Related Research Articles
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems.

Social network analysis (SNA) is the process of investigating social structures through the use of networks and graph theory. It characterizes networked structures in terms of nodes and the ties, edges, or links that connect them. Examples of social structures commonly visualized through social network analysis include social media networks, meme spread, information circulation, friendship and acquaintance networks, peer learner networks, business networks, knowledge networks, difficult working relationships, collaboration graphs, kinship, disease transmission, and sexual relationships. These networks are often visualized through sociograms in which nodes are represented as points and ties are represented as lines. These visualizations provide a means of qualitatively assessing networks by varying the visual representation of their nodes and edges to reflect attributes of interest.

Constructivism is a theory in education which posits that individuals or learners do not acquire knowledge and understanding by passively perceiving it within a direct process of knowledge transmission, rather they construct new understandings and knowledge through experience and social discourse, integrating new information with what they already know. For children, this includes knowledge gained prior to entering school. It is associated with various philosophical positions, particularly in epistemology as well as ontology, politics, and ethics. The origin of the theory is also linked to Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development.
Asynchronous learning is a general term used to describe forms of education, instruction, and learning that do not occur in the same place or at the same time. It uses resources that facilitate information sharing outside the constraints of time and place among a network of people. In many instances, well-constructed asynchronous learning is based on constructivist theory, a student-centered approach that emphasizes the importance of peer-to-peer interactions. This approach combines self-study with asynchronous interactions to promote learning, and it can be used to facilitate learning in traditional on-campus education, distance education, and continuing education. This combined network of learners and the electronic network in which they communicate are referred to as an asynchronous learning network.
Educational technology is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning. When referred to with its abbreviation, edtech, it often refers to the industry of companies that create educational technology.
Sheltered instruction is an approach to teaching English-language learners that integrates language and content instruction. The phrase "sheltered instruction", the original concept, and the underlying theory of comprehensible input are all credited to Stephen Krashen.
Networked learning is a process of developing and maintaining connections with people and information, and communicating in such a way so as to support one another's learning. The central term in this definition is connections. It adopts a relational stance in which learning takes place both in relation to others and in relation to learning resources. In design and practice, networked learning is intended to facilitate evolving sets of connections between learners and their interpersonal communities, knowledge contexts, and digital technologies.
Computer-supported collaborative learning (CSCL) is a pedagogical approach wherein learning takes place via social interaction using a computer or through the Internet. This kind of learning is characterized by the sharing and construction of knowledge among participants using technology as their primary means of communication or as a common resource. CSCL can be implemented in online and classroom learning environments and can take place synchronously or asynchronously.

Open education is an educational movement founded on openness, with connections to other educational movements such as critical pedagogy, and with an educational stance which favours widening participation and inclusiveness in society. Open education broadens access to the learning and training traditionally offered through formal education systems and is typically offered through online and distance education. The qualifier "open" refers to the elimination of barriers that can preclude both opportunities and recognition for participation in institution-based learning. One aspect of openness or "opening up" education is the development and adoption of open educational resources in support of open educational practices.
Connectivism is a theoretical framework for understanding learning in a digital age. It emphasizes how internet technologies such as web browsers, search engines, wikis, online discussion forums, and social networks contributed to new avenues of learning. Technologies have enabled people to learn and share information across the World Wide Web and among themselves in ways that were not possible before the digital age. Learning does not simply happen within an individual, but within and across the networks.
Online tutoring is the process of tutoring in an online, virtual, or networked, environment, in which teachers and learners participate from separate physical locations. Aside from space, literature also states that participants can be separated by time.
Learning analytics is the measurement, collection, analysis and reporting of data about learners and their contexts, for purposes of understanding and optimizing learning and the environments in which it occurs. The growth of online learning since the 1990s, particularly in higher education, has contributed to the advancement of Learning Analytics as student data can be captured and made available for analysis. When learners use an LMS, social media, or similar online tools, their clicks, navigation patterns, time on task, social networks, information flow, and concept development through discussions can be tracked. The rapid development of massive open online courses (MOOCs) offers additional data for researchers to evaluate teaching and learning in online environments.
Online communication between home and school is the use of digital telecommunication to convey information and ideas between teachers, students, parents, and school administrators. As the use of e-mail and the internet becomes even more widespread, these tools become more valuable and useful in education for the purposes of increasing learning for students, and facilitating conversations between students, parents, and schools.
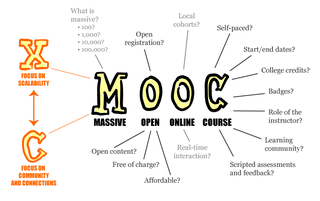
A massive open online course or an open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012, a year called the "Year of the MOOC".
Mobile computer-supported collaborative learning may have different meanings depending on the context in which it is applied. Mobile CSCL includes any in-class and out-of-class use of handheld mobile devices such as cell phones, smart phones, and personal digital assistants (PDAs) to enable collaborative learning.
Random walk closeness centrality is a measure of centrality in a network, which describes the average speed with which randomly walking processes reach a node from other nodes of the network. It is similar to the closeness centrality except that the farness is measured by the expected length of a random walk rather than by the shortest path.

