Road signs in the Republic of Ireland do not differ greatly from those used elsewhere in Europe – with the notable exception that hazard or warning signs follow the "New World" style of a yellow diamond. The symbols used on these warning signs do, nevertheless, resemble much more closely those used in the rest of Europe than many of those seen in the United States.

Road signs in Sweden are regulated in Vägmärkesförordningen, VMF (2007:90), and are to be placed 2 metres from the road with the sign 1.6 m from the base for motorized roads. Except for route numbers, there are a maximum of three signs on a pole, with the most important sign at the top. All signs have a reflective layer added on selected parts of the sign as is custom in European countries; most larger signs also have their own illumination.

Road signs in Malaysia are standardised road signs similar to those used in Europe but with certain distinctions. Until the early 1980s, Malaysia closely practice in road sign design, with diamond-shaped warning signs and circular restrictive signs to regulate traffic. Signs usually use the Transport Heavy font on non-tolled roads and highways. Tolled expressways signs use a font specially designed for the Malaysian Highway Authority (LLM) which is LLM Lettering. It has two type of typefaces, LLM Narrow and LLM Normal. Older road signs used the FHWA Series fonts typeface also used in the United States, Canada, and Australia.
Road signs in Singapore closely follow those laid down in the traffic sign regulations used in the United Kingdom, although a number of changes over the years have introduced some slight deviations that suit local road conditions. Road signs in Singapore conform to the local Highway Code under the authority of Singapore Traffic Police.

Road signs in Thailand are standardized road signs similar to those used in other nations but much of it resembles road signage systems used in South American countries with certain differences, such as using a blue circle instead of a red-bordered white circle to indicate mandatory actions. Until the early 1980s, Thailand closely followed American, European, Australian, and Japanese practices in road sign design, with diamond-shaped warning signs and circular restrictive signs to regulate traffic. The Department of Railway maintains a standard on the typeface used in the sign, with custom made type for Thai text, unofficially named "Thang Luang" (อักษรทางหลวง) and a small derivation of FHWA Series fonts typeface, which is used on American road signage, for Latin text. In most Bangkok Metropolitan Area's routes, TS Lopburi is still used.

Road signs in the Czech Republic are regulated by the Ministry of Transport and the police. The signs are nearly the same as the European norm, but with small changes. The law governing the road signs is Decree number 30/2001 Sb., many times amended, and replaced by decree 294/2015 Sb., in force since 1 January 2016.

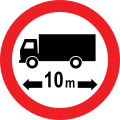
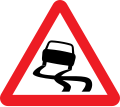
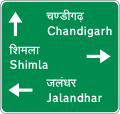
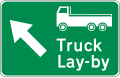
Road signs in Pakistan are modelled on the British road sign system, with an exceptional difference being that they are bilingual and contain messages in Urdu, the national language, and English, and in some cases, the local regional or provincial languages. Pakistan drives on the left side of the road and follows the left-hand traffic system. Vehicles must be overtaken on their right.

Road signs in Mauritius are standardised traffic signs used in Mauritius according to the Traffic Signs Regulations 1990. They are heavily modelled on road signs in the United Kingdom, since Mauritius is a former British colony and drives on the left.

Road signs in Hong Kong are standardised by the Transport Department. Due to being a former British territory, the road signage in Hong Kong is similar to road signs in the United Kingdom, with the addition of Traditional Chinese characters.

Road signs in Cambodia are standardized road signs are similar to those used in Europe but much of it resembles road signage systems used in South American countries with certain differences. The designs of road signage match their neighbours of Thailand and Malaysia, both of which adopt a modified version of the South American road signage system. Until the early 1980s, Cambodia closely followed American, European, Australian, and Japanese practices in road sign design, with diamond-shaped warning signs and circular restrictive signs to regulate traffic. Unlike Thailand and Malaysia, Cambodia does not use the FHWA Series fonts typeface, favouring Helvetica instead.

Road signs in Laos generally follow those used in most European countries as set out in the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. Despite this, the country itself has never signed the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signal. Inscriptions on traffic signs are in Lao, the national language of Laos. However, English is also used for stop and important public places such as tourist attractions, airports, railway stations, and immigration checkpoints. Both Lao and English are used on directional signage.

Road signs in Bangladesh are similar to those used in some parts of the United Kingdom, except that they are multilingual.

Road signs in Vietnam follow Chinese and French road signs. Some signs are written in both Vietnamese and English. The signs are prescribed by the Ministry of Transportation of Vietnam.

Road signs in Georgia are similar to the road sign system of other post-Soviet states that ensure that transport vehicles move safely and orderly, as well as to inform the participants of traffic built-in graphic icons. However, some road signs look a bit different from Soviet ones and closer to the European ones. These icons are governed by the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic and Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.

Road signs in United Arab Emirates are modelled on the British road sign system that are regulated by the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) Dubai and Department of Transport (DoT) Abu Dhabi. The English language typeface is Transport and the Arabic language typeface is Naskh.

Road signs in Kyrgyzstan are similar to the road sign system of other post-Soviet states that ensure that transport vehicles move safely and orderly, as well as to inform the participants of traffic built-in graphic icons. These icons are governed by the Vienna Convention on Road Traffic and Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.

Road signs in Uzbekistan are regulated by the O'zDst 3283-2017 standard. Due to the country being a former Soviet Socialist Republic between 1924 and 1991, road signs are similar in design to those used in the Soviet Union before its dissolution in 1991, as well as in most other post-Soviet states. Uzbekistan acceded to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals on January 17, 1995. The Soviet Union itself was once a signatory to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals.

Road signs in Lithuania conform to the general pattern of those used in most other European countries as set out in the 1968 Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals. Due to the country being occupied and annexed by the Soviet Union between 1940 and 1990, when it restored its independence, modern road signs used in Lithuania are in many ways similar in design to road signs used in the Soviet Union before its dissolution in 1991. This design of road signs is still used in most post-Soviet states, in particular Russia, Belarus, and Ukraine. Neighboring post-Soviet Baltic countries Latvia and Estonia, which were also occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940, have significantly modified their road sign designs, resulting road signs in these two countries being extremely different in design from road signs used in most other post-Soviet states.

Road signs in the Philippines are regulated and standardized by the Department of Public Works and Highways (DPWH). Most of the signs reflect minor influences from American and Australian signs but keep a design closer to the Vienna Convention on Road Signs and Signals, to which the Philippines is an original signatory. The Philippines signed the convention on November 8, 1968, and ratified it on December 27, 1973.

Road signs in Portugal are governed by the "Regulamento de Sinalização do Trânsito" of the Republic of Portugal.