
The Colombian Liberal Party is a centre to centre-left political party in Colombia. It was founded as a classical liberal party but later developed a more social-democratic tradition, joining the Socialist International in 1999.

The Alternative Democratic Pole is a left-wing political party in Colombia, active from 2005 to the present. In 2022 it was successful at the polls and formed the Government of Colombia.

The Colombian Conservative Party is a conservative political party in Colombia. The party was formally established in 1849 by Mariano Ospina Rodríguez and José Eusebio Caro.
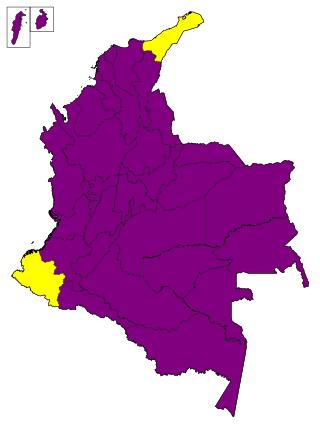
Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 28 May 2006. Álvaro Uribe was re-elected as President for another four-year term, starting on 7 August 2006. Uribe obtained 62.35% of the vote, surpassing the 50% needed to avoid a runoff against the second-placed candidate.

The Union Party for the People, or Party of the U, is a liberal political party in Colombia. The Party is led by former president Juan Manuel Santos.
Colombia First was a non-profit foundation and later conservative political movement in Colombia which supported the candidacy of Álvaro Uribe in the 2002 and 2006 presidential elections.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 26 May 2002. Álvaro Uribe, the candidate of the recently created Colombia First movement, was elected, receiving 53% of the vote by the first round. Uribe took office on 7 August.
National Front was a period in the history of Colombia in which the two main political parties, the Liberal Party and the Conservative Party, agreed to rotate power, intercalating for a period of four presidential terms. The National Front Presidents were Alberto Lleras Camargo (Liberal), Guillermo León Valencia (Conservative), Carlos Lleras Restrepo (Liberal), and Misael Pastrana Borrero (Conservative).

Piedad Esneda Córdoba Ruiz was a Colombian lawyer and politician who served as a senator from 1994 to 2010. A Liberal Party politician, she also served as a member of the Chamber of Representatives of Colombia for Antioquia from 1992 to 1994.

Germán Vargas Lleras is a Colombian politician who recently served as Vice President of Colombia under President Juan Manuel Santos Calderón. A member of the Radical Change political party, he served four consecutive terms in the Senate, having been elected in 1994. German Vargas also served in the Cabinet as the Minister of Interior and then as the Minister of Housing, City and Territory. He was elected Vice President of Colombia in 2014, running alongside Juan Manuel Santos who was seeking re-election for a second term as President. On 15 March 2017, Vargas Lleras resigned as Vice President in order to be eligible to run for President in the 2018 presidential elections. He finished in fourth place.

Gina María Parody d'Echeona is a Colombian politician. Born in Bogotá in 1973, Parody graduated as a lawyer from Pontifical Xavierian University and became a politician. She has served as Director of the National Learning Service (SENA), as a Senator, as member of the Chamber of Representatives of Colombia, and most recently as Minister of Education.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia in 2010. They took place under a two-round system, with an initial vote held on 30 May and a second poll held three weeks later on 20 June. A referendum proposal that would have allowed incumbent President Álvaro Uribe the opportunity to run for a third term was rejected by the Constitutional Court of Colombia in a 7–2 ruling on 26 February 2010. Because no candidate received a majority of the votes cast in the 30 May poll, the candidates with the two highest vote totals competed in a runoff election on 20 June: Juan Manuel Santos of the liberal-conservative Social Party of National Unity which unites supporters of former President Uribe, and Antanas Mockus from the Green Party. Santos won the election with 69% of the votes.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 25 May 2014. Since no candidate received 50% of the vote in the first round, a run-off between the two candidates with the most votes took place three weeks later on 15 June 2014. According to the official figures released by the National Registry office, as of 22 May 2014 32,975,158 Colombians were registered and entitled to vote in the 2014 presidential election, including 545,976 Colombians resident abroad. Incumbent president Juan Manuel Santos was allowed to run for a second consecutive term. In the first round, Santos and Óscar Iván Zuluaga of the Democratic Center were the two highest-polling candidates and were the contestants in the 15 June run-off. In the second round, Santos was re-elected president, gaining 51% of the vote compared with 45% for Zuluaga.

Democratic Centre is a conservative political party in Colombia founded in 2013 by Álvaro Uribe, former President of Colombia, former Vice President Francisco Santos Calderón and former Minister of Finance and Public Credit Óscar Iván Zuluaga. It is a self-described party of the centre, although in opinion groups it is often considered right-wing to far-right.

Presidential elections were held in Colombia on 27 May 2018. As no candidate received a majority of the vote, the second round of voting was held on 17 June. Incumbent president Juan Manuel Santos was ineligible to seek a third term. Iván Duque, a senator, defeated Gustavo Petro, former mayor of Bogotá, in the second round. Duque's victory made him one of the youngest individuals elected to the presidency, aged 42. His running mate, Marta Lucía Ramírez, was the first woman elected to the vice presidency in Colombian history.
The following lists events that happened during 2014 in Colombia.

Federico Andrés Gutiérrez Zuluaga is a Colombian politician, civil engineer, who currently serves as the mayor of Medellín, having held this office previously from 2016 to 2019. Before being mayor, he had been a member of the Medellín municipal council from 2004 to 2011. A member of the Creemos Colombia party, Gutiérrez was the candidate for the 2022 Colombian presidential election as the winner of the primary of the conservative Team for Colombia coalition.

Juan Manuel Santos's term as the 32nd president of Colombia began with his first inauguration on August 7, 2010, and ended on August 7, 2018. Santos, a center-right leader from Bogotá, took office after a landslide victory over the leftist leader. Antanas Mockus in the 2010 presidential election. Four years later, in the 2014 presidential election, he narrowly defeated the Democratic Center candidate Óscar Iván Zuluaga to win re-election. Santos was succeeded by right-wing leader Iván Duque, who won the 2018 presidential election.

Carlos Fernando Galán Pachón is a Colombian politician and journalist. The youngest son of the presidential candidate Luis Carlos Galán Sarmiento, assassinated in 1989, and brother of the senator Juan Manuel Galán. Galán has been a Bogotá Councilor and a Senator of the Republic of Colombia, a position he resigned after resigning from the Radical Change Party due to ideological differences, the main of them, the support that his party decided to give Iván Duque for the 2018 presidential elections.

The first family of Colombia is the family of the president of Colombia, who is both head of state and head of government of Colombia. It is an unofficial title for the family of a republic's head of state. Members of the first family consist of the president, the First Lady of Colombia, and any of their children. However, other close relatives of the president and first spouse, such as parents, grandchildren, stepchildren, and in-laws, may be classified as members of the first family for context purposes. The first family of Colombia live in the presidential residence Casa de Nariño in Bogotá, Colombia.

















