Related Research Articles
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a sequence of numbers that represent samples of a continuous variable in a domain such as time, space, or frequency. In digital electronics, a digital signal is represented as a pulse train, which is typically generated by the switching of a transistor.

Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing signals, such as sound, images, potential fields, seismic signals, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality, and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal.
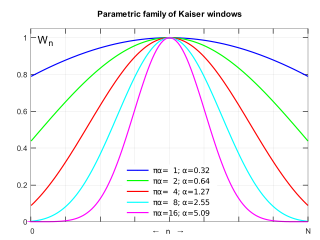
The Kaiser window, also known as the Kaiser–Bessel window, was developed by James Kaiser at Bell Laboratories. It is a one-parameter family of window functions used in finite impulse response filter design and spectral analysis. The Kaiser window approximates the DPSS window which maximizes the energy concentration in the main lobe but which is difficult to compute.

William "Velvel" Morton Kahan is a Canadian mathematician and computer scientist, who received the Turing Award in 1989 for "his fundamental contributions to numerical analysis", was named an ACM Fellow in 1994, and inducted into the National Academy of Engineering in 2005.
Lawrence R. Rabiner is an electrical engineer working in the fields of digital signal processing and speech processing; in particular in digital signal processing for automatic speech recognition. He has worked on systems for AT&T Corporation for speech recognition.
In digital signal processing, downsampling, compression, and decimation are terms associated with the process of resampling in a multi-rate digital signal processing system. Both downsampling and decimation can be synonymous with compression, or they can describe an entire process of bandwidth reduction (filtering) and sample-rate reduction. When the process is performed on a sequence of samples of a signal or a continuous function, it produces an approximation of the sequence that would have been obtained by sampling the signal at a lower rate.
James William Cooley was an American mathematician. Cooley received a B.A. degree in 1949 from Manhattan College, Bronx, NY, an M.A. degree in 1951 from Columbia University, New York, NY, and a Ph.D. degree in 1961 in applied mathematics from Columbia University. He was a programmer on John von Neumann's computer at the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton, NJ, from 1953 to 1956, where he notably programmed the Blackman–Tukey transformation.
Thomas Kailath is an Indian born American electrical engineer, information theorist, control engineer, entrepreneur and the Hitachi America Professor of Engineering emeritus at Stanford University. Professor Kailath has authored several books, including the well-known book Linear Systems, which ranks as one of the most referenced books in the field of linear systems.

James H. McClellan is the Byers Professor of Signal Processing at the Georgia Institute of Technology. He is widely known for his creation of the McClellan transform and for his co-authorship of the Parks–McClellan filter design algorithm.
Alan Victor Oppenheim is a professor of engineering at MIT's Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. He is also a principal investigator in MIT's Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE), at the Digital Signal Processing Group.
Arun N. Netravali is an Indian–American computer engineer credited with contributions in digital technology including HDTV. He conducted research in digital compression, signal processing and other fields. Netravali was the ninth President of Bell Laboratories and has served as Lucent's Chief Technology Officer and Chief Network Architect. He received his undergraduate degree from IIT Bombay, India, and an M.S. and a Ph.D. from Rice University in Houston, Texas, all in electrical engineering. Several global universities, including the Ecole Polytechnique Federale in Lausanne, Switzerland, have honored him with honorary doctorates.
The IEEE Emanuel R. Piore Award was a Technical Field Award given each year by the IEEE to an individual or team of two people who have made outstanding contributions to information processing systems in relation to computer science. The award was discontinued in 2012.
Fumitada Itakura is a Japanese scientist. He did pioneering work in statistical signal processing, and its application to speech analysis, synthesis and coding, including the development of the linear predictive coding (LPC) and line spectral pairs (LSP) methods.
The IEEE Jack S. Kilby Signal Processing Medal is presented "for outstanding achievements in signal processing" theory, technology or commerce. The recipients of this award will receive a gold medal, together with a replica in bronze, a certificate and an honorarium.
Peter A. Franaszek is an American information theorist, an IEEE Fellow, a research staff member emeritus at the IBM T.J. Watson Research Center and a former member of the IBM Academy of Technology. He received his Sc.B. from Brown University in 1962, and his Ph.D. from Princeton University in 1966.
Thomas W. Parks was an American electrical engineer and Professor Emeritus of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Cornell University. He is best known for his contributions to digital signal processing, especially digital filter design and computation of the fast Fourier transform. His last work before retirement was in the area of demosaicing.

Peter (Petre) Stoica is a researcher and educator in the field of signal processing and its applications to radar/sonar, communications and bio-medicine. He is a professor of Signals and Systems Modeling at Uppsala University in Sweden, and a Member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Engineering Sciences, the United States National Academy of Engineering (International Member), the Romanian Academy, the European Academy of Sciences, and the Royal Society of Sciences. He is also a Fellow of IEEE, EURASIP, IETI, and the Royal Statistical Society.

S. Hamid Nawab is Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Biomedical Engineering at Boston University who is a researcher, educator, and engineer in the signal processing and machine perception subfields of Electrical Engineering and their application to the machine/computer analysis of complex biosignals from auditory, speech, and neuromuscular systems.
Palghat P. Vaidyanathan is the Kiyo and Eiko Tomiyasu Professor of Electrical Engineering at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California, USA, where he teaches and leads research in the area of signal processing, especially digital signal processing (DSP), and its applications. He has authored four books, and authored or coauthored close to six hundred papers in various IEEE journals and conferences. Prof. Vaidyanathan received his B.Tech. and M.Tech. degrees from the Institute of Radiophysics and Electronics, Science College campus of University of Kolkata, and a Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering from University of California Santa Barbara in 1982.
References
- ↑ "IEEE Emanuel R. Piore Award Recipients" (PDF). IEEE. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 24, 2010. Retrieved December 30, 2010.
- ↑ "IEEE James H. Mulligan, Jr. Education Medal Recipients" (PDF). IEEE . Retrieved November 23, 2010.
- ↑ "IEEE Jack S. Kilby Signal Processing Medal Recipients" (PDF). IEEE . Retrieved February 27, 2011.
- ↑ "IEEE Jack S. Kilby Signal Processing Medal Recipients - 2010 - Ronald W. Schafer". IEEE . Retrieved February 28, 2011.