Related Research Articles

The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.

The Bilateria or bilaterians are animals with bilateral symmetry as an embryo, i.e. having a left and a right side that are mirror images of each other. This also means they have a head and a tail as well as a belly and a back. Nearly all are bilaterally symmetrical as adults as well; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which achieve secondary pentaradial symmetry as adults, but are bilaterally symmetrical during embryonic development.
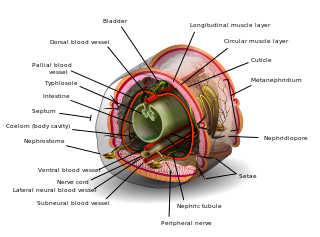
The coelom is the main body cavity in most animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it remains undifferentiated. In the past, and for practical purposes, coelom characteristics have been used to classify bilaterian animal phyla into informal groups.

Ecdysozoa is a group of protostome animals, including Arthropoda, Nematoda, and several smaller phyla. They were first defined by Aguinaldo et al. in 1997, based mainly on phylogenetic trees constructed using 18S ribosomal RNA genes. A large study in 2008 by Dunn et al. strongly supported the Ecdysozoa as a clade, that is, a group consisting of a common ancestor and all its descendants.
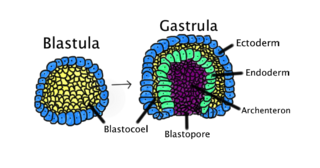
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula, or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. Before gastrulation, the embryo is a continuous epithelial sheet of cells; by the end of gastrulation, the embryo has begun differentiation to establish distinct cell lineages, set up the basic axes of the body, and internalized one or more cell types including the prospective gut.

The blastocoel, also spelled blastocoele and blastocele, and also called cleavage cavity, or segmentation cavity is a fluid-filled or yolk-filled cavity that forms in the blastula during very early embryonic development. At this stage in mammals the blastula develops into the blastocyst containing an inner cell mass, and outer trophectoderm.
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans produce two or three primary germ layers. Some animals, like cnidarians, produce two germ layers making them diploblastic. Other animals such as bilaterians produce a third layer between these two layers, making them triploblastic. Germ layers eventually give rise to all of an animal’s tissues and organs through the process of organogenesis.
The primary gut that forms during gastrulation in a developing embryo is known as the archenteron, the gastrocoel or the primitive digestive tube. It develops into the endoderm and mesoderm of an animal.

In developmental biology, animal embryonic development, also known as animal embryogenesis, is the developmental stage of an animal embryo. Embryonic development starts with the fertilization of an egg cell (ovum) by a sperm cell, (spermatozoon). Once fertilized, the ovum becomes a single diploid cell known as a zygote. The zygote undergoes mitotic divisions with no significant growth and cellular differentiation, leading to development of a multicellular embryo after passing through an organizational checkpoint during mid-embryogenesis. In mammals, the term refers chiefly to the early stages of prenatal development, whereas the terms fetus and fetal development describe later stages.
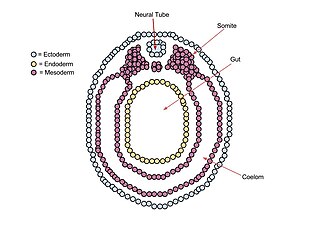
A neurula is a vertebrate embryo at the early stage of development in which neurulation occurs. The neurula stage is preceded by the gastrula stage; consequentially, neurulation is preceded by gastrulation. Neurulation marks the beginning of the process of organogenesis.
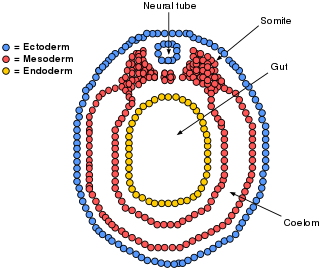
The lateral plate mesoderm is the mesoderm that is found at the periphery of the embryo. It is to the side of the paraxial mesoderm, and further to the axial mesoderm. The lateral plate mesoderm is separated from the paraxial mesoderm by a narrow region of intermediate mesoderm. The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers, between the outer ectoderm and inner endoderm.

Enterocoely describes both the process by which some animal embryos develop and the origin of the cells involved. In enterocoely, a mesoderm is formed in a developing embryo, in which the coelom appears from pouches growing and separating from the digestive tract. As the incipient coelomic epithelium originates from archenteral diverticula, the endoderm therefore gives rise to the mesodermal cells.

