Related Research Articles
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases.
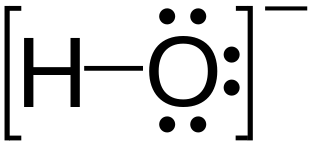
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Both the hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively charged sodium ions and negatively charged chloride ions.

Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, and precursors to catalysts.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.
The term chloride refers either to a chloride ion, which is negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond. Many inorganic chlorides are salts. Many organic compounds are chlorides. The pronunciation of the word "chloride" is.

Sodium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood, sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the Chlor-alkali process.

A lye is an alkali metal hydroxide traditionally obtained by leaching wood ashes, or a strong alkali which is highly soluble in water producing caustic basic solutions. "Lye" most commonly refers to sodium hydroxide (NaOH), but historically has been used for potassium hydroxide (KOH).

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.
Saponification is a process of converting esters into soaps and alcohols by the action of aqueous alkali. Soaps are salts of fatty acids, which in turn are carboxylic acids with long carbon chains. Sodium stearate is a typical soap.
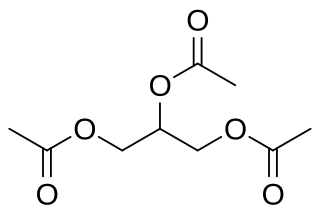
Glycerides, more correctly known as acylglycerols, are esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids, and are generally very hydrophobic.
Biodiesel production is the process of producing the biofuel, biodiesel, through the chemical reactions of transesterification and esterification. This involves vegetable or animal fats and oils being reacted with short-chain alcohols. The alcohols used should be of low molecular weight. Ethanol is the most used because of its low cost, however, greater conversions into biodiesel can be reached using methanol. Although the transesterification reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, the base-catalyzed reaction is more common. This path has lower reaction times and catalyst cost than those acid catalysis. However, alkaline catalysis has the disadvantage of high sensitivity to both water and free fatty acids present in the oils.

Saponification value or saponification number represents the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) required to saponify one gram of fat under the conditions specified. It is a measure of the average molecular weight of all the fatty acids present in the sample in form of triglycerides. The higher the saponification value, the lower the fatty acids average length, the lighter the mean molecular weight of triglycerides and vice versa. Practically, fats or oils with high saponification value are more suitable for soap making.
Alkali salts or basic salts are salts that are the product of incomplete neutralization of a strong base and a weak acid.
The Polenske value is a value determined when examining fat. It is an indicator of how much volatile fatty acid can be extracted from fat through saponification. It is equal to the number of milliliters of 0.1 normal alkali solution necessary for the neutralization of the water-insoluble volatile fatty acids distilled and filtered from 5 grams of a given saponified fat. It is measure of the steam volatile and water insoluble fatty acids, chiefly caprylic, capric and lauric acids, present in oil and fat. The value is named for the chemist who developed it, Eduard Polenske.
The alkali hydroxides are a class of chemical compounds which are composed of an alkali metal cation and the hydroxide anion (OH−). The alkali hydroxides are:

Cleaning agents or hard-surface cleaners are substances used to remove dirt, including dust, stains, foul odors, and clutter on surfaces. Purposes of cleaning agents include health, beauty, removing offensive odor, and avoiding the spread of dirt and contaminants to oneself and others. Some cleaning agents can kill bacteria and clean at the same time. Others, called degreasers, contain organic solvents to help dissolve oils and fats.
Potassium methoxide is the alkoxide of methanol with the counterion potassium and is used as a strong base and as a catalyst for transesterification, in particular for the production of biodiesel.
A metallic soap is a metallic salt of a fatty acid. Theoretically, soaps can be made of any metal, although not all enjoy practical uses. Varying the metal can strongly affect the properties of the compound, particularly its solubility.
References
- ↑ A BRIEF SOAP HISTORY
- ↑ Sub: An Oral History of U.S. Navy Submarines, page 137, By Mark K. Roberts
- ↑ Lessons in Chemistry, page 215, By William Houston Greene
- ↑ High Adventure, page 42, By Joe Miller
- ↑ What Einstein Told His Barber: More Scientific Answers to Everyday Questions, page 244, By Robert Wolke
- ↑ Naval History and Heritage Command, Page 65
- ↑ US Navy, All hands, Oct. 1980, Tin Can Sailor, page 4
- ↑ IUPAC , Compendium of Chemical Terminology , 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) " soap ". doi : 10.1351/goldbook.S05721
- 1 2 Cavitch, Susan Miller. The Natural Soap Book. Storey Publishing, 1994 ISBN 0-88266-888-9.