In computer science, a B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree generalizes the binary search tree, allowing for nodes with more than two children. Unlike other self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is well suited for storage systems that read and write relatively large blocks of data, such as databases and file systems.
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970. A database management system used to maintain relational databases is a relational database management system (RDBMS). Many relational database systems are equipped with the option of using SQL for querying and updating the database.

In computer science, the treap and the randomized binary search tree are two closely related forms of binary search tree data structures that maintain a dynamic set of ordered keys and allow binary searches among the keys. After any sequence of insertions and deletions of keys, the shape of the tree is a random variable with the same probability distribution as a random binary tree; in particular, with high probability its height is proportional to the logarithm of the number of keys, so that each search, insertion, or deletion operation takes logarithmic time to perform.
A surrogate key in a database is a unique identifier for either an entity in the modeled world or an object in the database. The surrogate key is not derived from application data, unlike a natural key.
A B+ tree is an m-ary tree with a variable but often large number of children per node. A B+ tree consists of a root, internal nodes and leaves. The root may be either a leaf or a node with two or more children.

In computer science a T-tree is a type of binary tree data structure that is used by main-memory databases, such as Datablitz, eXtremeDB, MySQL Cluster, Oracle TimesTen and MobileLite.
A database trigger is procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain events on a particular table or view in a database. The trigger is mostly used for maintaining the integrity of the information on the database. For example, when a new record is added to the employees table, new records should also be created in the tables of the taxes, vacations and salaries. Triggers can also be used to log historical data, for example to keep track of employees' previous salaries.
In mathematical analysis and computer science, functions which are Z-order, Lebesgue curve, Morton space-filling curve, Morton order or Morton code map multidimensional data to one dimension while preserving locality of the data points. It is named in France after Henri Lebesgue, who studied it in 1904, and named in the United States after Guy Macdonald Morton, who first applied the order to file sequencing in 1966. The z-value of a point in multidimensions is simply calculated by interleaving the binary representations of its coordinate values. Once the data are sorted into this ordering, any one-dimensional data structure can be used, such as simple one dimensional arrays, binary search trees, B-trees, skip lists or hash tables. The resulting ordering can equivalently be described as the order one would get from a depth-first traversal of a quadtree or octree.
A database index is a data structure that improves the speed of data retrieval operations on a database table at the cost of additional writes and storage space to maintain the index data structure. Indexes are used to quickly locate data without having to search every row in a database table every time said table is accessed. Indexes can be created using one or more columns of a database table, providing the basis for both rapid random lookups and efficient access of ordered records.
Extensible Storage Engine (ESE), also known as JET Blue, is an ISAM data storage technology from Microsoft. ESE is the core of Microsoft Exchange Server, Active Directory, and Windows Search. It is also used by a number of Windows components including Windows Update client and Help and Support Center. Its purpose is to allow applications to store and retrieve data via indexed and sequential access.
In a database, a view is the result set of a stored query, which can be queried in the same manner as a persistent database collection object. This pre-established query command is kept in the data dictionary. Unlike ordinary base tables in a relational database, a view does not form part of the physical schema: as a result set, it is a virtual table computed or collated dynamically from data in the database when access to that view is requested. Changes applied to the data in a relevant underlying table are reflected in the data shown in subsequent invocations of the view.
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of database system used in transaction-oriented applications, such as many operational systems. "Online" refers to that such systems are expected to respond to user requests and process them in real-time. The term is contrasted with online analytical processing (OLAP) which instead focuses on data analysis.
Database tables and indexes may be stored on disk in one of a number of forms, including ordered/unordered flat files, ISAM, heap files, hash buckets, or B+ trees. Each form has its own particular advantages and disadvantages. The most commonly used forms are B-trees and ISAM. Such forms or structures are one aspect of the overall schema used by a database engine to store information.
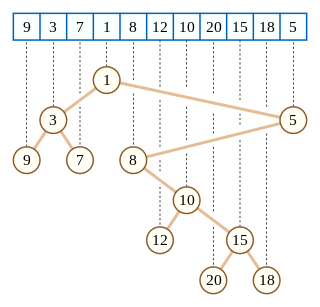
In computer science, a Cartesian tree is a binary tree derived from a sequence of distinct numbers. To construct the Cartesian tree, set its root to be the minimum number in the sequence, and recursively construct its left and right subtrees from the subsequences before and after this number. It is uniquely defined as a min-heap whose symmetric (in-order) traversal returns the original sequence.
In pattern recognition, the iDistance is an indexing and query processing technique for k-nearest neighbor queries on point data in multi-dimensional metric spaces. The kNN query is one of the hardest problems on multi-dimensional data, especially when the dimensionality of the data is high. The iDistance is designed to process kNN queries in high-dimensional spaces efficiently and it is especially good for skewed data distributions, which usually occur in real-life data sets. The iDistance can be augmented with machine learning models to learn the data distributions for searching and storing the multi-dimensional data.
In computer science, the Bx tree is a query that is used to update efficient B+ tree-based index structures for moving objects.
In database management systems, block contention refers to multiple processes or instances competing for access to the same index or data block at the same time. In general this can be caused by very frequent index or table scans, or frequent updates. Concurrent statement executions by two or more instances may also lead to contention, and subsequently busy waiting for the process without the lock.
InfinityDB is an all-Java embedded database engine and client/server DBMS with an extended java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentNavigableMap interface that is deployed in handheld devices, on servers, on workstations, and in distributed settings. The design is based on a proprietary lockless, concurrent, B-tree architecture that enables client programmers to reach high levels of performance without risk of failures.
A Block Range Index or BRIN is a database indexing technique. They are intended to improve performance with extremely large tables.
Database scalability is the ability of a database to handle changing demands by adding/removing resources. Databases use a host of techniques to cope.