Construction and materials
The stoptail bridge consists of two parts: an adjustable fixed bridge piece, such as a Tune-o-matic and a separate stopbar (or stop bar) tailpiece.
A stopbar tailpiece is, as the name implies, a bar-shaped formed metal piece commonly made of pot metal or zinc alloys although aluminum and brass may be used. Many manufacturers claim that the use of lightweight metals and alloys, such as aluminum, provide a greater transfer of the string's vibrational energy or "resonant quality" to the guitar body since there is less mass to excite. Aluminum was also used in the early examples of stoptail bridges from the 1950s, so it carries the mantle of "vintage" vibe.
The "stop" part comes from the fact that the string ends are held in place or they "stop" inside the bar. The bar is mounted on top of the guitar body usually by means of sturdy threaded metal studs screwed into threaded sleeves embedded into the body of the guitar. The studs and stopbar are located behind the separate bridge piece.
The stopbar can either simply slip onto notches on top of the studs, or be held in place using set screws. One danger to be aware of is that the stopbar can fall out of the notches when changing strings and put a ding in the guitar's finish. When it is held in place using the screws, it is sometimes referred to as a "locking stopbar". In these designs, the Tune-o-matic bridge section is also usually fastened to its embedded studs by set screws. This fastening of the key components in a stoptail bridge system is claimed to impart more sustain and tone to the guitar's sound.
Function and advantages
The stopbar has holes drilled into it that allow the guitar strings to be threaded from the rear and out through the front. The string path then goes over the bridge saddles and the string nut to the machine heads located on the headstock.
The stopbar tailpiece is meant to be adjusted for string tension. The threaded posts can be lowered or raised to increase or relieve the string tension at pitch. This is an important adjustment especially when changing the gauge of the string set on the guitar. There are practical limits to this technique: too high and it could bend the posts and the strings will not seat properly into the bridge saddles; too low and the string break will rest on the rear of the bridge, killing sustain and tone. Some players prefer to tighten the stopbar all the way down in an attempt to increase sustain and tone. This requires a different stringing technique.
Some players, like Duane Allman, deviate from the norm and "top wrap" their strings. This is when the direction of the string path is reversed so that the strings are threaded through the leading edge of the stopbar then come out the rear and wrapped over the top of the stop bar. The advantage is that strings are supposedly easier to bend because of the decreased string break angle. Also, the "nonspeaking" string length is increased, which may have an effect on the strings' harmonic vibration (see sympathetic resonance ). The increased tendency for the strings to produce natural harmonics may make techniques such as pinch harmonics easier to accomplish. This is the same way that a wraparound stoptail bridge is strung. Regardless of the technique used, the tension provided by tightening the strings to pitch is the only thing keeping the stopbar in place, unless it is a "locking" type.
The supposed advantages of using a stoptail bridge over a tremolo bridge are: greater ability to keep the strings in tune, especially under the duress of hard note-bending; better string path stability and ability to intonate; and, better sustain due to a more direct resonance of the guitar's tonewood excited by the transmission of sound wave energy from the vibrating string. This is not a universally accepted opinion and guitarists will argue over the virtues of stoptail, hard-tail and tremolo bridges probably for as long as they all exist.

An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickups to convert the vibration of its strings into electrical signals, which ultimately are reproduced as sound by loudspeakers. The sound is sometimes shaped or electronically altered to achieve different timbres or tonal qualities from that of an acoustic guitar via amplifier settings or knobs on the guitar. Often, this is done through the use of effects such as reverb, distortion and "overdrive"; the latter is considered to be a key element of electric blues guitar music and jazz and rock guitar playing. Designs also exist combining attributes of the electric and acoustic guitars: the semi-acoustic and acoustic-electric guitars.

The guitar is a fretted musical instrument that typically has six strings. It is usually held flat against the player's body and played by strumming or plucking the strings with the dominant hand, while simultaneously pressing selected strings against frets with the fingers of the opposite hand. A plectrum or individual finger picks may also be used to strike the strings. The sound of the guitar is projected either acoustically, by means of a resonant chamber on the instrument, or amplified by an electronic pickup and an amplifier.

The violin, sometimes known as a fiddle, is a wooden chordophone in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument (soprano) in the family in regular use. The violin typically has four strings, usually tuned in perfect fifths with notes G3, D4, A4, E5, and is most commonly played by drawing a bow across its strings. It can also be played by plucking the strings with the fingers (pizzicato) and, in specialized cases, by striking the strings with the wooden side of the bow.
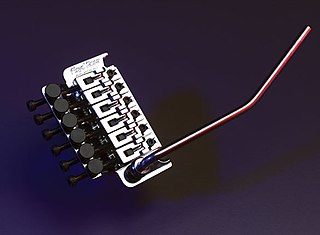
The Floyd Rose Locking Tremolo, or simply Floyd Rose, is a type of locking vibrato arm for a guitar. Floyd D. Rose invented the locking vibrato in 1976, the first of its kind, and it is now manufactured by a company of the same name. The Floyd Rose gained popularity in the 1980s through guitarists like Eddie Van Halen, Neal Schon, Brad Gillis, Joe Satriani, Steve Vai, and Alex Lifeson, who used its ability to stay in tune even with extreme changes in pitch. Its tuning stability comes through the double-locking design that has been widely regarded as revolutionary; the design has been listed on Guitar World's "10 Most Earth Shaking Guitar Innovations" and Guitar Player's "101 Greatest Moments in Guitar History 1979–1983."

