Republicanism in Australia is a movement to change Australia's system of government from a constitutional parliamentary monarchy to a republic, typically a parliamentary republic that would replace the monarch of Australia with an Australian head of State. Republicanism was first espoused in Australia before Federation in 1901. After a period of decline after Federation, the movement again became prominent at the end of the 20th century after successive legal and socio-cultural changes loosened Australia's ties with the United Kingdom.
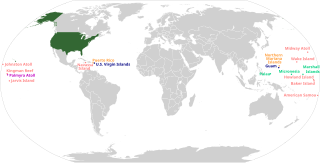
The 51st state is a term in American political discourse that refers to areas considered to be candidates for U.S. statehood, joining the 50 United States existing since 1959. The phrase has been applied to external territories, as well as the country's capital for the District of Columbia and parts of already-existing states which would be admitted as separate states in their own right.

The second question of the 1967 Australian referendum of 27 May 1967, called by the Holt government, related to Indigenous Australians. Voters were asked whether to give the Federal Government the power to make special laws for Indigenous Australians in states, and whether Indigenous Australians should be included in official population counts for constitutional purposes. The term "the Aboriginal Race" was used in the question.
In Australia, referendums are public votes held on important issues where the electorate may approve or reject a certain proposal. The term is commonly used in reference to a constitutional referendum which is legally required to make a change to the Constitution of Australia.

The Australian republic referendum held on 6 November 1999 was a two-question referendum to amend the Constitution of Australia. The first question asked whether Australia should become a republic, with a President appointed by Parliament following a bi-partisan appointment model which had been approved by a half-elected, half-appointed Constitutional Convention held in Canberra in February 1998. The second question, generally deemed to be far less important politically, asked whether Australia should alter the Constitution to insert a preamble. Since the early 1990s opinion polls had suggested that a majority of the electorate favoured a republic. Nonetheless, the republic referendum was defeated.
The 1977 Referendums question was a successful amendment to the Australian constitution that allowed Australians living in territories to vote on future referendums. This question was put to voters alongside four others during 1977. With the success of the vote, the Constitution Alteration (Referendums) Bill 1977 passed. In future referenda, the votes of electors in the territories would be counted towards the national total, but would not be counted toward any state total.
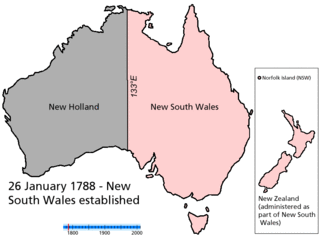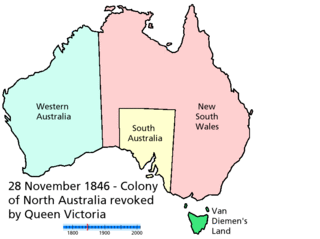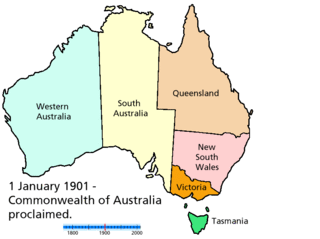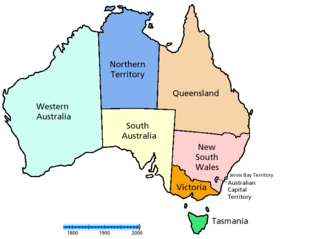
There have been numerous proposals for the creation or incorporation of new states of Australia, since the late 19th century. Chapter VI of the Constitution of Australia provides for the admission of new states to the federation. Proposals have included admitting territories to statehood, admitting independent countries, and forming new states from parts of existing states. However, no new states have been added since the federation of six former British self-governing colonies in 1901, as states of the new Commonwealth of Australia.

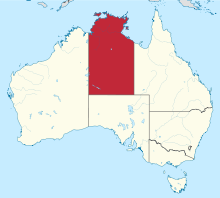
The Government of the Northern Territory of Australia, also referred to as the Northern Territory Government, is the Australian territorial democratic administrative authority of the Northern Territory. The Government of Northern Territory was formed in 1978 with the granting of self-government to the Territory. The Northern Territory is a territory of the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Constitution of Australia and Commonwealth law regulates its relationship with the Commonwealth.
A referendum was held in the Northern Territory on Saturday, 3 October 1998, to decide whether the Territory should become a State of the Commonwealth of Australia. The Country Liberal Party government, and its federal counterpart, supported the Yes case. The opposition Labor Party supported the No case.

