Resonance is the tendency of a physical system to oscillate at great amplitude at certain frequencies.
Contents
Resonance may also refer to:
Resonance is the tendency of a physical system to oscillate at great amplitude at certain frequencies.
Resonance may also refer to:

Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished from each other by the number of protons that are in their atoms. For example, any atom that contains 11 protons is sodium, and any atom that contains 29 protons is copper. Atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons are called isotopes of the same element.

The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum (spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, ħ. Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, per the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavelength for a given energy.

The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol
n
or
n0
, which has a neutral charge, and a mass slightly greater than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons constitute the nuclei of atoms. Since protons and neutrons behave similarly within the nucleus, they are both referred to as nucleons. Nucleons have a mass of approximately one atomic mass unit, or dalton. Their properties and interactions are described by nuclear physics. Protons and neutrons are not elementary particles; each is composed of three quarks.

In physics and chemistry, a nucleon is either a proton or a neutron, considered in its role as a component of an atomic nucleus. The number of nucleons in a nucleus defines the atom's mass number.
A timeline of atomic and subatomic physics.

Liquid Tension Experiment (LTE) is an American instrumental progressive metal supergroup founded by Mike Portnoy, in 1997. The band initially released two albums, between 1998 and 1999. An extension of their second regular album, with the absence of John Petrucci was released in 2007 under the name "Liquid Trio Experiment".

Jordan Rudess is an American keyboardist, composer, and software developer best known as a member of the progressive metal band Dream Theater and the supergroup Liquid Tension Experiment.

A Penning trap is a device for the storage of charged particles using a homogeneous magnetic field and a quadrupole electric field. It is mostly found in the physical sciences and related fields of study as a tool for precision measurements of properties of ions and stable subatomic particles, like for example mass, fission yields and isomeric yield ratios. One initial object of study were the so-called geonium atoms, which represent a way to measure the electron magnetic moment by storing a single electron. These traps have been used in the physical realization of quantum computation and quantum information processing by trapping qubits. Penning traps are in use in many laboratories worldwide, including CERN, to store and investigate anti-particles such as antiprotons. The main advantages of Penning traps are the potentially long storage times and the existence of a multitude of techniques to manipulate and non-destructively detect the stored particles. This makes Penning traps versatile tools for the investigation of stored particles, but also for their selection, preparation or mere storage.

In physics, a Fano resonance is a type of resonant scattering phenomenon that gives rise to an asymmetric line-shape. Interference between a background and a resonant scattering process produces the asymmetric line-shape. It is named after Italian-American physicist Ugo Fano, who in 1961 gave a theoretical explanation for the scattering line-shape of inelastic scattering of electrons from helium; however, Ettore Majorana was the first to discover this phenomenon. Fano resonance is a weak coupling effect meaning that the decay rate is so high, that no hybridization occurs. The coupling modifies the resonance properties such as spectral position and width and its line-shape takes on the distinctive asymmetric Fano profile. Because it is a general wave phenomenon, examples can be found across many areas of physics and engineering.

Muon spin spectroscopy, also known as µSR, is an experimental technique based on the implantation of spin-polarized muons in matter and on the detection of the influence of the atomic, molecular or crystalline surroundings on their spin motion. The motion of the muon spin is due to the magnetic field experienced by the particle and may provide information on its local environment in a very similar way to other magnetic resonance techniques, such as electron spin resonance and, more closely, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
Quantum mechanics is the study of matter and its interactions with energy on the scale of atomic and subatomic particles. By contrast, classical physics explains matter and energy only on a scale familiar to human experience, including the behavior of astronomical bodies such as the moon. Classical physics is still used in much of modern science and technology. However, towards the end of the 19th century, scientists discovered phenomena in both the large (macro) and the small (micro) worlds that classical physics could not explain. The desire to resolve inconsistencies between observed phenomena and classical theory led to a revolution in physics, a shift in the original scientific paradigm: the development of quantum mechanics.
Asım Orhan Barut was a Turkish-American theoretical physicist.

