Related Research Articles

Kołobrzeg is a port city in the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in north-western Poland with about 47,000 inhabitants. Kołobrzeg is located on the Parsęta River on the south coast of the Baltic Sea. It is the capital of Kołobrzeg County.

The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians, were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his Germania who called them the Rugii, and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some centuries later, they were considered one of the "Gothic" or "Scythian" peoples who were located in the Middle Danube region. Like several other Gothic peoples there, they possibly arrived in the area as allies of Attila until his death in 453. They settled in what is now Lower Austria after the defeat of the Huns at Nedao in 454.
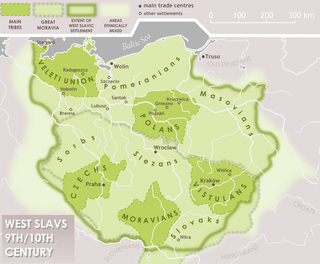
The Pomeranians, first mentioned as such in the 10th century, were a West Slavic tribe, which from the 5th to the 6th centuries had settled at the shore of the Baltic Sea between the mouths of the Oder and Vistula Rivers. They spoke the Pomeranian language that belonged to the Lechitic languages, a branch of the West Slavic language family.

The history of Pomerania starts shortly before 1000 AD, with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polan rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern times Pomerania has been split between Germany and Poland. Its name comes from the Slavic po more, which means "land at the sea".

The Lemovii were a Germanic tribe, only once named by Tacitus in the late 1st century. He noted that they lived near the Rugii and Goths and that they had short swords and round shields.

The Condrusi were an ancient Belgic-Germanic tribe dwelling in what is now eastern Belgium during the Gallic Wars and the Roman period. Their ethnic identity remains uncertain. Caesar described them as part of the Germani Cisrhenani, but their tribal name is probably of Celtic origin. Like other Germani Cisrhenani tribes, it is possible that their old Germanic endonym came to be abandoned after a tribal reorganization, that they received their names from their Celtic neighbours, or else that they were fully or partially assimilated into Celtic culture at the time of the Roman invasion of the region in 57 BC.

Wolin is a town in northwestern Poland, situated on the southern tip of the Wolin island off the Baltic coast of the historic region of Western Pomerania. The island lies at the edge of the strait of Dziwna in Kamień County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship.

The Dębczyn culture is an archeological culture in Pomerania from the third to sixth centuries. It was derived from the neighboring Wielbark culture with influences from the Elbe region. The culture was superseded as the result of the later migrations of West Slavs, in particular of the Pomeranians.

The city of Danzig (Gdańsk) was captured by the State of the Teutonic Order on 13 November 1308, resulting in a massacre of its inhabitants and marking the beginning of tensions between Poland and the Teutonic Order. Originally the knights moved into the fortress as an ally of Poland against the Margraviate of Brandenburg. However, after disputes over the control of the city between the Order and the King of Poland arose, the knights murdered a number of citizens within the city and took it as their own. Thus the event is also known as Gdańsk massacre or Gdańsk slaughter. Though in the past a matter of debate among historians, a consensus has been established that many people were murdered and a considerable part of the town was destroyed in the context of the takeover.

The Bishopric of Cammin was both a former Roman Catholic diocese in the Duchy of Pomerania from 1140 to 1544, and a secular territory of the Holy Roman Empire (Prince-Bishopric) in the Kołobrzeg area from 1248 to 1650.
The County of Gützkow was a county located within the Duchy of Pomerania in the High Middle Ages. It was established in 1129 from the Castellany of Gützkow. Following the death of its last count in 1359, it was re-established into the Vogtei Gützkow.

