
A passerine is any bird of the order Passeriformes, which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds or songbirds, passerines are distinguished from other orders of birds by the arrangement of their toes, which facilitates perching.

Microbats constitute the suborder Microchiroptera within the order Chiroptera (bats). Bats have long been differentiated into Megachiroptera (megabats) and Microchiroptera, based on their size, the use of echolocation by the Microchiroptera and other features; molecular evidence suggests a somewhat different subdivision, as the microbats have been shown to be a paraphyletic group.

Megabats constitute the family Pteropodidae of the order Chiroptera (bats). They are also called fruit bats, Old World fruit bats, or—especially the genera Acerodon and Pteropus—flying foxes. They are the only member of the superfamily Pteropodoidea, which is one of two superfamilies in the suborder Yinpterochiroptera. Internal divisions of Pteropodidae have varied since subfamilies were first proposed in 1917. From three subfamilies in the 1917 classification, six are now recognized, along with various tribes. As of 2018, 197 species of megabat had been described.

The globins are a superfamily of heme-containing globular proteins, involved in binding and/or transporting oxygen. These proteins all incorporate the globin fold, a series of eight alpha helical segments. Two prominent members include myoglobin and hemoglobin. Both of these proteins reversibly bind oxygen via a heme prosthetic group. They are widely distributed in many organisms.

The Apocrita are a suborder of insects in the order Hymenoptera. It includes wasps, bees, and ants, and consists of many families. It contains the most advanced hymenopterans and is distinguished from Symphyta by the narrow "waist" (petiole) formed between the first two segments of the actual abdomen; the first abdominal segment is fused to the thorax, and is called the propodeum. Therefore, it is general practice, when discussing the body of an apocritan in a technical sense, to refer to the mesosoma and metasoma rather than the "thorax" and "abdomen", respectively. The evolution of a constricted waist was an important adaption for the parasitoid lifestyle of the ancestral apocritan, allowing more maneuverability of the female's ovipositor. The ovipositor either extends freely or is retracted, and may be developed into a stinger for both defense and paralyzing prey. Larvae are legless and blind, and either feed inside a host or in a nest cell provisioned by their mothers.

Monoplacophora, meaning "bearing one plate", is a polyphyletic superclass of molluscs with a cap-like shell now living at the bottom of the deep sea. Extant representatives were not recognized as such until 1952; previously they were known only from the fossil record, and were thought to have become extinct over 380 million years ago.

Horseshoe bats are bats in the family Rhinolophidae. In addition to the single living genus, Rhinolophus, which has about 106 species, the extinct genus Palaeonycteris has also been recognized. Horseshoe bats are closely related to the Old World leaf-nosed bats, family Hipposideridae, which have sometimes been included in Rhinolophidae. The horseshoe bats are divided into six subgenera and many species groups. The most recent common ancestor of all horseshoe bats lived 34–40 million years ago, though it is unclear where the geographic roots of the family are, and attempts to determine its biogeography have been indecisive. Their taxonomy is complex, as genetic evidence shows the likely existence of many cryptic species, as well as species recognized as distinct that may have little genetic divergence from previously recognized taxa. They are found in the Old World, mostly in tropical or subtropical areas, including Africa, Asia, Europe, and Oceania.
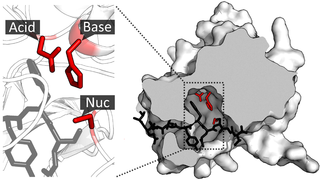
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes. An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to release the product and regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine or even selenocysteine. The 3D structure of the enzyme brings together the triad residues in a precise orientation, even though they may be far apart in the sequence.

Nycteribiidae is a family of the true fly superfamily Hippoboscoidea are known as "bat flies", together with their close relatives the Streblidae. As the latter do not seem to be a monophyletic group, it is conceivable not to unite all bat flies in a single family.

The Austrochiloidea or austrochiloids are a group of araneomorph spiders, treated as a superfamily. The taxon contains two families of eight-eyed spiders:
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the base of a rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Each node in the tree corresponds to a clade; i.e., clade C may be described as basal within a larger clade D if its root is directly linked to the root of D. The terms deep-branching or early-branching are similar in meaning.
In evolutionary biology, the flying primate hypothesis is that megabats, a subgroup of Chiroptera, form an evolutionary sister group of primates. The hypothesis began with Carl Linnaeus in 1758, and was again advanced by J.D. Smith in 1980. It was proposed in its modern form by Australian neuroscientist Jack Pettigrew in 1986 after he discovered that the connections between the retina and the superior colliculus in the megabat Pteropus were organized in the same way found in primates, and purportedly different from all other mammals. This was followed up by a longer study published in 1989, in which this was supported by the analysis of many other brain and body characteristics. Pettigrew suggested that flying foxes, colugos, and primates were all descendants of the same group of early arboreal mammals. The megabat flight and the colugo gliding could be both seen as locomotory adaptations to a life high above the ground.

Testicular receptor 4 also known as NR2C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C2 gene.

The Yinpterochiroptera is a suborder of the Chiroptera, which includes taxa formerly known as megabats and five of the microbat families: Rhinopomatidae, Rhinolophidae, Hipposideridae, Craseonycteridae, and Megadermatidae. This suborder is primarily based on molecular genetics data. This proposal challenged the traditional view that megabats and microbats form monophyletic groups of bats. Further studies are being conducted, using both molecular and morphological cladistic methodology, to assess its merit.

Artiofabula is a clade made up of the Suina and the Cetruminantia. The clade was found in molecular phylogenetic analyses and contradicted traditional relationships based on morphological analyses.

Cyrus Homi Chothia was an English biochemist who was an emeritus scientist at the Medical Research Council (MRC) Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) at the University of Cambridge and emeritus fellow of Wolfson College, Cambridge.
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred. Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent. Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term protein clan is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems.

Corvoidea is a superfamily of birds in the order of Passeriformes.
hAT transposons are a superfamily of DNA transposons, or Class II transposable elements, that are common in the genomes of plants, animals, and fungi.

Noctilionoidea is a superfamily of bats containing seven families: Thyropteridae, Furipteridae, Noctilionidae, Mormoopidae, Phyllostomidae, Myzopodidae, and Mystacinidae.




















