
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby.

In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)–. The simplest ketone is acetone, with the formula CH3C(O)CH3. Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids, and the solvent acetone.

In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate, millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds, along with a few other exceptions, are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive.

Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms. Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable.

In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound.
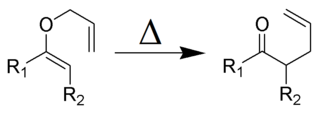
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis, organic reactions are used in the construction of new organic molecules. The production of many man-made chemicals such as drugs, plastics, food additives, fabrics depend on organic reactions.
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as inorganic chemistry.

The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all degree levels and in all fields of chemistry, chemical engineering, and related fields. It is one of the world's largest scientific societies by membership. The ACS is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization and holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Its headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., and it has a large concentration of staff in Columbus, Ohio.
Donald James Cram was an American chemist who shared the 1987 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Jean-Marie Lehn and Charles J. Pedersen "for their development and use of molecules with structure-specific interactions of high selectivity." They were the founders of the field of host–guest chemistry.

Medicinal or pharmaceutical chemistry is a scientific discipline at the intersection of chemistry and pharmacy involved with designing and developing pharmaceutical drugs. Medicinal chemistry involves the identification, synthesis and development of new chemical entities suitable for therapeutic use. It also includes the study of existing drugs, their biological properties, and their quantitative structure-activity relationships (QSAR).
Organic Syntheses is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and experiments reported in an article must be successfully repeated in the laboratory of a member of the editorial board as a check for reproducibility prior to publication. The journal is published by Organic Syntheses, Inc., a non-profit corporation. An annual print version is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of Organic Syntheses, Inc.

The Journal of Organic Chemistry, colloquially known as JOC, is a peer-reviewed scientific journal for original contributions of fundamental research in all branches of theory and practice in organic and bioorganic chemistry. It is published by the publishing arm of the American Chemical Society, with 24 issues per year. According to the Journal Citation Reports, the journal had a 2017 impact factor of 4.805 and it is the journal that received the most cites in the field of organic chemistry. According to Web of Knowledge, eleven papers from the journal have received more than 1,000 citations, with the most cited paper having received 7,967 citations. The current editor-in-chief is Scott J. Miller from Yale University.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).

The National Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Armenia is the Armenian national academy, functioning as the primary body that conducts research and coordinates activities in the fields of science and social sciences in Armenia. It is a member of the International Science Council.
Bioorganic chemistry is a scientific discipline that combines organic chemistry and biochemistry. It is that branch of life science that deals with the study of biological processes using chemical methods. Protein and enzyme function are examples of these processes.
Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and reactivity, in particular, applying experimental tools of physical chemistry to the study of organic molecules. Specific focal points of study include the rates of organic reactions, the relative chemical stabilities of the starting materials, reactive intermediates, transition states, and products of chemical reactions, and non-covalent aspects of solvation and molecular interactions that influence chemical reactivity. Such studies provide theoretical and practical frameworks to understand how changes in structure in solution or solid-state contexts impact reaction mechanism and rate for each organic reaction of interest.
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among the possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry publishes many books which contain its complete list of definitions. The definitions are divided into seven "colour books": Gold, Green, Blue, Purple, Orange, White, and Red. There is also an eighth book—the "Silver Book".
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) has published four sets of rules to standardize chemical nomenclature.



