Human embryonic development, or human embryogenesis, is the development and formation of the human embryo. It is characterised by the processes of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, the development of the human body entails growth from a one-celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilization occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form the single cell zygote and the germinal stage of development commences. Embryonic development in the human, covers the first eight weeks of development; at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus. Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilization. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is about nine months or 40 weeks.
The urbilaterian is the hypothetical last common ancestor of the bilaterian clade, i.e., all animals having a bilateral symmetry.

Deuterostomia are animals typically characterized by their anus forming before their mouth during embryonic development. The group's sister clade is Protostomia, animals whose digestive tract development is more varied. Some examples of deuterostomes include vertebrates, sea stars, and crinoids.

Phoronids are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore, and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies. They live in most of the oceans and seas, including the Arctic Ocean but excluding the Antarctic Ocean, and between the intertidal zone and about 400 meters down. Most adult phoronids are 2 cm long and about 1.5 mm wide, although the largest are 50 cm long.

Protostomia is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's members, although the reverse is typically true of its sister clade, Deuterostomia. Well known examples of protostomes are arthropods, molluscs, annelids, flatworms and nematodes. They are also called schizocoelomates since schizocoely typically occurs in them.
In evolutionary developmental biology, inversion refers to the hypothesis that during the course of animal evolution, the structures along the dorsoventral (DV) axis have taken on an orientation opposite that of the ancestral form.

Nephrozoa is a major clade of bilaterians, divided into the protostomes and the deuterostomes, containing almost all animal phyla and over a million extant species. Its sister clade is the Xenacoelomorpha. The Ambulacraria was formerly thought to be sister to the Xenacoelomorpha, forming the Xenambulacraria as basal Deuterostomes, or basal Bilateria invalidating Nephrozoa and Deuterostomes in earlier studies. The coelom, the digestive tract and excretory organs (nephridia), and nerve cords developed in the Nephrozoa. It has been argued that, because protonephridia are only found in protostomes, they cannot be considered a synapomorphy of this group. This would make Nephrozoa an improper name, leaving Eubilateria as this clade's name.

Xenacoelomorpha is a small phylum of bilaterian invertebrate animals, consisting of two sister groups: xenoturbellids and acoelomorphs. This new phylum was named in February 2011 and suggested based on morphological synapomorphies, which was then confirmed by phylogenomic analyses of molecular data.
References
- 1 2 Moore, Janet; Overhill, Raith (2006). An introduction to the invertebrates. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521857369.
- ↑ Lüter, Carsten (2000-06-01). "The origin of the coelom in Brachiopoda and its phylogenetic significance". Zoomorphology. 120 (1): 15–28. doi:10.1007/s004359900019. ISSN 1432-234X. S2CID 24929317.
- ↑ Bailly, Anatole (1981-01-01). Abrégé du dictionnaire grec français. Paris: Hachette. ISBN 2010035283. OCLC 461974285.
- ↑ Bailly, Anatole. "Greek-french dictionary online". www.tabularium.be. Retrieved 2020-03-05.
- ↑ Adoutte, André; Balavoine, Guillaume; Lartillot, Nicolas; Rosa, Renaud de; Adoutte, André; Balavoine, Guillaume; Lartillot, Nicolas; Rosa, Renaud de (1999-03-01). "Animal evolution: the end of the intermediate taxa?". Trends in Genetics. 15 (3): 104–108. doi:10.1016/S0168-9525(98)01671-0. ISSN 0168-9525. PMID 10203807.
- ↑ Technau, Ulrich; Scholz, Corinna B. (2003). "Origin and evolution of endoderm and mesoderm". The International Journal of Developmental Biology. 47 (7–8): 531–539. ISSN 0214-6282. PMID 14756329.
- ↑ Kaul-Strehlow, Sabrina; Stach, Thomas (2011-05-11). "The pericardium in the deuterostome Saccoglossus kowalevskii (Enteropneusta) develops from the ectoderm via schizocoely". Zoomorphology. 130 (2): 107. doi:10.1007/s00435-011-0125-0. ISSN 1432-234X. S2CID 22199440.