
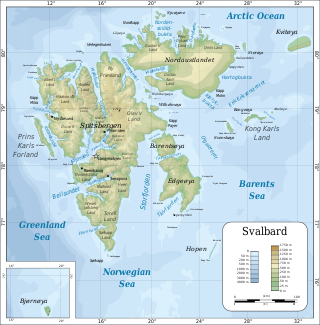
Svalbard, previously known as Spitsbergen or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it lies about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed in size by Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. The largest settlement is Longyearbyen on the west coast of Spitsbergen.

Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean roughly centered on 78° north latitude and 20° east longitude. It constitutes the northernmost territory of the Kingdom of Norway. The three main islands in the group consist of Spitsbergen, Nordaustlandet and Edgeøya. There are also a number of smaller islands, such as Barents Island (Barentsøya), Kvitøya, Prins Karls Forland, Kongsøya, Bear Island, Svenskøya, Wilhelm Island and other smaller islands or skerries.

Spitsbergen is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway.

Longyearbyen is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000, and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank of the Longyear Valley and on the shore of Adventfjorden, the short estuary leading into Isfjorden on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the island's broadest inlet. As of 2002 Longyearbyen Community Council became an official Norwegian municipality. It is the seat of the Governor of Svalbard. The town's mayor is Arild Olsen.
Barentsburg is the second-largest settlement in Svalbard, Norway, with about 455 inhabitants (2020). A coal mining town, the settlement was almost entirely made up of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians. With the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, most of the Ukrainian citizens were reported to have left.

Sveagruva, or simply Svea, was a mining settlement in the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard, lying at the head of Van Mijenfjord. When occupied by the workers, it was the third largest settlement in the archipelago but there were no permanent inhabitants. Around 300 workers living in Longyearbyen commuted to Sveagruva for work on a daily or weekly basis. The mine was operated by Store Norske Spitsbergen Kulkompani. There is no road to Longyearbyen or any other settlements, so travel is done by air from Svea Airport and coal transport by ship from a port 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) southwest. Sveagruva closed in 2020 and currently has no permanent inhabitants.
The polar archipelago of Svalbard was first discovered by Willem Barentsz in 1596, although there is disputed evidence of use by Pomors or Norsemen. Whaling for bowhead whales started in 1611, dominated by English and Dutch companies, though other countries participated. At that time there was no agreement about sovereignty. Whaling stations, the largest being Smeerenburg, were built during the 17th century, but gradually whaling decreased. Hunting was carried out from the 17th century by Pomors, but from the 19th century it became more dominated by Norwegians.

Pyramiden is an abandoned Soviet coal mining settlement on the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard which has become a tourist destination. Founded by Sweden in 1910 and sold to the Soviet Union in 1927, Pyramiden was closed in 1998 and has since remained largely abandoned with most of its infrastructure and buildings still in place, the cold climate preserving much of the infrastructure left behind.

Grumant is a former Soviet company town in Svalbard, Norway, established in 1912 and abandoned in 1965. The population—including Coles Bay, which served the settlement's port—peaked at 1,106 in 1951. The name Grumant is of Pomory origin, and is also used to refer to the whole of the Svalbard archipelago. It may be a corruption of Greenland, with which the land was confused.

Svalbard lies under the sovereignty of Norway, but the Svalbard Treaty places several restrictions. Norway cannot use the archipelago for warlike purposes, cannot discriminate economic activity based on nationality and is required to conserve the natural environment. Uniquely, Svalbard is an entirely visa-free zone. Everybody may live and work in Svalbard indefinitely regardless of country of citizenship. Svalbard Treaty grants treaty nationals equal right of abode as Norwegian nationals. Non-treaty nationals may live and work indefinitely visa-free as well. "Regulations concerning rejection and expulsion from Svalbard" is in force on non-discriminatory basis.

