
Cyberspace is an interconnected digital environment. It is a type of virtual world popularized with the rise of the Internet. The term entered popular culture from science fiction and the arts but is now used by technology strategists, security professionals, governments, military and industry leaders and entrepreneurs to describe the domain of the global technology environment, commonly defined as standing for the global network of interdependent information technology infrastructures, telecommunications networks and computer processing systems. Others consider cyberspace to be just a notional environment in which communication over computer networks occurs. The word became popular in the 1990s when the use of the Internet, networking, and digital communication were all growing dramatically; the term cyberspace was able to represent the many new ideas and phenomena that were emerging. As a social experience, individuals can interact, exchange ideas, share information, provide social support, conduct business, direct actions, create artistic media, play games, engage in political discussion, and so on, using this global network. Cyberspace users are sometimes referred to as cybernauts.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods.
Smartdust is a system of many tiny microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) such as sensors, robots, or other devices, that can detect, for example, light, temperature, vibration, magnetism, or chemicals. They are usually operated on a computer network wirelessly and are distributed over some area to perform tasks, usually sensing through radio-frequency identification. Without an antenna of much greater size the range of tiny smart dust communication devices is measured in a few millimeters and they may be vulnerable to electromagnetic disablement and destruction by microwave exposure.
UVC-based preservation is an archival strategy for handling the preservation of digital objects. It employs the use of a Universal Virtual Computer (UVC)—a virtual machine (VM) specifically designed for archival purposes, that allows both emulation and migration to a language-neutral format like XML.
Object hyperlinking is a term that refers to extending the Internet to objects and locations in the real world. Object hyperlinking aims to extend the Internet to the physical world by attaching tags with URLs to tangible objects or locations. These object tags can then be read by a wireless mobile device and information about objects and locations retrieved and displayed.
Locative media or location-based media (LBM) is a virtual medium of communication functionally bound to a location. The physical implementation of locative media, however, is not bound to the same location to which the content refers.

Paul A. Moskowitz works at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center in New York. Moskowitz is a graduate of Stuyvesant High School in New York City, received a Ph.D. in physics at New York University, and has held research and teaching positions at the Université Grenoble, Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz, and at the University of Colorado Boulder. His early work in the area of nuclear physics resulted in the publication of the Moskowitz-Lombardi rule.
The clipped tag is a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag designed to enhance consumer privacy. RFID is an identification technology in which information stored in semiconductor chips contained in RFID tags is communicated by means of radio waves to RFID readers. The most simple passive RFID tags do not have batteries or transmitters. They get their energy from the field of the reader. They transfer their information to the reader by modulating the signal that is reflected back to the reader by the tag. Because tags depend on the reader for power their range is limited, typically up to 10 meters (33 ft) for UHF RFID tags.
Paolo Magrassi is an Italian technologist known as one of the authors of the Supranet concept, the co-creator of the AlphaIC methodology for assessing the value of information technology expenditures, and the manager of the Pontifex project, which in the mid-1980s introduced a novel approach to complex fleet scheduling.
The Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communications networks. The Internet of things encompasses electronics, communication, and computer science engineering. "Internet of things" has been considered a misnomer because devices do not need to be connected to the public internet; they only need to be connected to a network and be individually addressable.