A microwave cavity or radio frequency cavity is a special type of resonator, consisting of a closed metal structure that confines electromagnetic fields in the microwave or RF region of the spectrum. The structure is either hollow or filled with dielectric material. The microwaves bounce back and forth between the walls of the cavity. At the cavity's resonant frequencies they reinforce to form standing waves in the cavity. Therefore, the cavity functions similarly to an organ pipe or sound box in a musical instrument, oscillating preferentially at a series of frequencies, its resonant frequencies. Thus it can act as a bandpass filter, allowing microwaves of a particular frequency to pass while blocking microwaves at nearby frequencies.
The timeline of quantum mechanics is a list of key events in the history of quantum mechanics, quantum field theories and quantum chemistry.
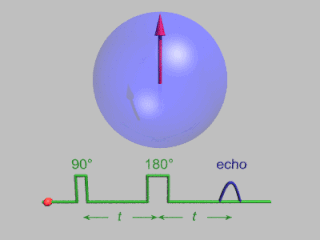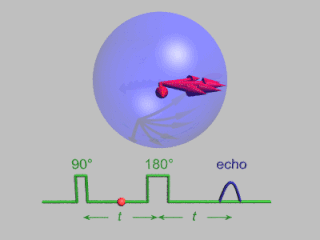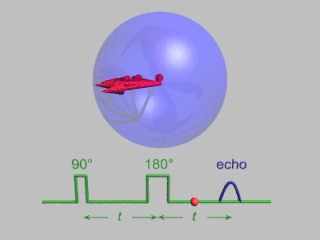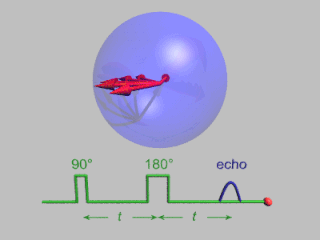
Pulsed electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) is an electron paramagnetic resonance technique that involves the alignment of the net magnetization vector of the electron spins in a constant magnetic field. This alignment is perturbed by applying a short oscillating field, usually a microwave pulse. One can then measure the emitted microwave signal which is created by the sample magnetization. Fourier transformation of the microwave signal yields an EPR spectrum in the frequency domain. With a vast variety of pulse sequences it is possible to gain extensive knowledge on structural and dynamical properties of paramagnetic compounds. Pulsed EPR techniques such as electron spin echo envelope modulation (ESEEM) or pulsed electron nuclear double resonance (ENDOR) can reveal the interactions of the electron spin with its surrounding nuclear spins.
This glossary of physics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to physics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including mechanics, materials science, nuclear physics, particle physics, and thermodynamics. For more inclusive glossaries concerning related fields of science and technology, see Glossary of chemistry terms, Glossary of astronomy, Glossary of areas of mathematics, and Glossary of engineering.

The discography of the South Korean boy group NCT consists of four studio albums and thirteen singles. The multi-national boy group was formed by SM Entertainment in 2016 and comprises multiple sub-units that occasionally reunite to release new music as NCT and NCT U. In 2018, the group released their first studio album, NCT 2018 Empathy, which peaked at number two on South Korea's Circle Album Chart and received a 2× platinum certification, awarded by the Korea Music Content Association (KMCA). Their next album, NCT 2020 Resonance, was released in two parts, which topped the Circle Album Chart, earning NCT their first number-one in the country. Both parts sold over 1.5 million copies and were certified Million by the KMCA. The album became NCT's first entry on national charts in Canada, Hungary, the Flanders and the United States. One of its lead singles, "Make a Wish", reached number 14 on the Circle Digital Chart, becoming NCT's first top 15 hit in South Korea, and peaked at number 126 the Billboard 200, becoming NCT's first song to enter the chart. In 2021, the group released Universe, which became their third number-one album in South Korea and first number-one album in Japan. NCT released their fourth studio album, Golden Age, in 2023.
Donald Choy Chang is a founding professor of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST). He was also the founding President of the Biophysical Society of Hong Kong. He is currently Professor Emeritus and Adjunct Professor in HKUST. Chang has wide research interests. He was an experimental physicist by training; but his publication ranges from nuclear magnetic resonance, biophysics and quantum physics. He was elected American Physical Society Fellow in 2023.

NCT 2020 Resonance is the second studio album by South Korean boy band NCT, an unlimited group project under the management of SM Entertainment. Similar to their previous release NCT 2018 Empathy, NCT 2020 Resonance is part of the "NCT 2020" project; which saw all current NCT members from several units collaborating on a full-length release. This time, the album features all 23 members from three current units of NCT; NCT 127, NCT Dream, and WayV, while introducing two new NCT members, namely Shotaro and Sungchan. It would also be the final NCT album to feature Lucas due to his hiatus and eventual departure in 2023. The first part was released on October 12, 2020, and the second part was then released on November 23, 2020.
The nucleon magnetic moments are the intrinsic magnetic dipole moments of the proton and neutron, symbols μp and μn. The nucleus of an atom comprises protons and neutrons, both nucleons that behave as small magnets. Their magnetic strengths are measured by their magnetic moments. The nucleons interact with normal matter through either the nuclear force or their magnetic moments, with the charged proton also interacting by the Coulomb force.