Svalbard has a population of approximately 2,395 people as of 2011. Approximately 70% of the people are Norwegians; the remaining 30% are Russian and Ukrainian. The official language of Svalbard is Norwegian. Russian is used in the Russian settlements.
Arktikugol is a Russian coal mining unitary enterprise which operates on the island of Spitsbergen in Svalbard, Norway. Owned by the government of Russia, Arktikugol currently performs limited mining in Barentsburg. It has carried out mining operations in the towns of Pyramiden and Grumant, which it still owns, and once operated a port at Colesbukta. The company is headquartered in Moscow and is the official agency through which Russia, and previously the Soviet Union, exercised its Svalbard policy.

The economy of Svalbard is dominated by coal mining, tourism and research. In 2007, there were 484 people working in the mining sector, 211 people working in the tourism sector and 111 people working in the education sector. The same year, mining gave a revenue of 2.008 billion kr, tourism NOK 317 million and research 142 million. In 2006, the average income for economically active people was NOK 494,700, or 23% higher than on the mainland. Almost all housing is owned by the various employers and institutions and rented to their employees; there are only a few privately owned houses, most of which are recreational cabins. Because of this, it is nearly impossible to live on Svalbard without working for an established institution. The Spitsbergen Treaty and Svalbard Act established Svalbard as an economic free zone and demilitarized zone in 1925.

Svalbard, Norway, is a vast, very sparsely inhabited Arctic archipelago. With fewer than 3,000 inhabitants in three main communities, plus some smaller meteorological and scientific outposts, there are no communities connected by road. Off-road motorized transport is prohibited on bare ground, but snowmobiles are used extensively during winter, both for commercial and recreational activities. Transport from Longyearbyen to Barentsburg and Pyramiden is possible by snowmobile at winter, or by ship all year round. Road systems exist within the communities of Longyearbyen, Barentsburg, Ny-Ålesund and the now-closed Sveagruva. All settlements have ports and Longyearbyen has a bus system.

Barentsburg Heliport, Heerodden is a private heliport located at Heerodden, serving the mining town of Barentsburg in Svalbard, Norway. The airport is owned and operated by Arktikugol, which also owns the company town. The airport features a 91-by-21-meter runway, two hangars and an administration building with a control tower. There are two Mil Mi-8 helicopters based at Heerodden, which are operated by Spark+. Flights are provided to Svalbard Airport, Longyear and Pyramiden Heliport.

Pyramiden Heliport is a heliport located at Pyramiden in Svalbard, Norway. The airport is owned and operated by Arktikugol, who owns the mining town. The airport consists of a gravel runway and apron measuring 90 by 40 meters and a small terminal building. There is capacity for up to three helicopters on the apron. Flights are carried out by Spark+ using two Mil Mi-8 helicopters. Flights are flown to Barentsburg Heliport, Heerodden and Svalbard Airport, Longyear at irregular intervals.
Agriculture in Svalbard – the archipelago containing the world's northernmost permanently inhabited settlements – has a short history, and remains a minor economic factor, but has nonetheless had a culturally and socially significant role, as well as an ecologic impact. Svalbard is home to the Global Seed Vault, which serves to protect the world's biological and agricultural diversity. Polar Permaculture Solutions, AS was formed in January 2015. Polar Permaculture has been focused on producing locally grown food in town, and also with composting food waste.

The archaeology of Svalbard is the study of human activity in the northerly Arctic Ocean archipelago's past. The geography, environment and climate of Svalbard have resulted in exceptional preservation conditions. Archaeological fieldwork on Svalbard is both expensive and physically exhausting, but new technology and infrastructure has allowed easier access. This easier access has also resulted in more damage caused by tourists.

The Barentsburg Pomor Museum is a small museum located in Barentsburg, a town in Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. Founded during the 1920s by the Dutch, the coal mining settlement was sold to the Soviet Union in 1932, and so it was the USSR which founded the museum in 1963. Today owned entirely by the Government of Russia through Arktikugol, Barentsburg is a shadow of its former self, with only a few hundred inhabitants compared to over a thousand during its heyday. The museum remains intact, however, receiving most of its visitors in the form of tourists. It shares the same building as the town's Sports and Culture Centre.
















