Related Research Articles

Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula B(OH)3. It may also be called hydrogen borate or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salts, and can react with alcohols to form borate esters.
A borate is any of several boron oxyanions, negative ions consisting of boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate [BO3]3−, metaborate [BO2]−, or tetraborate [B4O7]2−; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, [Na+][BO−2] and disodium tetraborate [Na+]2[B2O2−4]. The name also refers to certain functional groups in molecules consisting of boron and oxygen, and esters with such groups, such as triethyl orthoborate B(OC2H5)3.

Borax is a salt (ionic compound), a hydrated borate of sodium, with chemical formula Na2H20B4O17 often written Na2B4O7·10H2O. It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution. It is commonly available in powder or granular form, and has many industrial and household uses, including as a pesticide, as a metal soldering flux, as a component of glass, enamel, and pottery glazes, for tanning of skins and hides, for artificial aging of wood, as a preservative against wood fungus, and as a pharmaceutic alkalizer. In chemical laboratories, it is used as a buffering agent.

The borate minerals are minerals which contain a borate anion group. The borate (BO3) units may be polymerised similar to the SiO4 unit of the silicate mineral class. This results in B2O5, B3O6, B2O4 anions as well as more complex structures which include hydroxide or halogen anions. The [B(O,OH)4]− anion exists as well.

In chemistry, tetraborate or pyroborate is an anion with formula B4O2−7; or a salt containing that anion, such as sodium tetraborate, Na2B4O7. It is one of the boron oxoacids, that is, a borate.

Sodium sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2S, or more commonly its hydrate Na2S·9H2O. Both the anhydrous and the hydrated salts in pure crystalline form are colorless solids, although technical grades of sodium sulfide are generally yellow to brick red owing to the presence of polysulfides and commonly supplied as a crystalline mass, in flake form, or as a fused solid. They are water-soluble, giving strongly alkaline solutions. When exposed to moist air, Na2S and its hydrates emit hydrogen sulfide, an extremely toxic, flammable and corrosive gas which smells like rotten eggs.
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written NaH
2BO
4, Na
2H
4B
2O
8, or, more properly, [Na+
]
2·[B
2O
4(OH)
4]2−
. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS.
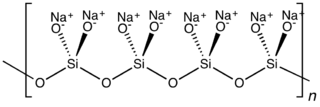
Sodium metasilicate is the chemical substance with formula Na
2SiO
3, which is the main component of commercial sodium silicate solutions. It is an ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+
and the polymeric metasilicate anions [–SiO2−
3–]n. It is a colorless crystalline hygroscopic and deliquescent solid, soluble in water but not in alcohols.
Tetrahydroxyborate is an inorganic anion with the chemical formula [BH4O4]− or [B(OH)4]−. It contributes no colour to tetrahydroxyborate salts. It is found in the mineral hexahydroborite, Ca(B(OH)4)2 · 2 H2O, originally formulated CaB2O4 · 6 H2O. It is one of the boron oxoanions, and acts as a weak base. The systematic names are tetrahydroxyboranuide (substitutive) and tetrahydroxidoborate(1−) (additive). It can be viewed as the conjugate base of boric acid.
Disodium octaborate is a borate of sodium, a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen — a salt with elemental formula Na2B8O13 or (Na+)2[B8O13]2−, also written as Na2O·4B2O3. It is a transparent colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water.

Chromium(III) sulfate usually refers to the inorganic compounds with the formula Cr2(SO4)3.x(H2O), where x can range from 0 to 18. Additionally, ill-defined but commercially important "basic chromium sulfates" are known. These salts are usually either violet or green solids that are soluble in water. It is commonly used in tanning leather.

Sodium metaborate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with formula NaBO
2. However, the metaborate ion is trimeric in the anhydrous solid, therefore a more correct formula is Na3B3O6 or (Na+)3[B3O6]3−. The formula can be written also as Na
2O·B
2O
3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron. The name is also applied to several hydrates whose formulas can be written NaBO2·nH2O for various values of n.

