Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year.

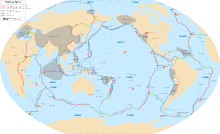
The Ring of Fire is a tectonic belt of volcanoes and earthquakes, about 40,000 km (25,000 mi) long and up to about 500 km (310 mi) wide, which surrounds most of the Pacific Ocean. The exact number of volcanoes within the Ring of Fire is not universally agreed but, depending on which regions are included in any particular count, it contains between 750 and 915 active or dormant volcanoes, around two-thirds of the world total. About 90% of the world's earthquakes, including most of its largest, occur within the belt.

The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of 76 million km2 (29 million sq mi), it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate.
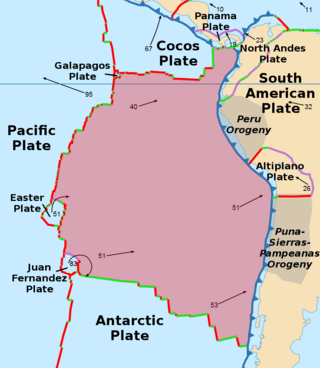
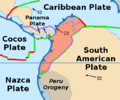
The Nazca Plate or Nasca Plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Nazca Plate under the South American Plate is largely responsible for the Andean orogeny. The Nazca Plate is bounded on the west by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Antarctic Plate through the East Pacific Rise and the Chile Rise respectively. The movement of the Nazca Plate over several hotspots has created some volcanic islands as well as east–west running seamount chains that subduct under South America. Nazca is a relatively young plate both in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate having been formed from the break-up of the Farallon Plate about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old.

The Antarctic Plate is a tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau, and some remote islands in the Southern Ocean and other surrounding oceans. After breakup from Gondwana, the Antarctic plate began moving the continent of Antarctica south to its present isolated location, causing the continent to develop a much colder climate. The Antarctic Plate is bounded almost entirely by extensional mid-ocean ridge systems. The adjoining plates are the Nazca Plate, the South American Plate, the African Plate, the Somali Plate, the Indo-Australian Plate, the Pacific Plate, and, across a transform boundary, the Scotia Plate.
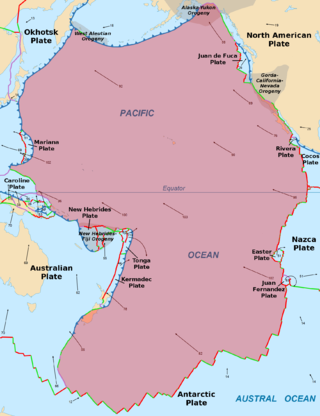
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million km2 (40 million sq mi), it is the largest tectonic plate.

The Cocos Plate is a young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it. The Cocos Plate was created approximately 23 million years ago when the Farallon Plate broke into two pieces, which also created the Nazca Plate. The Cocos Plate also broke into two pieces, creating the small Rivera Plate. The Cocos Plate is bounded by several different plates. To the northeast it is bounded by the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. To the west it is bounded by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Nazca Plate.
The Peru–Chile Trench, also known as the Atacama Trench, is an oceanic trench in the eastern Pacific Ocean, about 160 kilometres (99 mi) off the coast of Peru and Chile. It reaches a maximum depth of 8,065 m (26,460 ft) below sea level in Richards Deep and is approximately 5,900 km (3,666 mi) long; its mean width is 64 km (40 mi) and it covers an expanse of some 590,000 km2 (230,000 sq mi).
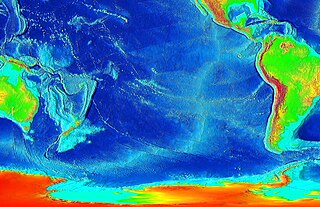
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise, at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55°S130°W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-southwest towards Antarctica, near New Zealand. Much of the rise lies about 3,200 km (2,000 mi) off the South American coast and rises about 1,800–2,700 m (5,900–8,900 ft) above the surrounding seafloor.

