
Clarke County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,783. Its county seat is Berryville. Clarke County is included in the Washington-Arlington-Alexandria, DC-VA-MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area.

Boyce is a small incorporated town in Clarke County, Virginia, United States. The population was 749 at the 2020 census, up from 589 at the 2010 census.

Daniel Morgan was an American pioneer, soldier, and politician from Virginia. One of the most respected battlefield tacticians of the American Revolutionary War of 1775–1783, he later commanded troops during the suppression of the Whiskey Rebellion of 1791–1794.

Andrew Pickens was a militia leader in the American Revolution. A planter and slaveowner, he developed his Hopewell plantation on the east side of the Keowee River across from the Cherokee town of Isunigu (Seneca) in western South Carolina. He was elected as a member of the United States House of Representatives from western South Carolina. Several treaties with the Cherokee were negotiated and signed at his plantation of Hopewell.

William Washington was a cavalry officer of the Virginia militia and Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, who also served on General George Washington's staff during the naval war with France in 1798 and held a final rank of brigadier general. Primarily known as a commander of light dragoons, he led mounted troops in a number of notable battles in the Carolinas during the campaigns of 1780 and 1781. Following the conflict, this William Washington moved to South Carolina, where he married and served in the state legislature as well as led the Seventh Brigade of the South Carolina militia. Cavalry Commander William Washington of Stafford County and South Carolina has often been confused with his distant cousin William Augustine Washington, also a Revolutionary War patriot and planter, who served as a delegate representing Westmoreland County, Virginia.

The Battle of Cowpens was an engagement during the American Revolutionary War fought on January 17, 1781 near the town of Cowpens, South Carolina, between American Patriot forces under Brigadier General Daniel Morgan and British forces, nearly half American Loyalists, under Lieutenant Colonel Banastre Tarleton, as part of the campaign in the Carolinas. The battle was a turning point in the American reconquest of South Carolina from the British.

Cowpens National Battlefield is a unit of the National Park Service just east of Chesnee, South Carolina, and near the state line with North Carolina. It preserves a major battlefield of the American Revolutionary War.

Greenway Court is a historic country estate near White Post in rural Clarke County, Virginia. The property is the site of the seat of the vast 18th-century land empire of Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron (1693–1781), the only ennobled British colonial proprietor to live in one of the North American colonies. The surviving remnants of his complex — a later replacement brick house and Fairfax's stone land office — were designated a National Historic Landmark in 1960.

Oatlands Historic House and Gardens is an estate located in Leesburg, Virginia, United States. Oatlands is operated by the National Trust for Historic Preservation and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as a National Historic Landmark. The Oatlands property is composed of the main mansion and 415 acres of farmland and gardens. The house is judged one of the finest Federal period country estate houses in the nation.

Walnut Grove Plantation, the home of Charles and Mary Moore, was built in 1765 on a land grant given by King George III. The property is located in Roebuck in Spartanburg, South Carolina. Charles Moore was a school teacher and used the 3,000-acre (12 km2) plantation as a farm. The Moores had ten children, and some of their descendants still live within the area.

Carter Hall was the Millwood, Virginia, USA estate of Lt. Col. Nathaniel Burwell (1750–1814). It is located in the upper Shenandoah Valley, off Virginia Route 255 northeast of Millwood. The estate includes a grand plantation house, a great lawn, and terraced gardens, and has panoramic views in all directions. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

Belvoir was the plantation and estate of colonial Virginia's prominent William Fairfax family. Operated with the forced labor of enslaved people, it was located on the west bank of the Potomac River on the present site of Fort Belvoir in Fairfax County, Virginia.

Long Branch is a historic family seat in Millwood, Virginia built in the early 19th century. Named after the creek that runs through the property, Long Branch was built on approximately 1,000 acres by Robert Carter Burwell in 1811 and was owned by the Burwell-Nelson family until 1957. The property was placed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 1, 1969.

Nathaniel Burwell was an American politician and plantation owner. Perhaps the most distinguished of five men of that name to serve in the Virginia General Assembly before the American Civil War, this Nathaniel Burwell won election to the Virginia House of Delegates as well as the Virginia Ratifying Convention, and also served as the county lieutenant for the James City County militia.

Old Chapel is a historic Episcopal church building located near Millwood, Clarke County, Virginia. Old Chapel is now the oldest Episcopal church building still in use west of the Blue Ridge Mountains. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. In 2014, the Chapel Rural Historic District was recognized, and which encompasses both Cunningham parish churches, discussed below, as well as approximately 700 other structures and an area of nearly 10,500 acres.

Annefield or Annfield is a historic plantation house located near Boyce, Clarke County, Virginia. Matthew Page (1762–1826) built it beginning around 1790, and named it after his new wife, Ann Randolph Meade (1781–1838), daughter of Richard Kidder Meade and sister of William Meade, whom he married in 1799.

Scaleby is a historic estate home and farm located near Boyce, Clarke County, Virginia. The main house and associated outbuildings were built between February 1909 and December 1911 for Henry Brook and Hattie Newcomer Gilpin. The 30,000-square-foot (2,800 m2) house was named for the wealthy family's ancestral home in England.

Greenway Historic District is a national historic district located near Boyce, Clarke County, Virginia. It encompasses 432 contributing buildings, 23 contributing sites, and 35 contributing structures. The districts includes the agricultural landscape and architectural resources of an area distinctively rural that contains numerous large antebellum estates. The district contributing buildings are primarily farm and estate residences and their associated outbuildings. Other contributing buildings include three schools, five churches, two mills, a gas station, a restaurant, and a railroad station. The contributing structures are mostly corncribs and the contributing sites are mainly cemeteries and ruins of historic buildings. The district contains ten individual properties and two historic districts already listed on the Virginia Landmarks Register and National Register of Historic Places.

Long Marsh Run Rural Historic District is a national historic district located just outside Berryville, in Clarke County, Virginia. It encompasses 315 contributing buildings, 16 contributing sites, and 35 contributing structures. The district includes the agricultural landscape and architectural resources of an area distinctively rural that contains numerous large antebellum and postbellum estates, and several smaller 19th-century farms, churches, schools and African-American communities.
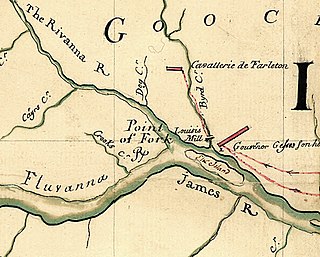
Point of Fork Arsenal was an arsenal established in the 18th century located near what is now Columbia, Virginia, United States. It was raided and destroyed on June 5, 1781, by Col. John Graves Simcoe of the Queen's Rangers. It was rebuilt and used for the manufacture and repair of arms and supplied material to combat the Whiskey Rebellion and to aid the Battle of Fallen Timbers. The arsenal remained in service until 1801, when it was abandoned in favor of a more centralized arsenal at Richmond, the Virginia Manufactory of Arms.

























