Related Research Articles
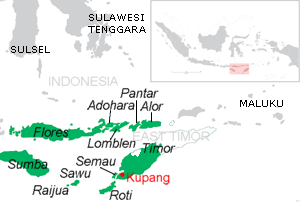
Pantar is the second largest island in the Indonesian Alor Archipelago, after Alor. To the east is the island of Alor and other small islands in the archipelago; to the west is the Alor Strait, which separates it from the Solor Archipelago. To the south is the Ombai Strait, and 72 kilometres (45 mi) away, the island of Timor. To the north is the Banda Sea. Pantar is about 50 kilometres (31 mi) north-to-south, and varies from 11 to 29 kilometres in east-west width. It has an area of 728 square kilometres (281 sq mi). The main towns on the island are Baranusa and Kabir. Administratively, the island is part of the Alor Regency.

Western Pantar, sometimes referred to by the name of one of its dialects, Lamma, is a Papuan language spoken in the western part of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. Western Pantar is spoken widely in the region by about 10,000 speakers. Although speakers often use Malay in political, religious, and educational contexts, Western Pantar remains the first language of children of the region, and is acquired to some extent by immigrants.
Nedebang is a Papuan language spoken in the villages of Balungada and Baulang in the eastern district of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. There are also Nedebang speakers in Air Panas, administratively part of Balungada but located 1 km from the main village.

Bomberai Peninsula is located in the Western New Guinea region, opposite to and to the south of the Bird's Head Peninsula. To the west lies the Sebakor Bay and to the south Kamrau Bay. Sabuda island lies off the western tip of the peninsula, and is separated from the mainland by Berau and Bintuni straits.
Abui is a non-Austronesian language of the Alor Archipelago. It is spoken in the central part of Alor Island in Eastern Indonesia, East Nusa Tenggara (NTT) province by the Abui people. The native name in the Takalelang dialect is Abui tanga which literally translates as 'mountain language'.

The West Bomberai languages are a family of Papuan languages spoken on the Bomberai Peninsula of western New Guinea and in East Timor and neighboring islands of Indonesia.

The Alor–Pantar languages are a family of clearly related Papuan languages spoken on islands of the Alor archipelago near Timor in southern Indonesia. They may be most closely related to the Papuan languages of western Timor, but this is not yet clear. A more distant relationship with the Trans–New Guinea languages of the Bomberai peninsula has been proposed based on pronominal evidence, but though often cited has never been firmly established.
The Tanglapui languages are a pair of closely related Papuan languages, Sawila and Kula, spoken on the island of Alor, which lies north of Timor in south east Indonesia. They have only marginal mutual intelligibility, and are ethnically distinct; nonetheless, the name 'Tanglapui' is used for either language.
The Timor–Alor–Pantar (TAP) languages are a family of Papuan (non-Austronesian) languages spoken in Timor, Kisar, and the Alor archipelago in Southern Indonesia.

The West Trans–New Guinea languages are a suggested linguistic linkage of Papuan languages, not well established as a group, proposed by Malcolm Ross in his 2005 classification of the Trans–New Guinea languages. Ross suspects they are an old dialect continuum, because they share numerous features that have not been traced to a single ancestor using comparative historical linguistics. The internal divisions of the languages are also unclear. William A. Foley considers the TNG identity of the Irian Highlands languages at least to be established.
Alorese is an Austronesian language spoken on Alor and the neighboring islands of the Alor archipelago in eastern Indonesia. It is not to be confused with non-Austronesian (Papuan) languages of the Alor–Pantar family which are also spoken in this region. It is also distinct from Alor Malay, a Malay variety which is currently supplanting Alorese as the language of wider communication in the region. Alorese is the native language of several immigrant communities located along the coast of the Alor archipelago, especially at Alor Kecil on Alor and at Baranusa and Marica on Pantar. It has also been used extensively as a trade language in the region.
Kui is a Timor–Alor–Pantar language spoken in several enclaves on Alor Island, East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. The language is called 'Masin lak' in Kui. Although the exact number of speakers is unknown, Kui is an endangered language since speakers are shifting to Alor Malay.

The Wersing language, also known as Kolana after its primary dialect, is spoken in scattered settlements around the coast of Alor in Indonesia. Due to this settlement pattern, Wersing speakers are in contact with Abui and Kamang speakers and often have some competence in these languages. Though not closely related, it has cultural connections with Tukudede on the neighboring island of Timor.
Kula (Kola) or Lamtoka (Lantoka), also known as Tanglapui, is a Papuan language spoken in villages on the north coast, south coast and mountainous interior of Alor Island in Indonesia. Dialects are Kula proper, Kulatela, Watena, Kula Watena, Iramang, Larena, Sumang, and Arumaka. Most settlements where Kula is spoken are "new villages" that have only been inhabited since the 1960s. Due to this recent resettlement, and since usage of the language is disencouraged in schools, Kula is an endangered language.

Blagar is a Papuan language of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. The Tereweng lect spoken on Tereweng island off the southeast coast of Pantar is sometimes considered a separate language.
Woisika, also known as Kamang, is a Papuan language of Alor Island of Indonesia. The three main dialects are Western Kamang, Lowland Kamang, and Upland Kamang. Dialects also include Lembur, Sibo, Kamang, Tiayai, Watang, Kamana-Kamang. They may constitute more than one language. Kamang is an endangered language, since children usually only have passive competence of the language, and instead are shifting to Malay.
Retta (Reta) is a Papuan language spoken on the south sides of Pura and Ternate islands, between Pantar and Alor in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. It is not mutually intelligible with Blagar, which is spoken on the north side of Pura Island, and is unrelated to Alorese, which is spoken on the north side of Ternate.
Kelon, or Klon, is a Papuan language of the western tip of Alor Island in the Alor archipelago of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia.
Kafoa, or Jafoo, is a Papuan language of Alor Island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. The name "Kafoa" is not recognized by speakers; it is not clear which name they use themselves. Kafoa speakers are frequently multilingual, also speaking Malay, Klon and Abui. Children are typically initially taught Malay by their parents and later acquire Kafoa after having reached school age.
Kaera is a Papuan language spoken on the northeastern coast of Pantar island in the Alor archipelago of Indonesia. It belongs to the Timor-Alor-Pantar language family. Kaera is used alongside Indonesian in religious contexts, but Kaera is not used in education.
References
- ↑ "The Alor-Pantar languages:".
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Sawila". Glottolog 3.0 . Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Kratochvíl, František (2014). "Sawila". In Schapper, Antoinette (ed.). The Papuan Languages of Timor, Alor and Pantar: Volume 1. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 351–438.