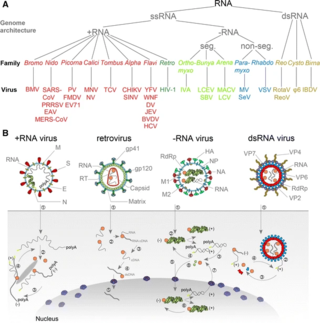
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.
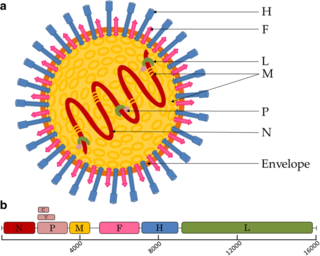
Paramyxoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has four subfamilies, 17 genera, three of which are unassigned to a subfamily, and 78 species.
Henipavirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae, order Mononegavirales containing six established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably pteropid fruit bats, microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern.

Morbillivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Mononegavirales, in the family Paramyxoviridae. Humans, dogs, cats, cattle, seals, and cetaceans serve as natural hosts. This genus includes six species, with a seventh species being extinct. Diseases in humans associated with viruses classified in this genus include measles; in animals, they include acute febrile respiratory tract infection and Canine distemper. In 2013, a wave of increased death among the Common bottlenose dolphin population was attributed to morbillivirus.
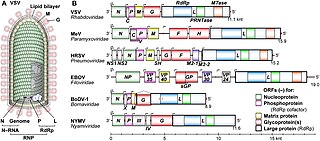
Mononegavirales is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some members that cause human disease in this order include Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. Important pathogens of nonhuman animals and plants are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus families: Artoviridae, Bornaviridae, Filoviridae, Lispiviridae, Mymonaviridae, Nyamiviridae, Paramyxoviridae, Pneumoviridae, Rhabdoviridae, Sunviridae, and Xinmoviridae.
Bornaviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Horses, sheep, cattle, rodents, birds, reptiles, and humans serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with bornaviruses include Borna disease, a fatal neurologic disease of mammals restricted to central Europe; and proventricular dilatation disease (PDD) in birds. Bornaviruses may cause encephalitis in mammals like horses or sheep. The family includes 11 species assigned to three genera.
Parechovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Picornaviridae. Humans, ferrets, and various rodents serve as natural hosts. The genus currently consists of six accepted species. Human parechoviruses may cause gastrointestinal or respiratory illness in infants, and they have been implicated in cases of myocarditis and encephalitis.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.

Rubulavirinae is a subfamily of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae. Humans, apes, pigs, and dogs serve as natural hosts. There are currently 18 species in the two genera Orthorubulavirus and Pararubulavirus. Diseases associated with this genus include mumps. Members of the subfamily are collectively called rubulaviruses. The subfamily was previously a genus named Rubulavirus but was elevated to subfamily in 2018. Viruses of this subfamily appear to be most closely related to members of Avulavirinae.
Picobirnavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only genus in the family Picobirnaviridae. Although amniotes, especially mammals, were thought to serve as hosts, it has been recently suggested that these viruses might infect bacteria and possibly some other invertebrates. If they do infect bacteria, then they are Bacteriophages. There are three species in this genus. Associated symptoms include gastroenteritis in animals and humans, though the disease association is unclear.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Entomobirnavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Birnaviridae. Its natural host is the fly Drosophila melanogaster. There are two species in this genus.
Ephemerovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Rhabdoviridae, order Mononegavirales. Cattle and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with viruses in this genus include: sudden fever.

Nyamiviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Ecdysozoa and birds serve as natural hosts. The name is a portmanteau of Nyamanini Pan and Midway Atoll and the suffix -viridae used to denote a virus family. There are seven genera in this family.
Aquaparamyxovirus is a genus of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae, order Mononegavirales. The genus includes two species. Fish serve as the natural hosts for AsaPV, in which the virus may cause proliferative gill inflammation.
Ferlavirus, also referred to as Ophidian paramyxovirus, is a genus of viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae, order Mononegavirales. Reptiles serve as natural hosts. There is currently only one species in this genus to accommodate a single virus, Fer-de-Lance virus (FDLV).

Pneumoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Humans, cattle, and rodents serve as natural hosts. Respiratory tract infections are associated with member viruses such as human respiratory syncytial virus. There are five species in the family which are divided between the genera Metapneumovirus and Orthopneumovirus. The family used to be considered as a sub-family of Paramyxoviridae, but has been reclassified as of 2016.

Avian metaavulavirus 2, formerly Avian paramyxovirus 2, is a species of virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae and genus Metaavulavirus. The virus is a negative strand RNA virus containing a monopartite genome. Avian metaavulavirus 2 is one of nine species belonging to the genus Metaavulavirus. The most common serotype of Avulavirinae is serotype 1, the cause of Newcastle disease (ND). Avian metaavulavirus 2 has been known to cause disease, specifically mild respiratory infections in domestic poultry, including turkeys and chickens, and has many economic effects on egg production and poultry industries. The virus was first isolated from a strain in Yucaipa, California in 1956. Since then, other isolates of the virus have been isolated worldwide.
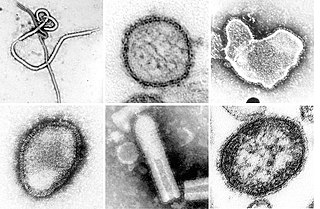
Negative-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented.
Bat mumps orthorubulavirus, formerly Bat mumps rubulavirus (BMV), is a member of genus Orthorubulavirus, family Paramyxoviridae, and order Mononegavirales. Paramyxoviridae viruses were first isolated from bats using heminested PCR with degenerate primers. This process was then followed by Sanger sequencing. A specific location of this virus is not known because it was isolated from bats worldwide. Although multiple paramyxoviridae viruses have been isolated worldwide, BMV specifically has not been isolated thus far. However, BMV was detected in African fruit bats, but no infectious form has been isolated to date. It is known that BMV is transmitted through saliva in the respiratory system of bats. While the virus was considered its own species for a few years, phylogenetic analysis has since shown that it is a member of Mumps orthorubulavirus.