The Australian flag debate is a question over whether the Australian flag should be changed, particularly to remove the Union Jack from the canton, but also to possibly introduce a completely new design without the Southern Cross. Acknowledgement of the significance of the issues, and corresponding changes are required to reflect Australia's multicultural society, as well as to reflect Australia's immensely rich, and intricate and complex shared history.

Malarndirri Barbara McCarthy is an Australian politician and former journalist who has been a Senator for the Northern Territory since 2016. She is an Assistant Minister in the Albanese Government, and previously served in the Northern Territory Legislative Assembly.

The Puerto Rico statehood movement aims to make Puerto Rico a state of the United States. Puerto Rico is an unincorporated territorial possession of the United States acquired in 1898 following the Spanish–American War, making it "the oldest colony in the modern world". As of 2019, the population of Puerto Rico is 3.2 million, around half the average state population and higher than that of 20 U.S. states. Statehood is one of several competing options for the future political status of Puerto Rico, including: maintaining its current status, becoming fully independent, or becoming a freely associated state. Puerto Rico has held six referendums on the topic. These are non-binding, as the power to grant statehood lies with the US Congress. The most recent referendum was in November 2020, with a majority (52.52%) of those who voted opting for statehood.

The political status of Puerto Rico is that of an unincorporated territory of the United States officially known as the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. As such, the island of Puerto Rico is neither a sovereign nation nor a U.S. state. It is because of that ambiguity, the territory, as a polity, lacks certain rights but enjoys certain benefits that other polities have or lack. For instance, in contrast to U.S. states, Puerto Rico residents cannot vote in U.S. presidential elections nor can they elect their own senators and representatives to the U.S. Congress. On the other hand, in contrast to U.S. states, only some residents of Puerto Rico are subject to federal income taxes. The political status of the island thus stems from how different Puerto Rico is politically from sovereign nations and from U.S. states.

The 1998 Australian Constitutional Convention was a Constitutional Convention which gathered at Old Parliament House, Canberra from 2 to 13 February 1998. It was called by the Howard government to discuss whether Australia should become a republic. The convention concluded with "in principle support" for an Australian republic and proposed a model involving appointment of the head of state by Parliament. The model was put to a referendum in November 1999 and rejected by the Australian electorate.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on November 6, 2012. It was the fourth referendum on status to be held in Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has been an unincorporated territory of the United States since the Spanish–American War in 1898.

Lia Emele Finocchiaro is an Australian politician. She has been a Country Liberal Party member of the Northern Territory Legislative Assembly for the seat of Spillett since her election in 2016. She became Leader of the Opposition in the Northern Territory after the resignation of Gary Higgins on 1 February 2020. She was previously the member for Drysdale from 2012 to 2016.
There are differing points of view on whether Puerto Rico's current political status as a territory of the United States should change. Four major viewpoints emerge in principle: that Puerto Rico maintains its current status, becomes a US state, becomes fully independent, or becomes a freely associated state.

The status quo movement in Puerto Rico refers to initiatives throughout the history of Puerto Rico aimed at maintaining the current political status of Puerto Rico, that of a commonwealth of the United States.
A referendum on the political status of Puerto Rico was held in Puerto Rico on June 11, 2017. The referendum had three options: becoming a state of the United States, independence/free association, or maintaining the current territorial status. Those who voted overwhelmingly chose statehood by 97%. This figure is attributed to a boycott led by the pro-status quo PPD party, which resulted in a 22.93% turnout.
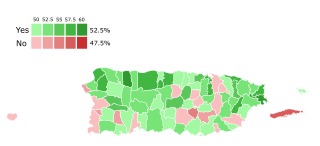
A referendum of the status of Puerto Rico was held on November 3, 2020, concurrently with the general election. The Referendum was announced by Puerto Rico Governor Wanda Vázquez Garced on May 16, 2020. This was the sixth referendum held on the status of Puerto Rico, with the previous one having taken place in 2017. This was the first referendum with a simple yes-or-no question, with voters having the option of voting for or against becoming a U.S. state. The New Progressive Party (PNP), of whom Vázquez is a member, supports statehood, while the opposition Popular Democratic Party (PDP) and Puerto Rican Independence Party (PIP) oppose it.