
A pension is a fund into which amounts are paid regularly during an individual's working career, and from which periodic payments are made to support the person's retirement from work. A pension may be:
A pension fund, also known as a superannuation fund in some countries, is any program, fund, or scheme which provides retirement income.

In the United States, Social Security is the commonly used term for the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program and is administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA). The Social Security Act was passed in 1935, and the existing version of the Act, as amended, encompasses several social welfare and social insurance programs.

The U.S. Railroad Retirement Board (RRB) is an independent agency in the executive branch of the United States government created in 1935 to administer a social insurance program providing retirement benefits to the country's railroad workers.

The Central Provident Fund Board (CPFB), commonly known as the CPF Board or simply the Central Provident Fund (CPF), is a compulsory comprehensive savings and pension plan for working Singaporeans and permanent residents primarily to fund their retirement, healthcare, education and housing needs in Singapore.
Pensions in the United Kingdom, whereby United Kingdom tax payers have some of their wages deducted to save for retirement, can be categorised into three major divisions - state, occupational and personal pensions.
Superannuation in Australia or "super" is a savings system for workplace pensions in retirement. It involves money earned by an employee being placed into an investment fund to be made legally available to fund members upon retirement. Employers make compulsory payments to these funds at a proportion of their employee's wages. From July 2023, the mandatory minimum "guarantee" contribution is 11%, rising to 12% from 2025. The superannuation guarantee was introduced by the Hawke government to promote self-funded retirement savings, reducing reliance on a publicly funded pension system. Legislation to support the introduction of the superannuation guarantee was passed by the Keating Government in 1992.
A life annuity is an annuity, or series of payments at fixed intervals, paid while the purchaser is alive. The majority of life annuities are insurance products sold or issued by life insurance companies however substantial case law indicates that annuity products are not necessarily insurance products.
Social security in India includes a variety of statutory insurances and social grant schemes bundled into a formerly complex and fragmented system run by the Indian government at the federal and the state level. The Directive Principles of State Policy, enshrined in Part IV of the Indian Constitution reflects that India is a welfare state. Food security to all Indians are guaranteed under the National Food Security Act, 2013 where the government provides highly subsidised food grains or a food security allowance to economically vulnerable people. The system has since been universalised with the passing of The Code on Social Security, 2020. These cover most of the Indian population with social protection in various situations in their lives.

Social security is divided by the French government into five branches: illness; old age/retirement; family; work accident; and occupational disease. From an institutional point of view, French social security is made up of diverse organismes. The system is divided into three main Regimes: the General Regime, the Farm Regime, and the Self-employed Regime. In addition there are numerous special regimes dating from prior to the creation of the state system in the mid-to-late 1940s.

Defined benefit (DB) pension plan is a type of pension plan in which an employer/sponsor promises a specified pension payment, lump-sum, or combination thereof on retirement that depends on an employee's earnings history, tenure of service and age, rather than depending directly on individual investment returns. Traditionally, many governmental and public entities, as well as a large number of corporations, provide defined benefit plans, sometimes as a means of compensating workers in lieu of increased pay.
The Japanese National Pension is a pension system that all registered residents of Japan, both Japanese and foreign, are required to enroll in. Since January 1, 2010, it has been managed by the Japan Pension Service.
India operates a complex pension system. There are however three major pillars to the Indian pension system: the solidarity social assistance called the National Social Assistance Programme (NSAP) for the elderly poor, the civil servants pension and the mandatory defined contribution pension programs run by the Employees' Provident Fund Organisation of India for private sector employees and employees of state owned companies, and several voluntary plans.

A limited form of the Social Security program began as a measure to implement "social insurance" during the Great Depression of the 1930s, when poverty rates among senior citizens exceeded 50 percent.

The Ghana Card is the national Identity card that is issued by the Ghanaian authorities to Ghanaian citizens – both resident and non-resident, legal and permanent residents of foreign nationals. It is proof of identity, citizenship and residence of the holder. The current version is in ID1 format and biometric. It is issued by the National Identification Authority of Ghana and Regarded as a property of the country as such. In July 2023, through the initiative of the Vice President, Dr. Mahamudu Bawumia, new card numbers were issued to newborn babies as part of pilot program to incorporate newborn babies unto the database.

GOIL PLC formerly known as GOIL Company Limited (GOIL) and Ghana Oil Company and also known as GOIL, is a state-owned Ghanaian oil and gas marketing company, formed on 14 June 1960. Currently it holds the place of Ghana's top oil marketing company, and is the only indigenous owned petroleum marketing company in Ghana.

The Social Security Institution is the governing authority of the Turkish social security system. It was established by the Social Security Institution Law No:5502, which was published in the Official Gazette No: 26173 on June 20, 2006. This brought five different retirement systems that affected civil servants, contractual paid workers, agricultural paid workers, and self-employed workers into a single retirement system offering equal actuarial rights and obligations.
The West Hills Mall is a shopping centre located at Dukonah, near Weija along the Accra – Cape Coast Highway in the Greater Accra Region of Ghana.
Pensions in Vietnam are provided through a state pension scheme called social insurance, and private life insurance-type schemes. The pension system of Vietnam was ranked 57th out of 70 economies according to a 2020 Allianz report. As of 2020, 11.4% of Vietnamese have reached retirement age, but this number is expected to triple by 2050.
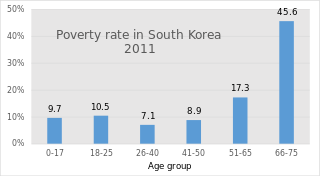
South Korea's pension scheme was introduced relatively recently, compared to other democratic nations. Half of the country's population aged 65 and over lives in relative poverty, or nearly four times the 13% average for member countries of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). This makes old age poverty an urgent social problem. Public social spending by general government is half the OECD average, and is the lowest as a percentage of GDP among OECD member countries.










