A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who does not hold a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. In contrast, commissioned officers usually enter directly from a military academy, officer training corps (OTC) or reserve officer training corps (ROTC), or officer candidate school (OCS) or officer training school (OTS), after receiving a post-secondary degree.
Sergeant (Sgt) is a rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The alternative spelling, serjeant, is used in The Rifles and other units that draw their heritage from the British light infantry. Its origin is the Latin serviens, 'one who serves', through the Old French term serjant.
A master sergeant is the military rank for a senior non-commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries.
Sergeant major is a senior non-commissioned rank or appointment in many militaries around the world.

The master chief petty officer of the Navy is a unique non-commissioned rank and position of office of the United States Navy, which is designated as a special paygrade above E-9. The holder of this position is the most senior enlisted member of the U.S. Navy, equivalent to the sergeant Major of the Army, chief master sergeant of the Air Force, sergeant major of the Marine Corps, master chief petty officer of the Coast Guard, and chief master sergeant of the Space Force. The holder of this rank and position is the most senior enlisted sailor in the Navy, unless an enlisted sailor is serving as the senior enlisted advisor to the chairman. The current MCPON is James Honea.
The chart below represents the current enlisted rank insignia of the United States Air Force.

A chief master sergeant is the military rank for a senior non-commissioned officer in the armed forces of some countries.

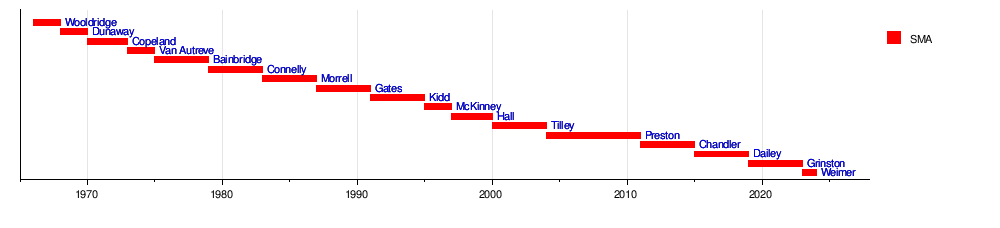
The Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force is a unique non-commissioned rank in the United States Air Force. The holder of this rank and position of office represents the highest enlisted level of leadership in the Air Force, unless an enlisted airman is serving as the senior enlisted advisor to the chairman. The CMSAF provides direction for the enlisted corps and represents their interests, as appropriate, to the American public, and to those in all levels of government. The CMSAF is appointed by the Air Force chief of staff (AF/CC) and serves as the senior enlisted advisor to the Air Force chief of staff and the secretary of the Air Force on all issues regarding the welfare, readiness, morale, and proper utilization and progress of the enlisted force.

The sergeant major of the Marine Corps is a billet, as well as a unique enlisted grade of rank, and is designated a special paygrade above E-9. The position also has a unique non-commissioned grade of rank insignia, in the United States Marine Corps. The holder of this rank and position is the most senior enlisted marine in the Marine Corps, unless an enlisted marine is serving as the senior enlisted advisor to the chairman, which is the case as of November 3, 2023.

A distinctive unit insignia (DUI) is a metallic heraldic badge or device worn by soldiers in the United States Army. The DUI design is derived from the coat of arms authorized for a unit. DUIs may also be called "distinctive insignia" (DI) or, imprecisely, a "crest" or a "unit crest" by soldiers or collectors. The U.S. Army Institute of Heraldry is responsible for the design, development and authorization of all DUIs.

In the United States Army, soldiers may wear insignia to denote membership in a particular area of military specialism and series of functional areas. Army branch insignia is similar to the line officer and staff corps officer devices of the U.S. Navy as well as to the Navy enlisted rating badges. The Medical, Nurse, Dental, Veterinary, Medical Service, Medical Specialist, Chaplains, and Judge Advocate General's Corps are considered "special branches", while the others are "basic branches".

The master chief petty officer of the Coast Guard (MCPOCG) is the senior enlisted member of the U.S. Coast Guard and the principal advisor to the commandant of the Coast Guard on all enlisted personnel matters.

The senior enlisted advisor to the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (SEAC) is the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) position overall in the United States Armed Forces. The SEAC is appointed by the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff to serve as a spokesperson to address the issues of enlisted personnel to the highest positions in the Department of Defense. As such, the SEAC is the primary enlisted advisor to the chairman, and serves at the pleasure of the secretary of defense. The SEAC's exact duties vary, depending on the chairman, though the SEAC generally devotes much of their time traveling throughout the Department of Defense, to observe training and communicating to service members and their families. The SEAC's normal term of assignment runs concurrently with the chairman, but an incumbent may be reappointed to serve longer. The first member to hold this post was William Gainey. The current SEAC is Troy E. Black, USMC who assumed the duties on 3 November 2023.

A senior enlisted advisor (SEA) in the United States Armed Forces is the most senior enlisted service member in a unit, and acts as an advisor to the commanding officer. Formally, E-9 billets for the senior enlisted advisor are established at service unit, command, major command, force, or fleet levels to the SEAs/CSELs of DoD Agencies and the Senior Enlisted Advisor to the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. SEAs are also known as command senior enlisted leaders (CSEL). Always a non-commissioned officer, the SEA is the main link between the commanding officer and the enlisted service members under his or her charge.
First sergeant is typically a senior non-commissioned officer rank, used in many countries.

The senior enlisted advisor to the chief of the National Guard Bureau is the top enlisted person in the National Guard of the United States; which is a joint reserve component of the United States Army and the United States Air Force.

The chief master sergeant of the Space Force (CMSSF) is the senior enlisted advisor to the chief of space operations and the secretary of the Air Force. The chief master sergeant of the Space Force is the most senior enlisted guardian in the U.S. Space Force, unless an enlisted guardian is serving as the senior enlisted advisor to the chairman.