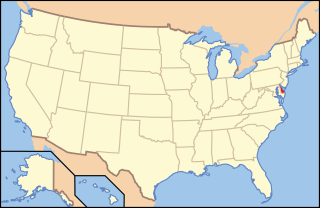
Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) persons in the U.S. state of Delaware enjoy the same legal protections as heterosexuals. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal in Delaware since January 1, 1973. On January 1, 2012, civil unions became available to same-sex couples, granting them the "rights, benefits, protections, and responsibilities" of married persons. Delaware legalized same-sex marriage on July 1, 2013.

Illinois is seen as one of the most progressive states in the United States in regard to lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBT) rights and often viewed as one of the most liberal states in the Midwestern United States. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1962, after Illinois became the first U.S. state to repeal its sodomy laws. Same-sex marriage was banned by statute in 1996, but has since been legalized in November 2013, after a law allowing such marriages was signed by then-Governor Pat Quinn on November 20 and went into effect on June 1, 2014. Civil unions also have been legal statewide since 2011 and same-sex couples are also allowed to adopt children. Additionally, discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and gender identity is banned in the state. Since 2016, conversion therapy on minors has also been forbidden.
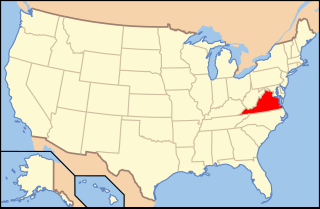
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia do not enjoy the same rights that non-LGBT residents do. Same-sex marriage has been legal in Virginia since October 6, 2014, when the U.S. Supreme Court refused to consider an appeal in the case of Bostic v. Rainey. Despite this, there is still only limited rights for LGBT persons in Virginia, since there is no statewide law protecting LGBT persons from discrimination in housing, credit, or any other area, with the exception of statewide employment, the state's hate crime laws do not protect against violence committed based on sexual orientation or gender identity, and Virginia's statute criminalizing sodomy between same-sex and opposite-sex couples, though declared unconstitutional in 2003, was not repealed until 11 years later in 2014.
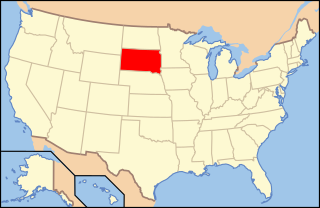
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) persons in the U.S. state of South Dakota may face some legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Same-sex sexual activity is legal in South Dakota, as is same-sex marriage. However, discrimination on the account of sexual orientation or gender identity is not expressly addressed in the state's civil right law.
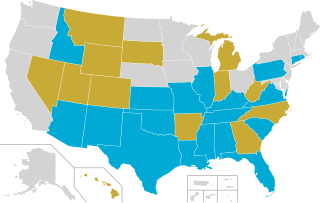
State Religious Freedom Restoration Acts are state laws based on the Religious Freedom Restoration Act (RFRA), a federal law that was passed almost unanimously by the U.S. Congress in 1993 and signed into law by President Bill Clinton. The laws mandate that religious liberty of individuals can only be limited by the "least restrictive means of furthering a compelling government interest". Originally, the federal law was intended to apply to federal, state, and local governments. In 1997, the U.S. Supreme Court in City of Boerne v. Flores held that the Religious Freedom Restoration Act only applies to the federal government but not states and other local municipalities within them. As a result, 21 states have passed their own RFRAs that apply to their individual state and local governments.
Arizona SB 1062 was an Arizona bill to amend an existing law to give any individual or legal entity an exemption from any state law if it substantially burdened their exercise of religion, including Arizona law requiring public accommodation.
The state of North Dakota has improved in its treatment of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender residents in the late 1990s and into the 21st Century, when LGBT residents began to openly establish events, organizations and outlets for fellow LGBT residents and allies, and increase in political and community awareness.

Mississippi House Bill 1523, also called the Religious Liberty Accommodations Act or Protecting Freedom of Conscience from Government Discrimination Act, is 2016 state legislation passed in direct response to federal rulings in support of same-sex marriage. MS H.B. 1523 provides protections for persons, religious organizations, and private associations who choose to provide or withhold services discriminatorily in accordance to the three "deeply held religious beliefs or moral convictions" which are specifically outlined in the bill. These protected beliefs are 1) that marriage is and should be an exclusively heterosexual union, 2) sex should not occur outside of marriage, and 3) that biologically-assigned sex is objective and immutably linked to gender.
