Related Research Articles

A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.

Saturn-Apollo 2 (SA-2) was the second flight of the Saturn I launch vehicle, the first flight of Project Highwater, and was part of the American Apollo program. The rocket was launched on April 25, 1962, from Cape Canaveral, Florida.

The Space Shuttle external tank (ET) was the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contained the liquid hydrogen fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplied the fuel and oxidizer under pressure to the three RS-25 main engines in the orbiter. The ET was jettisoned just over 10 seconds after main engine cut-off (MECO) and it re-entered the Earth's atmosphere. Unlike the Solid Rocket Boosters, external tanks were not re-used. They broke up before impact in the Indian Ocean, away from shipping lanes and were not recovered.
Fuel cell may refer to:

A fuel tank is a safe container for flammable fluids, often gasoline or diesel fuel. Though any storage tank for fuel may be so called, the term is typically applied to part of an engine system in which the fuel is stored and propelled or released into an engine. Fuel tanks range in size and complexity from the small plastic tank of a butane lighter to the multi-chambered cryogenic Space Shuttle external tank.
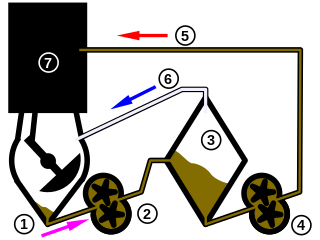
A dry-sump system is a method to manage the lubricating motor oil in four-stroke and large two-stroke piston driven internal combustion engines. The dry-sump system uses two or more oil pumps and a separate oil reservoir, as opposed to a conventional wet-sump system, which uses only the main sump below the engine and a single pump. A dry-sump engine requires a pressure relief valve to regulate negative pressure inside the engine, so internal seals are not inverted.

Crystallization is the process by which solids form, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposition directly from a gas. Attributes of the resulting crystal depend largely on factors such as temperature, air pressure, cooling rate, and in the case of liquid crystals, time of fluid evaporation.

A sump is a low space that collects often undesirable liquids such as water or chemicals. A sump can also be an infiltration basin used to manage surface runoff water and recharge underground aquifers. Sump can also refer to an area in a cave where an underground flow of water exits the cave into the earth.

A tank truck, gas truck, fuel truck, or tanker truck or tanker is a motor vehicle designed to carry liquids or gases on roads. The largest such vehicles are similar to railroad tank cars, which are also designed to carry liquid loads. Many variants exist due to the wide variety of liquids that can be transported. Tank trucks tend to be large; they may be insulated or non-insulated; pressurized or non-pressurized; and designed for single or multiple loads. Some are semi-trailer trucks. They are difficult to drive and highly susceptible to rollover due to their high center of gravity, and potentially the free surface effect of liquids sloshing in a partially filled tank.

Intermediate bulk containers are industrial-grade containers engineered for the mass handling, transport, and storage of liquids, semi-solids, pastes, or solids. The two main categories of IBC tanks are flexible IBCs and rigid IBCs. Many IBCs are reused or repurposed.
Baffle or baffles may refer to:

The free surface effect is a mechanism which can cause a watercraft to become unstable and capsize.

In fluid dynamics, slosh refers to the movement of liquid inside another object.

An LNG carrier is a tank ship designed for transporting liquefied natural gas (LNG).
Antiroll tanks are tanks fitted onto ships in order to improve the ship's response to roll motion. Fitted with baffles intended to slow the rate of water transfer from the port side of the tank to the starboard side and the reverse, the tanks are designed such that a larger amount of water is trapped on the higher side of the vessel. This is intended to reduce the roll period of the hull by acting in opposition to the free surface effect. They can be broadly classified into active and passive antiroll tanks.

The NASA Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for procurement of launch services for NASA uncrewed missions and oversight of launch integration and launch preparation activity, providing added quality and mission assurance to meet program objectives. LSP operates under the NASA Space Operations Mission Directorate (SOMD).
Load shifting is a dangerous phenomenon in water, air, and ground transportation where cargo shifts in a cargo vehicle. This causes the vehicle to tilt, which causes even more movement of the cargo, and further tilting, thereby creating a positive feedback loop. If not corrected, this will lead to severe tipping or even capsizing. Such a dangerous occurrence is prevented by active load management, avoiding high sea conditions for ships, and proper container/bulkhead design.
SLOSHSAT-FLEVO is a microsatellite launched to investigate the dynamics of fluids in microgravity. FLEVO stands for Facility for Liquid Experimentation and Verification in Orbit. Multiple sensors were used to monitor the behavior of water in an instrumented tank and how sloshing affects the attitude control of launchers and space vehicles.

Medhat Haroun was an Egyptian-American expert on earthquake engineering. He wrote more than 300 technical papers and received the Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award (2006) and the Walter Huber Civil Engineering Research Prize (1992) from the American Society of Civil Engineers.

Andrew John Stofan is an American engineer. He worked for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) at the Lewis Research Center. In the 1960s he played an important role in the development of the Centaur upper stage rocket, which pioneered the use of liquid hydrogen as a propellant. In the 1970s he managed the Atlas-Centaur and Titan-Centaur Project Offices, and oversaw the launch of the Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 probes to Jupiter and Saturn, the Viking missions to Mars, Helios probes to the Sun, and the Voyager probes to Jupiter and the outer planets. He was director of the Lewis Research Center from 1982 to 1986.
References
- ↑ Alan, Strahan; Hernandez, Humberto (31 July 2011). Slosh Baffle Design and Test for Spherical Liquid Oxygen and Liquid Methane Propellant Tank for a Lander. 47th AIAAfASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Meeting; San Diego, CA; United States. Houston, TX: NASA Johnson Space Center. 20110014009. Retrieved 1 May 2018.
- ↑ Ibrahim, Raouf A. (2005-05-19). Liquid Sloshing Dynamics: Theory and Applications. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139444132.