The clarinet is a single-reed musical instrument in the woodwind family, with a nearly cylindrical bore and a flared bell.

The recorder is a family of woodwind musical instruments in the group known as internal duct flutes: flutes with a whistle mouthpiece, also known as fipple flutes. A recorder can be distinguished from other duct flutes by the presence of a thumb-hole for the upper hand and seven finger-holes: three for the upper hand and four for the lower. It is the most prominent duct flute in the western classical tradition.

The tin whistle, also known as the penny whistle, is a simple six-holed woodwind instrument. It is a type of fipple flute, putting it in the same class as the recorder, Native American flute, and other woodwind instruments that meet such criteria. A tin whistle player is called a whistler. The tin whistle is closely associated with Irish traditional music and Celtic music. Other names for the instrument are the flageolet, English flageolet, Scottish penny whistle, tin flageolet, or Irish whistle.

A clef is a musical symbol used to indicate which notes are represented by the lines and spaces on a musical staff. Placing a clef on a staff assigns a particular pitch to one of the five lines or four spaces, which defines the pitches on the remaining lines and spaces.

A transposing instrument is a musical instrument for which music notation is not written at concert pitch. For example, playing a written middle C on a transposing instrument produces a pitch other than middle C; that sounding pitch identifies the interval of transposition when describing the instrument. Playing a written C on clarinet or soprano saxophone produces a concert B♭, so these are referred to as B♭ instruments. Providing transposed music for these instruments is a convention of musical notation. The instruments do not transpose the music; rather, their music is written at a transposed pitch. Where chords are indicated for improvisation they are also written in the appropriate transposed form.

The piccolo is a half-size flute and a member of the woodwind family of musical instruments. Sometimes referred to as a "baby flute" or piccolo flute, the modern piccolo has the same type of fingerings as the standard transverse flute, but the sound it produces is an octave higher. This has given rise to the name ottavino, by which the instrument is called in Italian and thus also in scores of Italian composers.

The sheng is a Chinese mouth-blown polyphonic free reed instrument consisting of vertical pipes.
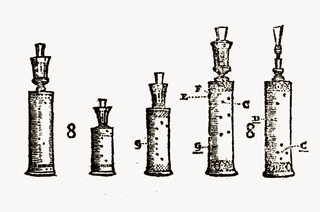
The rackett, raggett, cervelas, or sausage bassoon is a Renaissance-era double reed wind instrument, introduced late in the sixteenth century and already superseded by bassoons at the end of the seventeenth century.
The Western concert flute is a family of transverse (side-blown) woodwind instruments made of metal or wood. It is the most common variant of the flute. A musician who plays the flute is called a “flautist” in British English, and a “flutist” in American English.

The xaphoon is a chromatic keyless single-reed woodwind instrument. It has a closed cylindrical bore and a very slightly flared bell. The xaphoon has a full chromatic range of two octaves, and overblows at the twelfth like the clarinet.
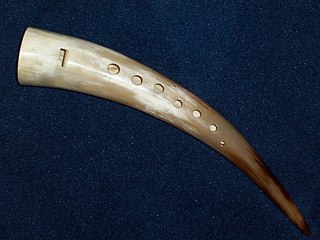
The gemshorn is an instrument of the ocarina family that was historically made from the horn of a chamois, goat, or other suitable animal. The gemshorn receives its name from the German language, in which Gemshorn means a "chamois horn". According to Etymologist Francesco Perono Cacciafoco, the form could have prehistoric origins and come from Proto-Germanic *gămĭtă-χŭrnă-n < Indo-European *gʱŏm-ĭdó-ḱrhₐ-nŏ-m (or *gʱŏm-ĭdó-ḱrhₐ-nŏ-m > Gämshorn, indicating a "'specific' wind instrument, crafted by using the horns of ungulated animals and different from a hunting horn or a signaling horn".

Zuffolo (also chiufolo, ciufolo) is an Italian fipple flute. First described in the 14th century, it has a rear thumb-hole, two front finger-holes, and a conical bore. It is approximately 8 cm in length and has a range of over two octaves, from B3 to C6 (Marcuse 1975c). A larger instrument of the same name, with a lowest note of C5 appeared in the early 17th century (Fuller-Maitland, Baines, and Térey-Smith 2001).

The great bass recorder is a member of the recorder family. With the revival of the recorder by Arnold Dolmetsch, who chose Baroque music and the corresponding recorder types as a fixed point, consideration was given to the design of recorder types larger than the bass recorder. The great bass recorder has up to seven keys, which serve to facilitate access to the finger holes. For modern large bass recorders woods like maple or African Bubinga are used. The term usually applies to an instrument with range is c–d2 (g2), but has also been used to describe an instrument descending to B♭ or else to the low bass recorder in F, alternatively known as a contrabass. When "great bass" is used for the instrument in low F, the instruments in C and B♭ are referred to as "quart-bass" and "quint-bass", respectively, because they are a fourth and fifth below the ordinary small bass, or "basset". The prefixes "great" and "contra" refer to the registers from C to B and from ͵C to ͵B, respectively, in Helmholtz pitch notation.
The sopranino recorder is the second smallest recorder of the modern recorder family, and was the smallest before the 17th century.
The alto recorder in F, also known as a treble (and, historically, as consort flute and common flute) is a member of the recorder family. Up until the 17th century the alto instrument was normally in G4 instead of F4. Its standard range is F4 to G6.
The garklein recorder in C, also known as the sopranissimo recorder or piccolo recorder, is the smallest size of the recorder family. Its range is C6–A7 (C8). The name garklein is German for "quite small", and is also sometimes used to describe the sopranino in G. Although some modern German makers use the single-word form Garkleinflötlein, this is without historical precedent. Double holes for the two lowest notes (used on the larger recorders to achieve a fully chromatic scale) are uncommon. The instrument is usually notated in the treble clef two octaves lower than its actual sound. The garklein recorder is only about 16 to 18 cm long and is different from larger recorders in that it is usually made in one piece due to its size.

A bass recorder is a wind instrument in F3 that belongs to the family of recorders.

The tenor recorder is a member of the recorder family. It has the same form as a soprano recorder and an alto recorder, but it produces a lower sound than either; a still lower sound is produced by the bass recorder and great bass recorder.

The contrabass recorder is a wind instrument in F2 that belongs to the family of recorders.

The voice flute (also the Italian flauto di voce and the French flûte de voix are found in English-language sources) is a recorder with the lowest note of D4, and is therefore intermediate in size between the alto and tenor recorders.













