
Russian is an East Slavic language, spoken primarily in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. It was the de facto and de jure official language of the former Soviet Union. Russian has remained an official language in independent Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Tajikistan, and is still commonly used as a lingua franca in Ukraine, Moldova, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to a lesser extent in the Baltic states and Israel.

The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is a regional intergovernmental organization in Eurasia. It was formed following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It covers an area of 20,368,759 km2 (7,864,422 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 239,796,010. The CIS encourages cooperation in economic, political, and military affairs and has certain powers relating to the coordination of trade, finance, lawmaking, and security, including cross-border crime prevention.
An oblast is a type of administrative division in Bulgaria and several post-Soviet states, including Belarus, Russia and Ukraine. Historically, it was used in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union. The term oblast is often translated into English as region or province. In some countries, oblasts are also known by cognates of the Russian term.

Music of Russia denotes music produced from Russia and/or by Russians. Russia is a large and culturally diverse country, with many ethnic groups, each with their own locally developed music. Russian music also includes significant contributions from ethnic minorities, who populated the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and modern-day Russia. Russian music went through a long history, beginning with ritual folk songs and the sacred music of the Russian Orthodox Church. The 19th century saw the rise of highly acclaimed Russian classical music, and in the 20th century major contributions by various composers such as Igor Stravinsky as well as Soviet composers, while the modern styles of Russian popular music developed, including Russian rock, Russian hip hop and Russian pop.
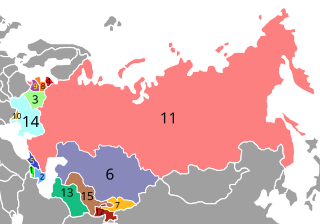
The post-Soviet states, also referred to as the former Soviet Union (FSU) or the former Soviet republics, are the independent sovereign states that emerged/re-emerged from the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Prior to their independence, they existed as Union Republics, which were the top-level constituents of the Soviet Union. There are 15 post-Soviet states in total: Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Latvia, Lithuania, Moldova, Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. Each of these countries succeeded their respective Union Republics: the Armenian SSR, the Azerbaijan SSR, the Byelorussian SSR, the Estonian SSR, the Georgian SSR, the Kazakh SSR, the Kirghiz SSR, the Latvian SSR, the Lithuanian SSR, the Moldavian SSR, the Russian SFSR, the Tajik SSR, the Turkmen SSR, the Ukrainian SSR, and the Uzbek SSR. In Russia, the term "near abroad" is sometimes used to refer to the post-Soviet states other than Russia.
Russian hip hop refers to hip hop music recorded in Russia or in the Russian language in former Soviet states such as Ukraine, Belarus, and Kazakhstan. Hits by Russian rappers are included in the soundtracks of some PC-games and have formed part of several popular internet memes.

Belarusians are a major ethnic group in Russia. At the census of 2010, 521,443 Russian citizens indicated Belarusian ancestry. Major Belarusian groups live in the regions of Moscow, St. Petersburg, Kaliningrad, Karelia and Siberia. Most Belarusians in Russia are migrants from modern Belarus or their descendants, while a minor part of Belarusians in Russia are indigenous.

Philipp Bedrosovich Kirkorov PAR is a Bulgarian-born Russian pop singer. He is a five-time winner of the "Best Selling Russian Artist" title at the World Music Awards ceremonies. He has been a star of Russian pop and dance music since 1989.
Pop music in Ukraine is Western influenced pop music in its various forms that has been growing in popularity in Ukraine since the 1960s.
The New Union Treaty was a draft treaty that would have replaced the 1922 Treaty on the Creation of the USSR to salvage and reform the Soviet Union. A ceremony of the Russian SFSR signing the treaty was scheduled for 20 August 1991, but was prevented by the August Coup a day earlier. The preparation of this treaty was known as the Novo-Ogaryovo process, named after Novo-Ogaryovo, a governmental estate where the work on the document was carried out and where Soviet President and CPSU General Secretary Mikhail Gorbachev talked with leaders of Union republics.

Oleg Mikhaylovich Gazmanov is a Soviet and Russian singer, composer and poet, specializing in patriotic and nationalist songs, as well as songs which cover more conventional pop themes. Gazmanov is leader of pop group "Эскадрон" (Squadron). His songs have been covered by others in the Russian chanson style, such as Mikhail Shufutinsky. He is also a Candidate for Master of Sport of the USSR in gymnastics and is well known for his acrobatics performed during live shows, especially at the beginning of his musical career in the early 1990s.

Nikolay Victorovich Baskov is a Russian tenor who performs in both operatic and popular music styles. His honors include commendations as Meritorious Artist and People's Artist of the Russian Federation.
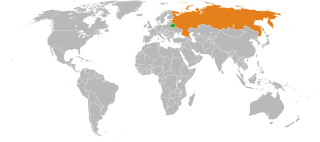
Belarus and Russia share a land border and constitute the supranational Union State. Several treaties have been concluded between the two nations bilaterally. Russia is Belarus' largest and most important economic and political partner. Both are members of various international organizations, including the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Eurasian Economic Union, the Collective Security Treaty Organization, and the United Nations.
VIA is an abbreviation for Vocal and Instrumental Ensemble. It is the general name used for popular music bands that were formally recognized by the Soviet government from the 1960s to the 1980s.
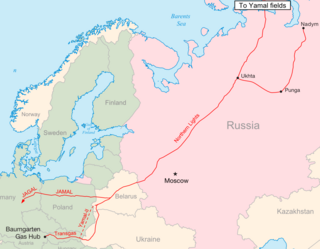
Northern Lights is a natural gas pipeline system in Russia and Belarus. It is one of the main pipelines supplying north-western Russia and is an important transit route for Russian gas to Europe.

Valery Yakovlevich Leontiev is a Soviet and Russian pop singer, sometimes songwriter and actor whose popularity peaked in the early 1980s. He was titled a People's Artist of Russia in 1996. He is known as one of the most prominent artists of Soviet and Russian music. Over the course of his decades-long career, he has recorded more than 30 albums, many of which sold millions of copies. The media refers to Leontiev as a megastar and a legend of the Russian stage.

Pesnya goda, meaning Song of the Year, is an annual televised music festival and gala in Russia, honoring standout songs from the previous year. The event began in the Soviet period, and prior to the dissolution of the USSR also included songs in languages other than Russian.
The following lists events that happened during 1991 in the Soviet Union and Russia.

The Evangelical Lutheran Church in Russia, Ukraine, Kazakhstan and Central Asia, also known as the Evangelical Lutheran Church in Russia and the Other States (ELCROS), is a Lutheran denomination that itself comprises seven regional Lutheran denominations in Belarus, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan as well as individual congregations in Azerbaijan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan. Established in its current form in 1999, ELCROS currently has about 24,050 members in more than 400 congregations within its jurisdiction.
The Lisbon Protocol to the 1991 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty was a document signed by representatives of Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan that recognized the four states as successors of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and all of them assume obligations of the Soviet Union under the START I treaty. The protocol was signed in Lisbon, Portugal, on 23 May 1992.