The Treaty of Stettin or Alliance of Stettin was the legal framework for the occupation of the Duchy of Pomerania by the Swedish Empire during the Thirty Years' War. Concluded on 25 August (O.S.) or 4 September 1630 (N.S.), it was predated to 10 July (O.S.) or 20 July 1630 (N.S.), the date of the Swedish Landing. Sweden assumed military control, and used the Pomeranian bridgehead for campaigns into Central and Southern Germany. After the death of the last Pomeranian duke in 1637, forces of the Holy Roman Empire invaded Pomerania to enforce Brandenburg's claims on succession, but they were defeated by Sweden in the ensuing battles. Some of the Pomeranian nobility had changed sides and supported Brandenburg. By the end of the war, the treaty was superseded by the Peace of Westphalia (1648) and the subsequent Treaty of Stettin (1653), when Pomerania was partitioned into a western, Swedish part, and an eastern, Brandenburgian part.
Treaty of Prenzlau or Peace of Prenzlau may refer to several treaties during a series of wars between the Margraviate of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Pomerania fought for control of Pomerania-Stettin, and possession of the Uckermark in the 15th century. The First Peace of Prenzlau ended a war fought between 1445 and 1448, while the Second Peace of Prenzlau ended a war fought between 1466 and 1468. In older documents, Prenzlau may be spelled Prenzlow, which was the common spelling during the time period the treaties were drawn and was only changed during the 19th century. Prenzlau is situated in the center of Uckermark.

Pomerania during the Early Middle Ages covers the History of Pomerania from the 7th to the 11th centuries.

After the glaciers of the Ice Age in the Early Stone Age withdrew from the area, which since about 1000 AD is called Pomerania, in what are now northern Germany and Poland, they left a tundra. First humans appeared, hunting reindeer in the summer. A climate change in 8000 BC allowed hunters and foragers of the Ertebølle-Ellerbek culture to continuously inhabit the area. These people became influenced by farmers of the Linear Pottery culture who settled in southern Pomerania. The hunters of the Ertebølle-Ellerbek culture became farmers of the Funnelbeaker culture in 3000 BC. The Havelland culture dominated in the Uckermark from 2500 to 2000 BC. In 2400 BC, the Corded Ware culture reached Pomerania and introduced the domestic horse. Both Linear Pottery and Corded Ware culture have been associated with Indo-Europeans. Except for Western Pomerania, the Funnelbeaker culture was replaced by the Globular Amphora culture a thousand years later.
Medieval Pomerania was converted from Slavic paganism to Christianity by Otto von Bamberg in 1124 and 1128, and in 1168 by Absalon.
The Gustow group is an archaeological culture of the Roman Iron Age in Western Pomerania. The Gustow group is associated with the Germanic tribe of the Rugii.
The Wolinians were a Lechitic tribe in Early Middle Age Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Velunzani" with 70 civitates by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845. Associated with both the Veleti and the Pomeranians, they were based on the island of Wolin and the adjacent mainland. Compared to other tribes of these groups, the Wolinians' territory was relatively small but densely settled: in the 11th century, there was one settlement per four square kilometers. The Wolinians are described by Jan Maria Piskorski as the most powerful Pomeranian tribe. This position resulted from the multi-ethnic emporium at the site of the present-day town of Wolin (Wollin), then known as Jomsborg, Jumne, Julin or Vineta.
The Prissani or Pyritzans were a medieval tribe in Pomerania. They were first mentioned as "Prissani" with 70 civitas by the Bavarian Geographer, ca. 845. They are associated with the Pomeranians, and were based in the lower Oder region around the modern town of Pyrzyce (Pyritz). The mention in the Bavarian Geographer is the only written record referring to the tribe.

The Treaty of Grimnitz was the final settlement of a long-standing dispute between the House of Pomerania and the House of Hohenzollern regarding the legal status and succession in the Duchy of Pomerania. It renewed and amended the Treaty of Pyritz of 1493.
References
- 1 2 Johannes Hoops, Herbert Jankuhn, Heinrich Beck, Dieter Geuenich, Heiko Steuer, Reallexikon der germanischen Altertumskunde, 2nd edition, Walter de Gruyter, 2004, pp.452ff, ISBN 3-11-017733-1
- 1 2 3 David Fraesdorff, Der barbarische Norden: Vorstellungen und Fremdheitskategorien bei Rimbert, Thietmar von Merseburg, Adam von Bremen und Helmold von Bosau, Akademie Verlag, 2005, p.55, ISBN 3-05-004114-5
- ↑ Joachim Herrmann, Welt der Slawen: Geschichte, Gesellschaft, Kultur, C.H. Beck, 1986, p.265, ISBN 3-406-31162-8