The Mississippi Religious Freedom Restoration Act is a 2014 act that states that "government should not substantially burden religious exercise without compelling justification. The act protects religious people from legal repercussions if they verbally condemn the lifestyle or actions of LGBT persons. Additionally, the bill expands the definition of an individual to include businesses, and so if a business owner thinks their religious beliefs would be violated by delivering service to an LGBT person, the Act allows them to deny them service, a move that some commentators have called "anti-gay segregation".
The Mississippi Student Religious Liberties Act of 2013 is a 2013 act which protects the views of students in any educational institution from being reprimanded for their religious views. Under the bill, a school may not discipline a student for expressing anti-LGBT views either verbally or through written assignments.
Senate Bill 175 is a 2016 Kansas legislative proposal that would prohibit public universities to "deny a religious student association any benefit available to any other student association" based on those organizations' "sincerely held religious beliefs" This bill is intended to protect student organizations who restrict membership in regards to LGBT students, which critics argue is discriminatory.
Senate Bill 2, officially called An act to allow magistrates, assistant registers of deeds, and deputy registers of deeds to recuse themselves from performing duties related to marriage ceremonies due to sincerely held religious objection., is a 2015 North Carolina anti-LGBT law that allows for an exemption for state magistrates, assistant register of deeds, or deputy register of deeds who object to participating to issuing marriage licenses for marriages they object to "based upon any sincerely held religious objection."
Senate Bill 297 is a 2015 Utah anti-LGBT act that allows for an exemption for individuals, religious officials, religious organizations, and government officers and employees who object to participating to issuing marriage licenses for marriages they object to based on "deeply held beliefs about marriage, family, and sexuality."
A bathroom bill is the common name for legislation or a statute that defines access to public toilets by gender (restrooms)—or transgender individual. Bathroom bills affect access to sex-segregated public facilities for an individual based on a determination of their sex as defined in some specific way—such as their sex as assigned at birth, their sex as listed on their birth certificate, or the sex that corresponds to their gender identity. A bathroom bill can either be inclusive or exclusive of transgender individuals, depending on the aforementioned definition of their sex.
House Bill 1111, officially called An act to amend Tennessee Code Annotated, Title 1, Chapter 3, relative to the construction of statutes, is a 2017 law in the state of Tennessee that added the following text: "undefined words shall be given their natural and ordinary meaning, without forced or subtle construction that would limit or extend the meaning of the language, except when a contrary intention is clearly manifest."
House Bill 142 is a 2017 law that was enacted in the state of North Carolina that repealed House Bill 2. The bill states that all "state agencies, boards, offices, departments, institutions, branches of government, including The University of North Carolina and the North Carolina Community College System, and political subdivisions of the State, are preempted from regulation of access to multiple occupancy restrooms, showers, or changing facilities, except in accordance with an act of the General Assembly." It also enacted that no local government in this state may enact or amend an ordinance regulating private employment practices or regulating public accommodations until December 1, 2020.
Child Placing Agency Inclusion Act is a 2017 anti-LGBT law that was enacted in the state of Alabama that permits taxpayer-funded adoption agencies to deny services on the basis of religious exemptions.
Senate Bill 1556, officially called An act to amend Tennessee Code Annotated, Title 4; Title 49 and Title 63, relative to conscientious objections to the provision of counseling and therapy, is a 2016 anti-LGBT law in the state of Tennessee that allows licensed counselors in private practice to use their own religious beliefs as an excuse for terminating care or referring away clients because of moral objections to how the client identifies.
Senate Bill 17 is a 2017 Kentucky law designed to protect religious freedoms at public schools and post-secondary institutions in the state. The law allows students to express religious views in their assignments, allows teachers to include religious lessons, and permits school clubs and other campus organizations to exclude members on religious grounds. The law has been criticized by LGBT advocates, who contend that this last provision permits student organizations to discriminate on the basis of sexual orientation.








