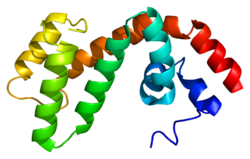
The μ-opioid receptors (MOR) are a class of opioid receptors with a high affinity for enkephalins and beta-endorphin, but a low affinity for dynorphins. They are also referred to as μ(mu)-opioid peptide (MOP) receptors. The prototypical μ-opioid receptor agonist is morphine, the primary psychoactive alkaloid in opium and for which the receptor was named, with mu being the Greek letter m. It is an inhibitory G-protein coupled receptor that activates the Gi alpha subunit, inhibiting adenylate cyclase activity, lowering cAMP levels.
Regulator of G protein signaling 4 also known as RGP4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS4 gene. RGP4 regulates G protein signaling.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS2 gene. It is part of a larger family of RGS proteins that control signalling through G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR).

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAQ gene. Together with GNA11, it functions as a Gq alpha subunit.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(o) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAO1 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS16 gene.
Regulator of G-protein signaling 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS19 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNB5 gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms exist.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS1 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 20 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS20 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS10 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS12 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS14 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS8 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signalling 9, also known as RGS9, is a human gene, which codes for a protein involved in regulation of signal transduction inside cells. Members of the RGS family, such as RGS9, are signaling proteins that suppress the activity of G proteins by promoting their deactivation.[supplied by OMIM]

Sorting nexin-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX13 gene.
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNA13 gene.
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(k) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAI3 gene.

Regulator of G-protein signaling 13 (RGS13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RGS13 gene.

CCG-4986 is a drug which is the first non-peptide compound discovered that acts as a selective inhibitor of the regulator of G protein signalling protein subtype RGS4. Regulators of G protein signalling are proteins which act to limit and shorten the response produced inside a cell following activation of a G protein-coupled receptor. Since different RGS subtypes are expressed in different tissues and are associated with particular receptors, this makes it possible for selective inhibitors of RGS proteins to be developed, which should be able to enhance the activity of a particular receptor in a defined target tissue, but not elsewhere in the body.