A metaborate is an anion (negative ion) consisting of boron and oxygen, with empirical formula BO−2; or any salt with such anions, such as sodium metaborate, Na+[BO2]− or calcium metaborate Ca2+([BO2]−)2. It is one of the boron oxoanions or borates
Magnesium hydroxychloride is the traditional term for several chemical compounds of magnesium, chlorine, oxygen, and hydrogen whose general formula xMgO·yMgCl
2·zH
2O, for various values of x, y, and z; or, equivalently, Mg
x+y(OH)
2xCl
2y(H
2O)
z−x. The simple chemical formula that is often used is MgClOH, which appears in high school subject, for example.Other names for this class are magnesium chloride hydroxide, magnesium oxychloride, and basic magnesium chloride. Some of these compounds are major components of Sorel cement.
In chemistry, a silicic acid is any chemical compound containing the element silicon attached to oxide and hydroxyl groups, with the general formula [H2xSiOx+2]n or, equivalently, [SiOx(OH)4-2x]n. Orthosilicic acid is a representative example. Silicic acids are rarely observed in isolation, but are thought to exist in aqueous solutions, including seawater, and play a role in biomineralization. They are typically colorless weak acids that are sparingly soluble in water. Like the silicate anions, which are their better known conjugate bases, silicic acids are proposed to be oligomeric or polymeric. No simple silicic acid has ever been identified, since these species being primarily of theoretical interest.
Disodium enneaborate is the traditional name for a salt of sodium, boron, oxygen, and hydrogen, with elemental formula Na2B9H22O20 or Na2B9O9·11H2O. It is the sodium borate with the highest boron/sodium ratio.
Sodium pentaborate, more properly disodium decaborate, is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen; a salt with elemental formula NaB5O8, Na2B10O16, or Na2O·5B2O3. It is a transparent colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water.
Trisodium borate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen, with formula Na3BO3, or (Na+)3[BO3]3−. It is a salt with the orthoborate anion [BO3]3−.

Sodium tetrahydroxyborate is a salt (ionic compound) of with chemical formula NaH4BO4 or Na+[B(OH)4]−. It is one of several sodium borates. At room temperature it is a colorless transparent crystalline solid.
Cobalt compounds are chemical compounds formed by cobalt with other elements. In the compound, the most stable oxidation state of cobalt is the +2 oxidation state, and in the presence of specific ligands, there are also stable compounds with +3 valence. In addition, there are cobalt compounds in high oxidation states +4, +5 and low oxidation states -1, 0, +1.
References
- 1 2 3 Doinita Neiner, Yulia V. Sevryugina, Larry S. Harrower, and David M. Schubert (2017): "Structure and Properties of Sodium Enneaborate, Na2[B8O11(OH)4]·B(OH)3·2H2O". Inorganic Chemistry, volume 56, issue 12, pages 7175–7181. doi : 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.7b00823
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Nelson P. Nies and Richard W. Hulbert (1967): "Solubility isotherms in the system sodium oxide-boric oxide-water. Revised solubility-temperature curves of boric acid, borax, sodium pentaborate, and sodium metaborate". Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data, volume 12, issue 3, pages 303–313. doi : 10.1021/je60034a005
- ↑ S. Stella Mary, S. Shahil Kirupavathy, P. Mythili, R. Gopalakrishnan (2008): "Growth and characterization of sodium pentaborate [Na(H4B5O10)] single crystals". Spectrochimica Acta Part A, volume 71, issue 4, 15 pages 1311-1316. doi : 10.1016/j.saa.2008.04.021
- ↑ Taha Cagri Senocak, Taha Alper Yilmaz, Hasan Feyzi Budak, Gokhan Gulten, Ahmet Melik Yilmaz, Kadri Vefa Ezirmik, Yasar Totikc (2022): "Influence of sodium pentaborate (B5H10NaO13) additive in plasma electrolytic oxidation process on WE43 magnesium alloys". Materials Today Communications, volume 30, article 103157. doi : 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103157
- ↑ Silvio Menchetti and Cesare Sabelli (1977): "The crystal structure of synthetic sodium pentaborate monohydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B, volume B33, pages 3730-3733. doi : 10.1107/S0567740877011959
- ↑ Charles Hutchens Burgess and Alfred Holt (1905): "Some physical characters of the sodium borates, with a new and rapid method for the determination of melting points." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London, volume 74, pages 285–295. doi : 10.1098/rspl.1904.0112