Virtual graffiti consists of virtual or digital media applied to public locations, landmarks or surfaces. Virtual graffiti applications utilize augmented reality and ubiquitous computing to anchor virtual graffiti to physical landmarks or objects in the real world. The virtual content can then be viewed through digital devices. Virtual graffiti is aimed at delivering messaging and social multimedia content to mobile applications and devices based on the identity, location, and community of the user.
Presence is a theoretical concept describing the extent to which media represent the world. Presence is further described by Matthew Lombard and Theresa Ditton as “an illusion that a mediated experience is not mediated." Today, it often considers the effect that people experience when they interact with a computer-mediated or computer-generated environment. The conceptualization of presence borrows from multiple fields including communication, computer science, psychology, science, engineering, philosophy, and the arts. The concept of presence accounts for a variety of computer applications and Web-based entertainment today that are developed on the fundamentals of the phenomenon, in order to give people the sense of, as Sheridan called it, “being there."
A projection augmented model is an element sometimes employed in virtual reality systems. It consists of a physical three-dimensional model onto which a computer image is projected to create a realistic looking object. Importantly, the physical model is the same geometric shape as the object that the PA model depicts.
A smart object is an object that enhances the interaction with not only people but also with other smart objects. Also known as smart connected products or smart connected things (SCoT), they are products, assets and other things embedded with processors, sensors, software and connectivity that allow data to be exchanged between the product and its environment, manufacturer, operator/user, and other products and systems. Connectivity also enables some capabilities of the product to exist outside the physical device, in what is known as the product cloud. The data collected from these products can be then analyzed to inform decision-making, enable operational efficiencies and continuously improve the performance of the product.
Dynamic Infrastructure is an information technology concept related to the design of data centers, whereby the underlying hardware and software can respond dynamically and more efficiently to changing levels of demand. In other words, data center assets such as storage and processing power can be provisioned to meet surges in user's needs. The concept has also been referred to as Infrastructure 2.0 and Next Generation Data Center.
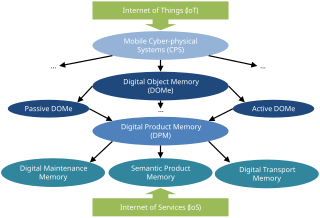
A digital object memory (DOMe) is a digital storage space intended to keep permanently all related information about a concrete physical object instance that is collected during the lifespan of this object and thus forms a basic building block for the Internet of Things (IoT) by connecting digital information with physical objects.
Nearables is a term for a type of smart object, invented by Estimote Inc.. The term is used to describe everyday items that have small, wireless computing devices attached to them. These devices can be equipped with a variety of sensors and work as transmitters to broadcast digital data through a variety of methods, but they usually use the Bluetooth Smart protocol. Due to this, these objects are able to provide mobile devices in range with information about their location, state and immediate surroundings. The word 'nearables' is a reference to wearable technology – electronic devices worn as part of clothing or jewellery.
A digital twin is a digital model of an intended or actual real-world physical product, system, or process that serves as the effectively indistinguishable digital counterpart of it for practical purposes, such as simulation, integration, testing, monitoring, and maintenance. The digital twin has been intended from its initial introduction to be the underlying premise for Product Lifecycle Management and exists throughout the entire lifecycle of the physical entity it represents. Since information is granular, the digital twin representation is determined by the value-based use cases it is created to implement. The digital twin can and does often exist before there is a physical entity, as for example with virtual prototyping. The use of a digital twin in the creation phase allows the intended entity's entire lifecycle to be modeled and simulated. A digital twin of an existing entity may be used in real-time and regularly synchronized with the corresponding physical system.
The industrial internet of things (IIoT) refers to interconnected sensors, instruments, and other devices networked together with computers' industrial applications, including manufacturing and energy management. This connectivity allows for data collection, exchange, and analysis, potentially facilitating improvements in productivity and efficiency as well as other economic benefits. The IIoT is an evolution of a distributed control system (DCS) that allows for a higher degree of automation by using cloud computing to refine and optimize the process controls.

Spatial computing is any of various human–computer interaction techniques that are perceived by users as taking place in the real world, in and around their natural bodies and physical environments, instead of constrained to and perceptually behind computer screens. This concept inverts the long-standing practice of teaching people to interact with computers in digital environments, and instead teaches computers to better understand and interact with people more naturally in the human world. This concept overlaps with others including extended reality, augmented reality, mixed reality, natural user interface, contextual computing, affective computing, and ubiquitous computing. The usage for labeling and discussing these adjacent technologies is imprecise.




