
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.

Acridine is an organic compound and a nitrogen heterocycle with the formula C13H9N. Acridines are substituted derivatives of the parent ring. It is a planar molecule that is structurally related to anthracene with one of the central CH groups replaced by nitrogen. Like the related molecules pyridine and quinoline, acridine is mildly basic. It is an almost colorless solid, which crystallizes in needles. There are few commercial applications of acridines; at one time acridine dyes were popular, but they are now relegated to niche applications, such as with acridine orange. The name is a reference to the acrid odour and acrid skin-irritating effect of the compound.
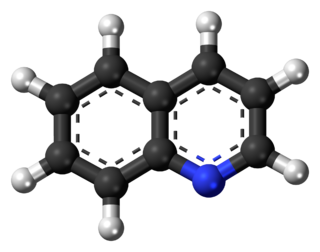
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only slightly soluble in cold water but dissolves readily in hot water and most organic solvents. Quinoline itself has few applications, but many of its derivatives are useful in diverse applications. A prominent example is quinine, an alkaloid found in plants. Over 200 biologically active quinoline and quinazoline alkaloids are identified. 4-Hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (HAQs) are involved in antibiotic resistance.
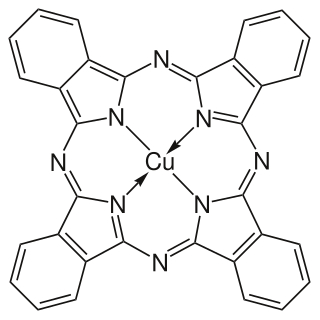
Copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), also called phthalocyanine blue, phthalo blue and many other names, is a bright, crystalline, synthetic blue pigment from the group of phthalocyanine dyes. Its brilliant blue is frequently used in paints and dyes. It is highly valued for its superior properties such as light fastness, tinting strength, covering power and resistance to the effects of alkalis and acids. It has the appearance of a blue powder, insoluble in most solvents including water.

Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl.

Acenaphthene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) consisting of naphthalene with an ethylene bridge connecting positions 1 and 8. It is a colourless solid. Coal tar consists of about 0.3% of this compound.
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis where the catalyst is in same phase as reactants, principally by a soluble catalyst a in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts.

Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.

Benzidine (trivial name), also called 1,1'-biphenyl-4,4'-diamine (systematic name), is an organic compound with the formula (C6H4NH2)2. It is an aromatic amine. It is a component of a test for cyanide. Related derivatives are used in the production of dyes. Benzidine has been linked to bladder and pancreatic cancer.
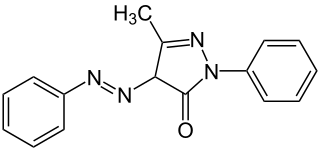
Sudan Yellow 3G, also known as Solvent Yellow 16, C.I. disperse yellow and C.I. 12700, is a yellow azo dye. It is soluble in fats and oils.

Quinaldine or 2-methylquinoline is an organic compound with the formula CH3C9H6N. It is one of the methyl derivatives of the heterocyclic compound quinoline. It is bioactive and is used in the preparation of various dyes. It is a colorless oil but commercial samples can appear colored.

3,3'-Dichlorobenzidine is an organic compound with the formula (C6H3Cl(NH2))2. The pure compound is pale yellow, but commercial samples are often colored. It is barely soluble in water and is often supplied as a wet paste. It is widely used in the production of diarylide yellow pigments used in the production of printing inks. Its use in the production of dyes has been largely discontinued because of concerns about carcinogenicity.

Phthalonitrile is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CN)2, which is an off-white crystal solid at room temperature. It is a derivative of benzene, containing two adjacent nitrile groups. The compound has low solubility in water but is soluble in common organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to phthalocyanine and other pigments, fluorescent brighteners, and photographic sensitizers.
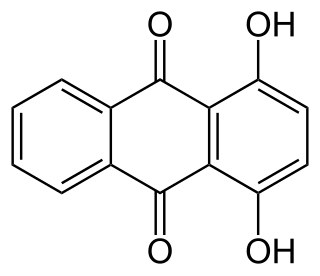
1,4-Dihydroxyanthraquinone, also called quinizarin or Solvent Orange 86, is an organic compound derived from anthroquinone. Quinizarin is an orange or red-brown crystalline powder. It is formally derived from anthraquinone by replacement of two hydrogen atoms by hydroxyl (OH) groups. It is one of ten dihydroxyanthraquinone isomers and occurs in small amounts in the root of the madder plant, Rubia tinctorum.

A rylene dye is a dye based on the rylene framework of naphthalene units linked in peri-positions. In homologues additional naphthalene units are added, forming compounds — or poly(peri-naphthalene)s — such as perylene, terrylene and quarterrylene.

Acetoacetanilide is an organic compound with the formula CH3C(O)CH2C(O)NHC6H5. It is the acetoacetamide derivative of aniline. It is a white solid that is poorly soluble in water. This chemical and many related compounds (prepared from various aniline derivatives) are used in the production of organic pigments called arylide yellows.

Perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride (PTCDA) is an organic dye molecule and an organic semiconductor. It is used as a precursor to a class of molecules known as Rylene dyes, which are useful as pigments and dyes. It is a dark red solid with low solubility in aromatic solvents. The compound has attracted much interest as an organic semiconductor.

Pigment yellow 139 is an organic compound that is used as a yellow-orange pigment. It is classified as a derivative of isoindoline. This yellow-orange solid is virtually insoluble in most solvents.
4-Chlorophenol is an organic compound with the formula C6H4ClOH. It is one of three monochlorophenol isomers. It is a colorless or white solid that melts easily and exhibits significant solubility in water. Its pKa is 9.14.

1,8-Naphthalic anhydride is an organic compound with the formula C10H6(C2O3). It is one of three isomers of naphthalic anhydride, the other two being the 1,2- and the 2,3-derivatives. The 1,8-isomer is prepared by aerobic oxidation of acenaphthene. 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid can be prepared from this anhydride. 1,8-Naphthalic anhydride is a precursor to the 4-chloro and 4,5-dichloro derivatives. These chloride groups are susceptible to displacement by amines and alkoxides, giving rise, ultimately, to a large family of naphthalimides, which are used as optical brighteners.



