The Fender Stratocaster, colloquially known as the Strat, is a model of electric guitar designed between 1952 and 1954 by Leo Fender, Bill Carson, George Fullerton, and Freddie Tavares. The Fender Musical Instruments Corporation has continuously manufactured the Stratocaster since 1954. It is a double-cutaway guitar, with an extended top "horn" shape for balance. Along with the Gibson Les Paul, Gibson SG, and Fender Telecaster, it is one of the most-often emulated electric guitar shapes. "Stratocaster" and "Strat" are trademark terms belonging to Fender. Guitars that duplicate the Stratocaster by other manufacturers are sometimes called S-Type or ST-type guitars.

The Bigsby vibrato tailpiece is a type of mechanical vibrato device for electric guitar designed by Paul Bigsby and produced by the Bigsby Electric Guitar Company. The device allows musicians to bend the pitch of notes or entire chords with their pick hand for various effects.
The Fender Jaguar is an electric guitar by Fender Musical Instruments characterized by an offset-waist body, a relatively unusual switching system with two separate circuits for lead and rhythm, and a short-scale 24" neck. Owing some roots to the Jazzmaster, it was introduced in 1962 as Fender's feature-laden top-of-the-line model, designed to lure players from Gibson. During its initial 13-year production run, the Jaguar did not sell as well as the less expensive Stratocaster and Telecaster, and achieved its most noticeable popularity in the surf music scene. After the Jaguar was taken out of production in 1975, vintage Jaguars became popular first with American punk rock players, and then more so during the alternative rock, shoegazing and indie rock movements of the 1980s and 1990s. Fender began making a version in Japan in the mid-1980s, and then introduced a USA-made reissue in 1999. Since then, Fender has made a variety of Jaguars in America, Mexico, Indonesia and China under both the Fender and Squier labels. Original vintage Jaguars sell for many times their original price.
A vibrato system on a guitar is a mechanical device used to temporarily change the pitch of the strings. They add vibrato to the sound by changing the tension of the strings, typically at the bridge or tailpiece of an electric guitar using a controlling lever, which is alternately referred to as a whammy bar, vibrato bar, or incorrectly as a tremolo arm. The lever enables the player to quickly and temporarily vary the tension and sometimes length of the strings, changing the pitch to create a vibrato, portamento, or pitch bend effect. Instruments without a vibrato have other bridge and tailpiece systems.

The Gibson Firebird is a solid-body electric guitar manufactured by Gibson beginning in 1963.
Variax is the name of a line of guitars developed and marketed by Line 6. They differ from typical electric and acoustic guitars in that internal electronics process the sound from individual strings to model (replicate) the sound of specific guitars and other instruments. The maker claims it is the first guitar family that can emulate the tones of other notable electric and acoustic guitars. It also provides a banjo and a sitar tone. The Variax is currently available as an electric guitar, but modeling acoustic guitars and modeling electric bass guitars have been available in the past.
Steinberger is a series of distinctive electric guitars and bass guitars, designed and originally manufactured by Ned Steinberger. The name "Steinberger" can be used to refer to either the instruments themselves or the company that originally produced them. Although the name has been applied to a variety of instruments, it is primarily associated with a minimalist "headless" design of electric basses and guitars.

A tailpiece is a component on many stringed musical instruments that anchors one end of the strings, usually opposite the end with the tuning mechanism.
The term hard-tail has several meanings:
The Gibson Melody Maker is an electric guitar made by Gibson Guitar Corporation. It has had many body shape variations since its conception in 1959.

Tune-o-matic is the name of a fixed or floating bridge design for electric guitars. It was designed by Ted McCarty and introduced on the Gibson Super 400 guitar in 1953 and the Les Paul Custom the following year. In 1955, it was used on the Gibson Les Paul Gold Top. It was gradually accepted as a standard on almost all Gibson electric guitars, replacing the previous wrap-around bridge design, except on the budget series.
The Fender Bullet was an electric guitar originally designed by John Page and manufactured and marketed by the Fender Musical Instruments Corporation. It was first introduced as a line of "student" guitars to replace the outgoing Mustang and Musicmaster models.

The SX SJM 62 or 57 or 75 is a tailed bridge guitar made by SX Guitars with features similar to the Fender Jaguar and Jazzmaster. It is also available as a "stop tail" guitar, comprising a Tune-o-matic bridge and a stopbar tailpiece.

The Gibson Spirit was a guitar model sold under Gibson and Epiphone USA nameplates in the 1980s. This article does not refer to the made-in-China Spirit guitar sold under the Gibson Baldwin Music Education nameplate.

The Stetsbar Tremolo system is a vibrato bridge system for the electric guitar. Eric Stets developed the device in the late ‘80s, and patented it in 1995. He originally designed the device to provide a stable vibrato system that could retrofit to “stop-tail” guitars such as the Gibson Les Paul with no permanent modifications to the instrument.

A bridge is a device that supports the strings on a stringed musical instrument and transmits the vibration of those strings to another structural component of the instrument—typically a soundboard, such as the top of a guitar or violin—which transfers the sound to the surrounding air. Depending on the instrument, the bridge may be made of carved wood, metal or other materials. The bridge supports the strings and holds them over the body of the instrument under tension.





















