Freeciv is a single- and multiplayer turn-based strategy game for workstations and personal computers inspired by the proprietary Sid Meier's Civilization series. It is available for most desktop computer operating systems and available in an online browser version. Released under the GNU GPL-2.0-or-later, Freeciv is free and open-source software. The game's default settings are closest to Civilization II, in both gameplay and graphics, including the units and the isometric grid. However, with a lot of multiplayer games being played in longturn communities, rulesets and additional variants have evolved away from the original ruleset. Freeciv is playable online at Longturn.net, fciv.net, freecivweb.org and some temporary private servers.
In computing, cross-platform software is computer software that is designed to work in several computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms.

Novell, Inc. was an American software and services company headquartered in Provo, Utah, that existed from 1980 until 2014. Its most significant product was the multi-platform network operating system known as Novell NetWare.

NetWare is a discontinued computer network operating system developed by Novell, Inc. It initially used cooperative multitasking to run various services on a personal computer, using the IPX network protocol.
DESQview (DV) is a text mode multitasking operating environment developed by Quarterdeck Office Systems which enjoyed modest popularity in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Running on top of DOS, it allows users to run multiple programs concurrently in multiple windows.
IPX/SPX stands for Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange. IPX and SPX are networking protocols used initially on networks using the Novell NetWare operating systems. They also became widely used on networks deploying Microsoft Windows LANS, as they replaced NetWare LANS, but are no longer widely used. IPX/SPX was also widely used prior to and up to Windows XP, which supported the protocols, while later Windows versions do not, and TCP/IP took over for networking.
Btrieve is a transactional database software product. It is based on Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM), which is a way of storing data for fast retrieval. There have been several versions of the product for DOS, Linux, older versions of Microsoft Windows, 32-bit IBM OS/2 and for Novell NetWare.

UnixWare is a Unix operating system. It was originally released by Univel, a jointly owned venture of AT&T's Unix System Laboratories (USL) and Novell. It was then taken over by Novell. Via Santa Cruz Operation (SCO), it went on to Caldera Systems, Caldera International, and The SCO Group before it was sold to UnXis. UnixWare is typically deployed as a server rather than a desktop. Binary distributions of UnixWare are available for x86 architecture computers. UnixWare is primarily marketed as a server operating system.

Pegasus Mail is a proprietary email client for Microsoft Windows. It was originally released in 1990 on NetWare networks with MS-DOS and later Apple Macintosh clients, before being ported to Windows which is now the only platform actively supported. Since its inception it has been developed by David Harris and is donationware after having previously been freeware.
The NetWare Core Protocol (NCP) is a network protocol used in some products from Novell, Inc. It is usually associated with the client-server operating system Novell NetWare which originally supported primarily MS-DOS client stations, but later support for other platforms such as Microsoft Windows, the classic Mac OS, Linux, Windows NT, Mac OS X, and various flavors of Unix was added.

Univel, Inc. was a joint venture of Novell and AT&T's Unix System Laboratories (USL) that was formed in December 1991 to develop and market the Destiny desktop Unix operating system, which was released in 1992 as UnixWare 1.0. Univel existed only briefly in the period between AT&T initially divesting parts of USL in 1991, and its eventual outright purchase by Novell, which completed in June 1993, thereby acquiring rights to the Unix operating system. Novell merged USL and Univel into their new Unix Systems Group (USG).
A NetWare Loadable Module (NLM) is a loadable kernel module that can be loaded into Novell's NetWare operating system. NLMs can implement hardware drivers, server functions, applications, system libraries or utilities.
Caldera OpenLinux (COL) is a defunct Linux distribution. Caldera originally introduced it in 1997 based on the German LST Power Linux distribution, and then taken over and further developed by Caldera Systems since 1998. A successor to the Caldera Network Desktop put together by Caldera since 1995, OpenLinux was an early "business-oriented distribution" and foreshadowed the direction of developments that came to most other distributions and the Linux community generally.
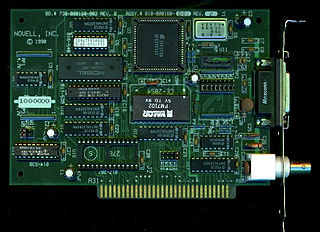
The NE1000 and NE2000 are members of an early line of low cost Ethernet network cards introduced by Novell in 1987. Their popularity had a significant impact on the pervasiveness of networks in computing. They are based on a reference design from National Semiconductor using their 8390 Ethernet chip.

NetWare Lite and Personal NetWare are a series of discontinued peer-to-peer local area networks developed by Novell for DOS- and Windows-based personal computers aimed at personal users and small businesses in the 1990s.

NetWars is an IPX-based 3D vector-graphics computer game released by Novell in 1993 for DOS to demonstrate NetWare capabilities. It was written by Edward N. Hill, Jr., one of Novell's engineers in its European Development Centre (EDC) in Hungerford, UK. Development started in 1989.

ZENworks, a suite of software products developed and maintained by OpenText for computer systems management, aims to manage the entire life cycle of servers, of desktop PCs, of laptops, and of handheld devices such as Android and iOS mobile phones and tablets. As of 2011 Novell planned to include Full Disk Encryption (FDE) functionality within ZENworks. ZENworks supports multiple server platforms and multiple directory services.

GroupWise is a messaging and collaboration platform from OpenText that supports email, calendaring, personal information management, instant messaging, and document management. The GroupWise platform consists of desktop client software, which is available for Windows,, and the server software, which is supported on Windows Server and Linux.

Mono is a free and open-source .NET Framework-compatible software framework. Originally by Ximian, it was later acquired by Novell, and is now being led by Xamarin, a subsidiary of Microsoft and the .NET Foundation. Mono can be run on many software systems.