
Masonry is the craft of building a structure with brick, stone, or similar material, including mortar plastering which are often laid in, bound and pasted together by mortar. The term masonry can also refer to the building units themselves.

Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenics, whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.

Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to an even greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.

Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar, to wall or cover formed structures.

An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side. A viaduct may be made from a series of arches, although other more economical structures are typically used today.

Ashlar is a cut and dressed stone, worked using a chisel to achieve a specific form, typically rectangular in shape. The term can also refer to a structure built from such stones.

Rustication is a range of masonry techniques used in classical architecture giving visible surfaces a finish texture that contrasts with smooth, squared-block masonry called ashlar. The visible face of each individual block is cut back around the edges to make its size and placing very clear. In addition the central part of the face of each block may be given a deliberately rough or patterned surface.

Murus Dacicus is a construction method for defensive walls and fortifications developed in ancient Dacia sometime before the Roman conquest. It is a mix between traditional construction methods particular to Dacian builders and methods imported from Greek and Roman architecture and masonry, and – although somewhat similar construction techniques were used before, during and long after the period – it has peculiarities that make it unique.

Opus reticulatum is a facing used for concrete walls in Roman architecture from about the first century BCE to the early first century CE. They were built using small pyramid shaped tuff, a volcanic stone embedded into a concrete core. Reticulate work was also combined with a multitude of other building materials to provide polychrome colouring and other facings to form new techniques. Opus reticulatum was generally used in central and southern Italy with the exception being its rare appearance in Africa and Jericho. This was because of tuff's wider availability and ease of local transport in central Italy and Campania compared to other regions.

An earth structure is a building or other structure made largely from soil. Since soil is a widely available material, it has been used in construction since prehistoric times. It may be combined with other materials, compressed and/or baked to add strength.

Chinese city walls refer to defensive walls built to protect important towns and cities in pre-modern China. In addition to walls, Chinese city defenses also included fortified towers and gates, as well as moats and ramparts around the walls.
Opus quadratum is an ancient Roman construction technique, in which squared blocks of stone of the same height were set in parallel courses, most often without the use of mortar. The Latin author Vitruvius describes the technique.
Core-and-veneer, brick and rubble, wall and rubble, ashlar and rubble, and emplekton all refer to a building technique where two parallel walls are constructed and the core between them is filled with rubble or other infill, creating one thick wall. Originally, and in later poorly constructed walls, the rubble was not consolidated. Later, mortar and cement were used to consolidate the core rubble and produce sturdier construction.

Opus spicatum, literally "spiked work," is a type of masonry construction used in Roman and medieval times. It consists of bricks, tiles or cut stone laid in a herringbone pattern.

Opus vittatum, also called opus listatum, was an ancient Roman construction technique introduced at the beginning of the fourth century, made by parallel horizontal courses of tuff blocks alternated with bricks.

Opus incertum was an ancient Roman construction technique, using irregularly shaped and randomly placed uncut stones or fist-sized tuff blocks inserted in a core of opus caementicium.

Opus mixtum, or opus vagecum and opus compositum, was an ancient Roman construction technique. It can consist in a mix of opus reticulatum and at the angles and the sides of opus latericium. It can also consist of opus vittatum and opus testaceum. Opus mixtum was also used from the 4th to 6th centuries AD.
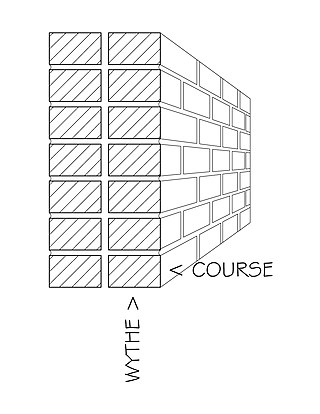
A course is a layer of the same unit running horizontally in a wall. It can also be defined as a continuous row of any masonry unit such as bricks, concrete masonry units (CMU), stone, shingles, tiles, etc.
The history of construction traces the changes in building tools, methods, techniques and systems used in the field of construction. It explains the evolution of how humans created shelter and other structures that comprises the entire built environment. It covers several fields including structural engineering, civil engineering, city growth and population growth, which are relatives to branches of technology, science, history, and architecture. The fields allow both modern and ancient construction to be analyzed, as well as the structures, building materials, and tools used.

Sadd el-Kafara was a masonry embankment dam on Wadi al-Garawi 10 km southeast of Helwan in Cairo, Egypt. The dam was built in the first half of the third millennium BC by the ancient Egyptians for flood control and is the oldest dam of such size in the world. Never completed, the dam was under construction for 10–12 years before being destroyed by a flood. It was rediscovered by Georg Schweinfurth in 1885.



















