetics encompasses a variety of overlapping fields including: classical genetics, cytogenetics, molecular genetics, biochemical genetics, genomics, population genetics, developmental genetics, clinical genetics, and genetic counseling.

X-linked ichthyosis is a skin condition caused by the hereditary deficiency of the steroid sulfatase (STS) enzyme that affects 1 in 2000 to 1 in 6000 males. XLI manifests with dry, scaly skin and is due to deletions or mutations in the STS gene. XLI can also occur in the context of larger deletions causing contiguous gene syndromes. Treatment is largely aimed at alleviating the skin symptoms. The term is from the Ancient Greek 'ichthys' meaning 'fish'.
Norrie disease is a rare X-linked recessive genetic disorder that primarily affects the eyes and almost always leads to blindness. It is caused by mutations in the Norrin cystine knot growth factor gene, also referred to as Norrie Disease Pseudoglioma (NDP) gene. Norrie disease manifests with vision impairment either at birth, or within a few weeks of life, following an ocular event like retinal detachment and is progressive through childhood and adolescence. It generally begins with retinal degeneration, which occurs before birth and results in blindness at birth (congenital) or early infancy, usually by 3 months of age.
Van der Woude syndrome (VDWS) is a genetic disorder characterized by the combination of lower lip pits, cleft lip with or without cleft palate (CL/P), and cleft palate only (CPO). The frequency of orofacial clefts ranges from 1:1000 to 1:500 births worldwide, and there are more than 400 syndromes that involve CL/P. VWS is distinct from other clefting syndromes due to the combination of cleft lip and palate (CLP) and CPO within the same family. Other features frequently associated with VWS include hypodontia in 10-81% of cases, narrow arched palate, congenital heart disease, heart murmur and cerebral abnormalities, syndactyly of the hands, polythelia, ankyloglossia, and adhesions between the upper and lower gum pads.

Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics.
Wilson-Turner syndrome (WTS), also known as mental retardation X linked syndromic 6 (MRXS6), and mental retardation X linked with gynecomastia and obesity is a congenital condition characterized by intellectual disability and associated with childhood-onset obesity. It is found to be linked to the X chromosome and caused by a mutation in the HDAC8 gene, which is located on the q arm at locus 13.1. Individuals with Wilson–Turner syndrome have a spectrum of physical characteristics including dysmorphic facial features, hypogonadism, and short stature. Females generally have milder phenotypes than males. This disorder affects all demographics equally and is seen in less than one in one million people.

Alice M. Lazzarini is a scientist, author and researcher on neurogenetic disorders, including Huntington's disease and Parkinson's disease. She is an assistant professor of Neurology at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, where her work helped establish the genetic basis of Parkinson's. Later in life, she was diagnosed with Parkinson's—the very disease she had spent decades researching.
Albert Fredrik de la Chapelle, MD, Ph.D was a Finnish human geneticist, long-time head of Finland's first Department of Medical Genetics at the University of Helsinki, and subsequently professor of Human Cancer Genetics at Ohio State University. He was best known for his role in the elucidation of the genetics of hereditary colorectal cancer and Lynch syndrome.
This glossary of genetics and evolutionary biology is a list of definitions of terms and concepts used in the study of genetics and evolutionary biology, as well as sub-disciplines and related fields, with an emphasis on classical genetics, quantitative genetics, population biology, phylogenetics, speciation, and systematics. Overlapping and related terms can be found in Glossary of cellular and molecular biology, Glossary of ecology, and Glossary of biology.
Multifactorial diseases are not confined to any specific pattern of single gene inheritance and are likely to be caused when multiple genes come together along with the effects of environmental factors.
References
- ↑ Bennett, RL. The Language of the Pedigree. In: The Practical Guide to the Genetic Family History. Wiley-Liss. ISBN 9780471459149
- 1 2 "Proband glossary entry". Genetics Home Reference. NIH . Retrieved 20 May 2011.