
Smackover is a small city in northern Union County, Arkansas, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population was at 1,865. It had a large oil boom in the 1920s, with production continuing for some time.

The Burgan field is an oil field situated in the desert of southeastern Kuwait. Burgan field can also refer to the Greater Burgan—a group of three closely spaced fields, which includes Burgan field itself as well as the much smaller Magwa and Ahmadi fields. Greater Burgan is the world's largest sandstone oil field, and the second-largest overall, after Ghawar. The Burgan Field is located on the coast of the Persian Gulf which played a huge part in the creation of this prominent reservoir formation many million years ago.

The Morrison Formation is a distinctive sequence of Upper Jurassic sedimentary rock found in the western United States which has been the most fertile source of dinosaur fossils in North America. It is composed of mudstone, sandstone, siltstone, and limestone and is light gray, greenish gray, or red. Most of the fossils occur in the green siltstone beds and lower sandstones, relics of the rivers and floodplains of the Jurassic period.

The Wilcox Group is an important geologic group in the Gulf of Mexico Basin and surrounding onshore areas from Mexico and Texas to Louisiana and Alabama. The group ranges in age from Paleocene to Eocene and is in Texas subdivided into the Calvert Bluff, Simsboro and Hooper Formations, and in Alabama into the Nanafalia and Hatchetigbee Formations. Other subdivisions are the Lower, Middle and Upper Wilcox Subgroups, and the Carrizo and Indio Formations.

South Arkansas lies within the southernmost portions of Arkansas Gulf Coastal Plain and Delta regions. It encompasses the lower 15 counties of the state.
The Arkansas Museum of Natural Resources is a museum and Arkansas state park in Smackover, Arkansas, in the United States. The museum was formed in the 1980s to tell the history of the petroleum industry and later the brine industry as key economic movements spurred by natural resources in South Arkansas.
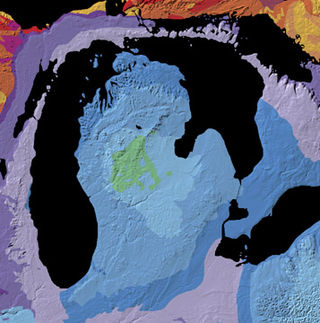
The Michigan Basin is a geologic basin centered on the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The feature is represented by a nearly circular pattern of geologic sedimentary strata in the area with a nearly uniform structural dip toward the center of the peninsula.
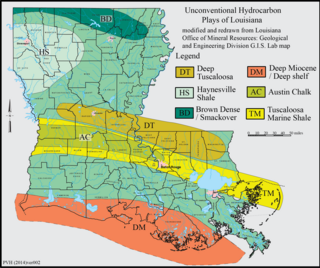
The Haynesville Shale is an informal, popular name for a Jurassic Period rock formation that underlies large parts of southwestern Arkansas, northwest Louisiana, and East Texas. It lies at depths of 10,500 to 13,000 feet below the land’s surface. It is part of a large rock formation which is known by geologists as the Haynesville Formation. The Haynesville Shale underlies an area of about 9,000 square miles and averages about 200 to 300 feet thick. The Haynesville Shale is overlain by sandstone of the Cotton Valley Group and underlain by limestone of the Smackover Formation.

The petroleum industry in Ohio dates from 1859. Ohio continues to produce significant quantities of oil and gas, having produced more than 1 billion barrels of oil and 9 trillion cubic feet of natural gas since 1860. Unconventional resources, primarily in eastern Ohio, are likely to increase production in Ohio.
Safaniya Oil Field, operated and owned by Saudi Aramco, is the largest offshore oil field in the world. It is located about 265 kilometres (165 mi) north of the company headquarters in Dhahran on the coast of the Persian Gulf, Saudi Arabia. Measuring 50 by 15 kilometres, the field has a producing capability of more than 1.2 million barrels per day.

The Brown Dense limestone is an informal name used by petroleum geologists for a layer of rock that lies beneath large parts of southern Arkansas and northwest Louisiana. The Brown Dense is a 300- to 500-foot thick interval within organic-rich, fine-grained carbonate rock that comprise the Lower Member of the Smackover Formation. Within this area, the Lower Smackover Member lies at depths of 8,000 to 10,000 feet beneath the land surface.
The Batesville Sandstone is a geologic formation in northern Arkansas, United States, that dates to the Chesterian Series of the late Mississippian. The base of the Batesville Sandstone, named the Hindsville Limestone Member, unconformably lies on the Moorefield Formation.
The De Queen Formation, formerly known as the DeQueen Limestone Member is a Mesozoic geological formation located in southwestern Arkansas and southeastern Oklahoma in the United States. Fossil sauropod and theropod tracks have been reported from the formation. It preserves fossils dating back to the Cretaceous period, particularly the Albian age.
The Morrow Formation is a geologic formation from the Pennsylvanian geological age that is found in locations ranging from Southeast New Mexico and West Texas to locations in Oklahoma, Southwestern Kansas, and Arkansas. It preserves fossils dating back to the Carboniferous period.

The Etchegoin Formation is a Pliocene epoch geologic formation in the lower half of the San Joaquin Valley in central California.

The West Siberian petroleum basin is the largest hydrocarbon basin in the world covering an area of about 2.2 million km2, and is also the largest oil and gas producing region in Russia.
Bromine production in the United States of 225,000 tonnes in 2013 made that country the second-largest producer of bromine, after Israel. The US supplied 29 percent of world production. Since 2007, all US bromine has been produced by two companies in southern Arkansas, which extract bromine from brine pumped from the Smackover Formation. At an advertised price of US$3.50 to US$3.90 per kg, the US 2013 US production would have a value of roughly US$800 million.
Brine mining is the extraction of useful materials which are naturally dissolved in brine. The brine may be seawater, other surface water, groundwater, or hyper-saline solutions from several industries. It differs from solution mining or in-situ leaching in that those methods inject water or chemicals to dissolve materials which are in a solid state; in brine mining, the materials are already dissolved.

The Bolivar Coastal Fields (BCF), also known as the Bolivar Coastal Complex, is located on the eastern margin of Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela. Bolivar Coastal Field is the largest oil field in South America with its 6,000-7,000 wells and forest of related derricks, stretches thirty-five miles along the north-east coast of Lake Maracaibo. They form the largest oil field outside of the Middle East and contain mostly heavy oil with a gravity less than 22 degrees API. Also known as the Eastern Coast Fields, Bolivar Coastal Oil Field consists of Tía Juana, Lagunillas, Bachaquero, Ceuta, Motatán, Barua and Ambrosio. The Bolivar Coast field lies in the Maracaibo dry forests ecoregion, which has been severely damaged by farming and ranching as well as oil exploitation. The oil field still plays an important role in production from the nation with approximately 2.6 million barrels of oil a day. It is important to note that the oil and gas industry refers to the Bolivar Coastal Complex as a single oilfield, in spite of the fact that the oilfield consists of many sub-fields as stated above.