The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the northern coast of South America.
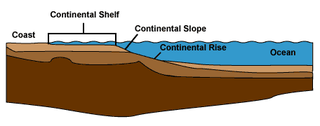
A continental margin is the outer edge of continental crust abutting oceanic crust under coastal waters. It is one of the three major zones of the ocean floor, the other two being deep-ocean basins and mid-ocean ridges. The continental margin consists of three different features: the continental rise, the continental slope, and the continental shelf. The continental shelf is the relatively shallow water area found in proximity to continents. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area.

A submarine, undersea, or underwater earthquake is an earthquake that occurs underwater at the bottom of a body of water, especially an ocean. They are the leading cause of tsunamis. The magnitude can be measured scientifically by the use of the moment magnitude scale and the intensity can be assigned using the Mercalli intensity scale.

The geology of Chile is a characterized by processes linked to subduction, such as volcanism, earthquakes, and orogeny. The building blocks of Chile's geology were assembled during the Paleozoic Era when Chile was the southwestern margin of the supercontinent Gondwana. In the Jurassic, Gondwana began to split, and the ongoing period of crustal deformation and mountain building known as the Andean orogeny began. In the Late Cenozoic, Chile definitely separated from Antarctica, and the Andes experienced a significant rise accompanied by a cooling climate and the onset of glaciations.

The Chile Triple Junction is a geologic triple junction located on the seafloor of the Pacific Ocean off Taitao and Tres Montes Peninsula on the southern coast of Chile. Here three tectonic plates meet: the South American Plate, the Nazca Plate and the Antarctic Plate. This triple junction is unusual in that it consists of a mid-oceanic ridge, the Chile Rise, being subducted under the South American Plate at the Peru–Chile Trench. The Chile Triple Junction is the boundary between the Chilean Rise and the Chilean margin, where the Nazca, Antarctic, and South American plates meet at the trench.

The Panama Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) that exists between two actively spreading ridges and moves relatively independently of its surrounding plates. The Panama Plate is located between the Cocos Plate and the Nazca Plate to the south and the Caribbean Plate to the north. Most of its borders are convergent boundaries, including a subduction zone to the west. It consists, for the most part, of the countries of Costa Rica and Panama.

The Nazca Ridge is a submarine ridge, located on the Nazca Plate off the west coast of South America. This plate and ridge are currently subducting under the South American Plate at a convergent boundary known as the Peru-Chile Trench at approximately 7.7 cm (3.0 in) per year. The Nazca Ridge began subducting obliquely to the collision margin at 11°S, approximately 11.2 Ma, and the current subduction location is 15°S. The ridge is composed of abnormally thick basaltic ocean crust, averaging 18 ±3 km thick. This crust is buoyant, resulting in flat slab subduction under Peru. This flat slab subduction has been associated with the uplift of Pisco Basin and the cessation of Andes volcanism and the uplift of the Fitzcarrald Arch on the South American continent approximately 4 Ma.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.
Ridge push is a proposed driving force for plate motion in plate tectonics that occurs at mid-ocean ridges as the result of the rigid lithosphere sliding down the hot, raised asthenosphere below mid-ocean ridges. Although it is called ridge push, the term is somewhat misleading; it is actually a body force that acts throughout an ocean plate, not just at the ridge, as a result of gravitational pull. The name comes from earlier models of plate tectonics in which ridge push was primarily ascribed to upwelling magma at mid-ocean ridges pushing or wedging the plates apart.

The Chile Ridge, also known as the Chile Rise, is a submarine oceanic ridge formed by the divergent plate boundary between the Nazca Plate and the Antarctic Plate. It extends from the triple junction of the Nazca, Pacific, and Antarctic plates to the Southern coast of Chile. The Chile Ridge is easy to recognize on the map, as the ridge is divided into several segmented fracture zones which are perpendicular to the ridge segments, showing an orthogonal shape toward the spreading direction. The total length of the ridge segments is about 550–600 km.