NodeXL is a network analysis and visualization software package for Microsoft Excel 2007/2010/2013/2016. The package is similar to other network visualization tools such as Pajek, UCINet, and Gephi. It is widely applied in ring, mapping of vertex and edge, and customizable visual attributes and tags. NodeXL enables researchers to undertake social network analysis work metrics such as centrality, degree, and clustering, as well as monitor relational data and describe the overall relational network structure. When applied to Twitter data analysis, it showed the total network of all users participating in public discussion and its internal structure through data mining. It allows social Network analysis (SNA) to emphasize the relationships rather than the isolated individuals or organizations, allowing interested parties to investigate the two-way dialogue between organizations and the public. SNA also provides a flexible measurement system and parameter selection to confirm the influential nodes in the network, such as in-degree and out-degree centrality. The software contains network visualization, social network analysis features, access to social media network data importers, advanced network metrics, and automation.

Online learning involves courses offered by primary institutions that are 100% virtual. Online learning, or virtual classes offered over the internet, is contrasted with traditional courses taken in a brick-and-mortar school building. It is a development in distance education that expanded in the 1990s with the spread of the commercial Internet and the World Wide Web. The learner experience is typically asynchronous but may also incorporate synchronous elements. The vast majority of institutions utilize a learning management system for the administration of online courses. As theories of distance education evolve, digital technologies to support learning and pedagogy continue to transform as well.
Language MOOCs are web-based online courses freely accessible for a limited period of time, created for those interested in developing their skills in a foreign language. As Sokolik (2014) states, enrolment is large, free and not restricted to students by age or geographic location. They have to follow the format of a course, i.e., include a syllabus and schedule and offer the guidance of one or several instructors. The MOOCs are not so new, since courses with such characteristics had been available online for quite a lot of time before Dave Cormier coined the term 'MOOC' in 2008. Furthermore, MOOCs are generally regarded as the natural evolution of OERs, which are freely accessible materials used in Education for teaching, learning and assessment.
In network theory, collective classification is the simultaneous prediction of the labels for multiple objects, where each label is predicted using information about the object's observed features, the observed features and labels of its neighbors, and the unobserved labels of its neighbors. Collective classification problems are defined in terms of networks of random variables, where the network structure determines the relationship between the random variables. Inference is performed on multiple random variables simultaneously, typically by propagating information between nodes in the network to perform approximate inference. Approaches that use collective classification can make use of relational information when performing inference. Examples of collective classification include predicting attributes of individuals in a social network, classifying webpages in the World Wide Web, and inferring the research area of a paper in a scientific publication dataset.
References
- 1 2 Brinton, Christopher G., and Mung Chiang. "Social learning networks: A brief survey." Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), 2014 48th Annual Conference on. IEEE, 2014.
- ↑ Haythornthwaite, Caroline, and Maarten De Laat. "Social networks and learning networks: Using social network perspectives to understand social learning." 7th International Conference on Networked Learning. 2010.
- ↑ Huang, Jeff JS, et al. "Social Learning Networks: Build Mobile Learning Networks Based on Collaborative Services." Educational Technology & Society 13.3 (2010): 78-92.
- ↑ Christopher Brinton, Mung Chiang, Shaili Jain, Henry Lam, Zhenming Liu, and Felix Ming Fai Wong. "Learning about social learning in moocs: From statistical analysis to generative model." arXiv preprint arXiv:1312.2159 (2013).
- ↑ Glance, David George, Martin Forsey, and Myles Riley. "The pedagogical foundations of massive open online courses." First Monday 18.5 (2013).
- ↑ Herreid, Clyde Freeman, and Nancy A. Schiller. "Case studies and the flipped classroom." Journal of College Science Teaching 42.5 (2013): 62-66.
- ↑ DiMicco, Joan, et al. "Motivations for social networking at work." Proceedings of the 2008 ACM conference on Computer supported cooperative work. ACM, 2008.
- ↑ Anderson, Ashton, et al. "Discovering value from community activity on focused question answering sites: a case study of stack overflow." Proceedings of the 18th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining. ACM, 2012.