Related Research Articles

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of electrical equipment and systems to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment, by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or even physical damage in operational equipment. The goal of EMC is the correct operation of different equipment in a common electromagnetic environment. It is also the name given to the associated branch of electrical engineering.

Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and private physical structures such as roads, railways, bridges, tunnels, water supply, sewers, electrical grids, and telecommunications. In general, infrastructure has been defined as "the physical components of interrelated systems providing commodities and services essential to enable, sustain, or enhance societal living conditions" and maintain the surrounding environment.

A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions. Between the generating station and consumer, electric power may flow through several substations at different voltage levels. A substation may include transformers to change voltage levels between high transmission voltages and lower distribution voltages, or at the interconnection of two different transmission voltages. They are a common component of the infrastructure, for instance there are 55,000 substations in the United States.

A data center or data centre is a building, a dedicated space within a building, or a group of buildings used to house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems.
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation, especially for environments in outer space, around nuclear reactors and particle accelerators, or during nuclear accidents or nuclear warfare.

Rexel is a French company specializing in the distribution of electrical, heating, lighting and plumbing equipment, but also in renewable energies and energy efficiency products and services. Founded in 1967, Rexel has broadened its scope of activity over the years. Today, its offer combines a wide range of equipment and services in the field of automation, technical expertise, energy management, lighting, security, climatic engineering, communication, home automation and renewable energies.

In materials science, work hardening, also known as strain hardening, is the strengthening of a metal or polymer by plastic deformation. Work hardening may be desirable, undesirable, or inconsequential, depending on the context.
Hardening is a metallurgical metalworking process used to increase the hardness of a metal. The hardness of a metal is directly proportional to the uniaxial yield stress at the location of the imposed strain. A harder metal will have a higher resistance to plastic deformation than a less hard metal.

Marine engineering is the engineering of boats, ships, submarines, and any other marine vessel. Here it is also taken to include the engineering of other ocean systems and structures – referred to in certain academic and professional circles as “ocean engineering.”
Subsea technology involves fully submerged ocean equipment, operations, or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term subsea is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marine or ocean engineering, ocean exploration, remotely operated vehicle (ROVs) autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), submarine communications or power cables, seafloor mineral mining, oil and gas, and offshore wind power.
The environmental benefits of renewable energy technologies are widely recognised, but the contribution that they can make to energy security is less well known. Renewable technologies can enhance energy security in electricity generation, heat supply, and transportation.

Electricity pricing can vary widely by country or by locality within a country. Electricity prices are dependent on many factors, such as the price of power generation, government taxes or subsidies, CO
2 taxes, local weather patterns, transmission and distribution infrastructure, and multi-tiered industry regulation. The pricing or tariffs can also differ depending on the customer-base, typically by residential, commercial, and industrial connections.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. It consists of:
Cegelec or Actemium is a French engineering company specialized in electrical infrastructure, HVAC, information technology, nuclear energy development, transport infrastructure, robotics and offering both public and private services. Cegelec was officially formed in 1989, and as of 2014 the company employs around 22,000 people and operates in 30 countries, with major activity in France, Brazil, Indonesia, the Middle East and Africa. It was acquired by Vinci Energies on 14 April 2010, assimilating the collection of Cegelec's sub-companies, which each specialize in a specific field or geographical region, into Vinci's corporate system.
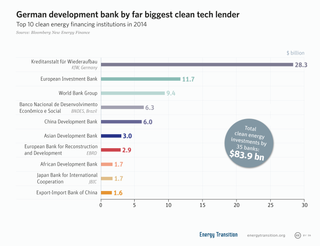
Climate finance is "finance that aims at reducing emissions, and enhancing sinks of greenhouse gases and aims at reducing vulnerability of, and maintaining and increasing the resilience of, human and ecological systems to negative climate change impacts", as defined by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Standing Committee on Finance. The term has been used in a narrow sense to refer to transfers of public resources from developed to developing countries, in light of their UN Climate Convention obligations to provide "new and additional financial resources", and in a wider sense to refer to all financial flows relating to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
National Innovations in Climate Resilient Agriculture (NICRA) was launched during February 2011 by Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) with the funding from Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India. The mega project has three major objectives of strategic research, technology demonstrations and capacity building. Assessment of the impact of climate change simultaneous with formulation of adaptive strategies is the prime approach under strategic research across all sectors of agriculture, dairying and fisheries.

Fiber to the office (FTTO) is an alternative cabling concept for local area network (LAN) network office environments. It combines passive elements and active mini-switches to provide end devices with Gigabit Ethernet. FTTO involves centralised optical fibre cabling techniques to create a combined backbone/horizontal channel; this channel is provided from the work areas to the centralised cross-connect or interconnect by allowing the use of pull-through cables or splices in the telecommunications room.

In February 2021, the state of Texas suffered a major power crisis, which came about during three severe winter storms sweeping across the United States on February 10–11, 13–17, and 15–20. The storms triggered the worst energy infrastructure failure in Texas state history, leading to shortages of water, food, and heat. More than 4.5 million homes and businesses were left without power, some for several days. At least 246 people were killed directly or indirectly, with some estimates as high as 702 killed as a result of the crisis.

The climate in Texas is changing partially due to global warming and rising trends in greenhouse gas emissions. As of 2016, most area of Texas had already warmed by 1.5 °F (0.83 °C) since the previous century because of greenhouse gas emissions by the United States and other countries. Texas is expected to experience a wide range of environmental impacts from climate change in the United States, including rising sea levels, more frequent extreme weather events, and increasing pressure on water resources.
References
- ↑ "Hardening and Resiliency: U.S. Energy Industry Response to Recent Hurricane Seasons" (PDF). US Department of Energy. Retrieved July 9, 2013.