Related Research Articles

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
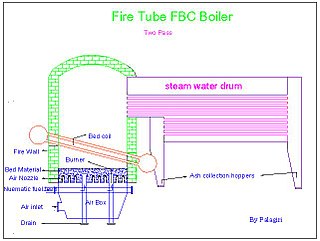
Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels.

A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam.

A high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.

In a steam engine, the firebox is the area where the fuel is burned, producing heat to boil the water in the boiler. Most are somewhat box-shaped, hence the name. The hot gases generated in the firebox are pulled through a rack of tubes running through the boiler.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.
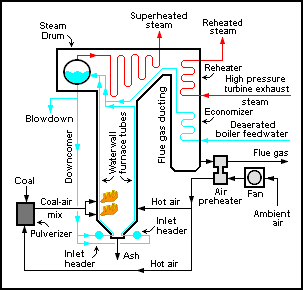
An air preheater is any device designed to heat air before another process (for example, combustion in a boiler With the primary objective of increasing the thermal efficiency of the process. They may be used alone or to replace a recuperative heat system or to replace a steam coil.

Cockenzie power station was a coal-fired power station in East Lothian, Scotland. It was situated on the south shore of the Firth of Forth, near the town of Cockenzie and Port Seton, 8 mi (13 km) east of the Scottish capital of Edinburgh. The station dominated the local coastline with its distinctive twin chimneys from 1967 until the chimneys' demolition in September 2015. Initially operated by the nationalised South of Scotland Electricity Board, it was operated by Scottish Power following the privatisation of the industry in 1991. In 2005 a WWF report named Cockenzie as the UK's least carbon-efficient power station, in terms of carbon dioxide released per unit of energy generated.

A pellet stove is a stove that burns compressed wood or biomass pellets to create a source of heat for residential and sometimes industrial spaces. By steadily feeding fuel from a storage container (hopper) into a burn pot area, it produces a constant flame that requires little to no physical adjustments. Today's central heating systems operated with wood pellets as a renewable energy source can reach an efficiency factor of more than 90%.
Co-firing is the combustion of two different types of materials at the same time. One of the advantages of co-firing is that an existing plant can be used to burn a new fuel, which may be cheaper or more environmentally friendly. For example, biomass is sometimes co-fired in existing coal plants instead of new biomass plants. Another example is that biomass primary fuel fractions can be cofired with waste-derived fuels in biomass plants leading to an environmentally friendly destruction of waste fractions and cost-effective heat and power production. Co-firing can also be used to improve the combustion of fuels with low energy content. For example, landfill gas contains a large amount of carbon dioxide, which is non-combustible. If the landfill gas is burned without removing the carbon dioxide, the equipment may not perform properly or emissions of pollutants may increase. Co-firing it with natural gas increases the heat content of the fuel and improves combustion and equipment performance. As long as the electricity or heat produced with the biomass and landfill gas was otherwise going to be produced with non-renewable fuels, the benefits are essentially equivalent whether they are cofired or combusted alone. Also, co-firing can be used to lower the emission of some pollutants. For example, co-firing biomass with coal results in less sulfur emissions than burning coal by itself.
A pulverizer or grinder is a mechanical device for the grinding of many different types of materials. For example, a pulverizer mill is used to pulverize coal for combustion in the steam-generating furnaces of coal power plants.
Grate firing is a type of industrial combustion system used for solid fuels. It now is used mainly for burning waste and biomass, but also for smaller coal furnaces.

A coal-fired power station or coal power plant is a thermal power station which burns coal to generate electricity. Worldwide there are over 2,400 coal-fired power stations, totaling over 2,000 gigawatts capacity. They generate about a third of the world's electricity, but cause many illnesses and the most early deaths, mainly from air pollution.

A boiler or steam generator is a device used to create steam by applying heat energy to water. Although the definitions are somewhat flexible, it can be said that older steam generators were commonly termed boilers and worked at low to medium pressure but, at pressures above this, it is more usual to speak of a steam generator.

A shell or flued boiler is an early and relatively simple form of boiler used to make steam, usually for the purpose of driving a steam engine. The design marked a transitional stage in boiler development, between the early haystack boilers and the later multi-tube fire-tube boilers. A flued boiler is characterized by a large cylindrical boiler shell forming a tank of water, traversed by one or more large flues containing the furnace. These boilers appeared around the start of the 19th century and some forms remain in service today. Although mostly used for static steam plants, some were used in early steam vehicles, railway locomotives and ships.
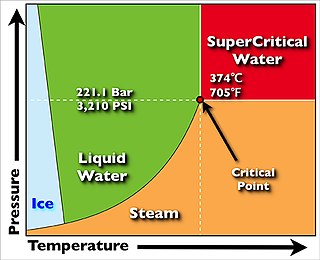
A supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure and temperature, frequently used in the production of electric power.
Boilers for generating steam or hot water have been designed in countless shapes, sizes and configurations. An extensive terminology has evolved to describe their common features. This glossary provides definitions for these terms.
An Advanced Thermal Recycling (ATR) system is an advancement of existing energy-from-waste (EfW) technology. An ATR system converts municipal solid waste (MSW) into either electricity or steam for district heating or industrial customers. The combustion bottom ash and the combustion fly ash, along with the air pollution control system fly ash, are treated to produce products that can be beneficially reused. Specifically, ATR systems consist of the following:

A coal burner is a mechanical device that burns pulverized coal into a flame in a controlled manner. Coal burner is mainly composed of pulverized coal machine, host of combustion machine control system, ignition system, the crater and others.
Butibori Power Project is a coal-based thermal power plant located at Butibori near Nagpur in the Indian state of Maharashtra. The power plant is operated by the Reliance Power.