Related Research Articles

A silanol is a functional group in silicon chemistry with the connectivity Si–O–H. It is related to the hydroxy functional group (C–O–H) found in all alcohols. Silanols are often invoked as intermediates in organosilicon chemistry and silicate mineralogy. If a silanol contains one or more organic residue, it is an organosilanol.

Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula. Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The color depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red.

An alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They are written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands. Alkoxides, although generally not stable in protic solvents such as water, occur widely as intermediates in various reactions, including the Williamson ether synthesis. Transition metal alkoxides are widely used for coatings and as catalysts.
Silicone resins are a type of silicone material which is formed by branched, cage-like oligosiloxanes with the general formula of RnSiXmOy, where R is a non reactive substituent, usually Methyl (Me) or Phenyl (Ph), and X is a functional group Hydrogen (H), Hydroxyl group (OH), Chlorine (Cl) or Alkoxy group (OR). These groups are further condensed in many applications, to give highly crosslinked, insoluble polysiloxane networks.
In materials science, the sol–gel process is a method for producing solid materials from small molecules. The method is used for the fabrication of metal oxides, especially the oxides of silicon (Si) and titanium (Ti). The process involves conversion of monomers into a colloidal solution (sol) that acts as the precursor for an integrated network of either discrete particles or network polymers. Typical precursors are metal alkoxides.

A siloxane is a functional group in organosilicon chemistry with the Si−O−Si linkage. The parent siloxanes include the oligomeric and polymeric hydrides with the formulae H(OSiH2)nOH and (OSiH2)n. Siloxanes also include branched compounds, the defining feature of which is that each pair of silicon centres is separated by one oxygen atom. The siloxane functional group forms the backbone of silicones, the premier example of which is polydimethylsiloxane. The functional group R3SiO− (where the three Rs may be different) is called siloxy. Siloxanes are manmade and have many commercial and industrial applications because of the compounds’ hydrophobicity, low thermal conductivity, and high flexibility.
Organosilicon compounds are organometallic compounds containing carbon–silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science of their preparation and properties. Most organosilicon compounds are similar to the ordinary organic compounds, being colourless, flammable, hydrophobic, and stable to air. Silicon carbide is an inorganic compound.

Lithium amide or lithium azanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiNH2. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure. Lithium amide can be made by treating lithium metal with liquid ammonia:

Hexamethyldisiloxane (HMDSO) is an organosilicon compound with the formula O[Si(CH3)3]2. This volatile colourless liquid is used as a solvent and as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is prepared by the hydrolysis of trimethylsilyl chloride. The molecule is the protypical disiloxane and resembles a subunit of polydimethylsiloxane.
An inorganic polymer is a polymer with a skeletal structure that does not include carbon atoms in the backbone. Polymers containing inorganic and organic components are sometimes called hybrid polymers, and most so-called inorganic polymers are hybrid polymers. One of the best known examples is polydimethylsiloxane, otherwise known commonly as silicone rubber. Inorganic polymers offer some properties not found in organic materials including low-temperature flexibility, electrical conductivity, and nonflammability. The term inorganic polymer refers generally to one-dimensional polymers, rather than to heavily crosslinked materials such as silicate minerals. Inorganic polymers with tunable or responsive properties are sometimes called smart inorganic polymers. A special class of inorganic polymers are geopolymers, which may be anthropogenic or naturally occurring.

Methyltrichlorosilane, also known as trichloromethylsilane, is an organosilicon compound with the formula CH3SiCl3. It is a colorless liquid with a sharp odor similar to that of hydrochloric acid. As methyltrichlorosilane is a reactive compound, it is mainly used a precursor for forming various cross-linked siloxane polymers.
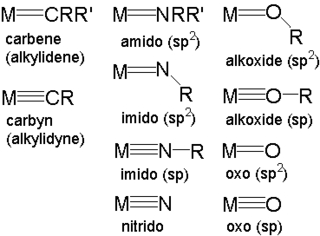
In Chemistry, a metal–ligand multiple bond describes the interaction of certain ligands with a metal with a bond order greater than one. Coordination complexes featuring multiply bonded ligands are of both scholarly and practical interest. Transition metal carbene complexes catalyze the olefin metathesis reaction. Metal oxo intermediates are pervasive in oxidation catalysis. oxygen evolving complex.
The direct process, also called the direct synthesis, Rochow process, and Müller-Rochow process is the most common technology for preparing organosilicon compounds on an industrial scale. It was first reported independently by Eugene G. Rochow and Richard Müller in the 1940s.
Silicon tetrabromide is the inorganic compound with the formula SiBr4. This colorless liquid has a suffocating odor due to its tendency to hydrolyze with release of hydrogen bromide. The general properties of silicon tetrabromide closely resemble those of the more commonly used silicon tetrachloride.

A silsesquioxane is an organosilicon compound with the chemical formula [RSiO3/2]n. Silsesquioxanes are colorless solids that adopt cage-like or polymeric structures with Si-O-Si linkages and tetrahedral Si vertices. Silsesquioxanes are members of polyoctahedral silsesquioxanes ("POSS"), which have attracted attention as preceramic polymer precursors to ceramic materials and nanocomposites. Diverse substituents (R) can be attached to the Si centers. The molecules are unusual because they feature an inorganic silicate core and an organic exterior. The silica core confers rigidity and thermal stability.
Silylation is the introduction of a (usually) substituted silyl group (R3Si) to a molecule. The process is the basis of organosilicon chemistry.

Disiloxane has the chemical formula Si
2H
6O. It is the simplest known siloxane with hydrogen only R groups. The molecule contains six equivalent Si-H bonds and two equivalent Si-O bonds. Disiloxane exists as a colorless, pungent gas under standard conditions. However, it is generally safe for human use as evidence in its widespread use in cosmetics. It is also commonly known as disilyl ether, disilyl oxide, and perhydrodisiloxane

Phosphinimide ligands, also known as phosphorane iminato ligands, are any of a class of organic compounds of the general formula NPR3−. The R groups represent organic substituents or, in rare cases, halides or NR2 groups. NPR3− is isoelectronic with phosphine oxides (OPR3) and siloxides ([OSiR3]−), but far more basic. By varying the R groups on P, a variety of ligands with different electronic and steric properties can be produced, and due to the high oxidation state of phosphorus, these ligands have good thermal stability. Many transition metal phosphinimide complexes have been well-developed as have main group phosphinimide complexes.

Tantalum(V) ethoxide is a metalorganic compound with formula Ta2(OC2H5)10, often abbreviated as Ta2(OEt)10. It is a colorless solid that dissolves in some organic solvents but hydrolyzes readily. It is used to prepare films of tantalum(V) oxide.

Sodium trimethylsiloxide is an organosilicon compound with the formula NaOSi(CH3)3. It is the sodium salt of the conjugate base derived from trimethylsilanol. A white solid, its molecular structure consists of a cluster with Na-O-Na linkages on the basis of closely related compounds.
References
- 1 2 Krempner, Clemens (2011). "Role of Siloxides in Transition Metal Chemistry and Homogeneous Catalysis". Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011 (11): 1689. doi:10.1002/ejic.201100044.