An identifier is a name that identifies either a unique object or a unique class of objects, where the "object" or class may be an idea, physical [countable] object, or physical [noncountable] substance. The abbreviation ID often refers to identity, identification, or an identifier. An identifier may be a word, number, letter, symbol, or any combination of those.
The International Standard Recording Code (ISRC) is an international standard code for uniquely identifying sound recordings and music video recordings. The code was developed by the recording industry in conjunction with the ISO technical committee 46, subcommittee 9, which codified the standard as ISO 3901 in 1986, and updated it in 2001.

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. As of 2019, clinical research on CBD included studies of anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that it is effective for these conditions.
The European Medicines Agency (EMA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) in charge of the evaluation and supervision of medicinal products. Prior to 2004, it was known as the European Agency for the Evaluation of Medicinal Products or European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA).

The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe.

Meprobamate—marketed as Miltown by Wallace Laboratories and Equanil by Wyeth, among others—is a carbamate derivative used as an anxiolytic drug. It was the best-selling minor tranquilizer for a time, but has largely been replaced by the benzodiazepines due to their wider therapeutic index and lower incidence of serious side effects.
Personal data, also known as personal information or personally identifiable information (PII) is any information relating to an identifiable person.
Nicorette is the brand name of a number of products for nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) that contain nicotine. Developed in the late 1970s in Sweden by AB Leo in the form of a chewing gum, Nicorette was the first nicotine replacement product on the market.
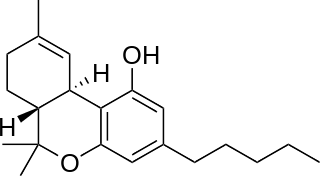
Nabiximols is a specific Cannabis extract that was approved in 2010 as a botanical drug in the United Kingdom despite a lack of convincing evidence of effectiveness for spasticity reduction. Nabiximols is sold as a mouth spray intended to alleviate neuropathic pain, spasticity, overactive bladder, and other symptoms of multiple sclerosis; it was developed by the UK company GW Pharmaceuticals. In 2019 it was proposed that following application of the spray, nabiximols is washed away from the oral mucosa by the saliva flow and ingested into the stomach, with subsequent absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract. Nabiximols is a combination drug standardized in composition, formulation, and dose. Its principal active cannabinoid components are the cannabinoids: tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Each spray delivers a dose of 2.7 mg THC and 2.5 mg CBD.

GS1 is a not-for-profit organisation that develops and maintains global standards for business communication. The best known of these standards is the barcode, a symbol printed on products that can be scanned electronically. Over 100 million products carry GS1 barcodes and they are scanned more than six billion times every day.
Proximity marketing is the localized wireless distribution of advertising content associated with a particular place. Transmissions can be received by individuals in that location who wish to receive them and have the necessary equipment to do so.

The European Directive on Traditional Herbal Medicinal Products (THMPD), formally the Directive 2004/24/EC amending, as regards traditional herbal medicinal products, Directive 2001/83/EC on the Community code relating to medicinal products for human use, was established by the European Parliament and Council on 31 March 2004 to provide a simplified regulatory approval process for traditional herbal medicines in the European Union (EU). Previously, there was no formal EU wide authorisation procedure, so each EU member state regulated these types of products at the national level.
The Commission on Human Medicines (CHM) is a committee of the UK's Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency. It was formed in October 2005, and assumed the responsibilities of the Medicines Commission and the Committee on Safety of Medicines. Membership in this various and extensive body is listed on a governmental website.
A biosimilar is a biologic medical product highly similar to another already approved biological medicine. Biosimilars are approved according to the same standards of pharmaceutical quality, safety and efficacy that apply to all biological medicines. Biosimilars are officially approved versions of original "innovator" products and can be manufactured when the original product's patent expires. Reference to the innovator product is an integral component of the approval.

Pandemrix is an influenza vaccine for influenza pandemics, such as the 2009 flu pandemic. The vaccine was developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) and patented in September 2006.
Marketing Authorisation Application (MAA) is an application submitted by a drug manufacturer seeking marketing authorisation, that is permission to bring a medicinal product to the market.
Marketing authorisation is the process of reviewing and assessing the evidence to support a medicinal product, such as a drug, in relation to its marketing, finalised by granting of a licence to be sold.
Drug distribution is the process by means of which people get access to medication.
The Falsified Medicines Directive is a legal framework introduced by the European Commission, to improve the protection of public health within the European Union. The directive applies since 2 January 2013. The European Commission Delegated Regulation, (EU) 2016/161, supplements Directive 2001/83/EC with rules regarding safety features for the packaging of medicinal products for human use. The regulation was adopted in October 2015. Measures to counteract to fake medicines include stricter record-keeping of wholesale distributors, tougher inspections of pharmaceutical producers, an EU-wide quality mark to identify online pharmacies and obligatory safety features on packages.
A hexavalent vaccine, or 6-in-1 vaccine, is a combination vaccine with six individual vaccines conjugated into one, intended to protect people from multiple diseases. The principal example is a pediatric vaccine, used in more than 90 countries around the world including in Europe, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, haemophilus B, and hepatitis B.








