The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Its most notable applications are remote login and command-line execution.
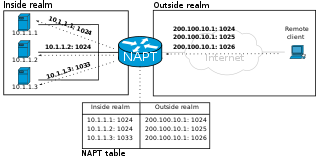
In computer networking, port forwarding or port mapping is an application of network address translation (NAT) that redirects a communication request from one address and port number combination to another while the packets are traversing a network gateway, such as a router or firewall. This technique is most commonly used to make services on a host residing on a protected or masqueraded (internal) network available to hosts on the opposite side of the gateway, by remapping the destination IP address and port number of the communication to an internal host.

WebGUI is an open-source content management system written in Perl and released under the GNU General Public License.
In computer science, automatic programming is a type of computer programming in which some mechanism generates a computer program to allow human programmers to write the code at a higher abstraction level.
Quattor is a generic open-source tool-kit used to install, configure, and manage computers. Quattor was originally developed in the framework of European Data Grid project (2001-2004). Since its first release in 2003, Quattor has been maintained and extended by a volunteer community of users and developers, primarily from the community of grid system administrators. The Quattor tool-kit, like other configuration management systems, reduces the staff required to maintain a cluster and facilitates reliable change management. However, three unique features make it particularly attractive for managing grid resources:

Capistrano is an open-source tool for running scripts on multiple servers; its main use is deploying web applications. It automates the process of making a new version of an application available on one or more web servers, including supporting tasks such as changing databases.

Catalyst is an open source web application framework written in Perl, that closely follows the model–view–controller (MVC) architecture, and supports a number of experimental web patterns. It is written using Moose, a modern object system for Perl. Its design is heavily inspired by frameworks such as Ruby on Rails, Maypole, and Spring.
A software factory is a structured collection of related software assets that aids in producing computer software applications or software components according to specific, externally defined end-user requirements through an assembly process. A software factory applies manufacturing techniques and principles to software development to mimic the benefits of traditional manufacturing. Software factories are generally involved with outsourced software creation.
This is a comparison of notable free and open-source configuration management software, suitable for tasks like server configuration, orchestration and infrastructure as code typically performed by a system administrator.
This page is a comparison of notable remote desktop software available for various platforms.

PowerShell is a task automation and configuration management program from Microsoft, consisting of a command-line shell and the associated scripting language. Initially a Windows component only, known as Windows PowerShell, it was made open-source and cross-platform on August 18, 2016, with the introduction of PowerShell Core. The former is built on the .NET Framework, the latter on .NET.
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.

Shinken is an open source computer system and network monitoring software application compatible with Nagios. It watches hosts and services, gathers performance data and alerts users when error conditions occur and again when the conditions clear.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:
Salt is a Python-based, open-source software for event-driven IT automation, remote task execution, and configuration management. Supporting the "infrastructure as code" approach to data center system and network deployment and management, configuration automation, SecOps orchestration, vulnerability remediation, and hybrid cloud control.
Ansible is a suite of software tools that enables infrastructure as code. It is open-source and the suite includes software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment functionality.
OpenLMI provides a common management infrastructure for Linux systems. Available operations include configuration of various operating system parameters and services, hardware components configuration, and monitoring of system resources. Services provided by OpenLMI can be accessed both locally and remotely, using multiple programming languages and standardized APIs.
Infrastructure as code (IaC) is the process of managing and provisioning computer data centers through machine-readable definition files, rather than physical hardware configuration or interactive configuration tools. The IT infrastructure managed by this process comprises both physical equipment, such as bare-metal servers, as well as virtual machines, and associated configuration resources. The definitions may be in a version control system. The code in the definition files may use either scripts or declarative definitions, rather than maintaining the code through manual processes, but IaC more often employs declarative approaches.






