
Field hockey is a team sport structured in standard hockey format, in which each team plays with ten outfield players and a goalkeeper. Teams must drive a round hockey ball by hitting it with a hockey stick towards the rival team's shooting circle and then into the goal. The match is won by the team that scores the most goals. Matches are played on grass, watered turf, artificial turf, synthetic field, or indoor boarded surface.

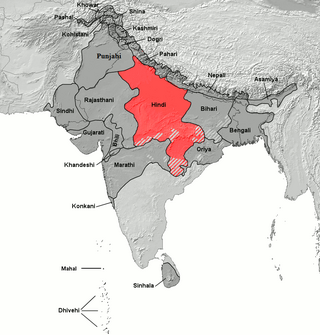
Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in the Hindi Belt region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern, and western India. Hindi has been described as a standardised and Sanskritised register of the Hindustani language, which itself is based primarily on the Khariboli dialect of Delhi and neighbouring areas of North India. Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, is one of the two official languages of the Government of India, along with English. It is an official language in nine states and three union territories and an additional official language in three other states. Hindi is also one of the 22 scheduled languages of the Republic of India.

Korfball is a ball sport, with similarities to netball and basketball. It is played by two teams of eight players with four female players and four male players in each team. The objective is to throw a ball into a netless basket that is mounted on a 3.5 m high pole.

Kabaddi is a contact team sport. Played between two teams of seven players, the objective of the game is for a single player on offence, referred to as a "raider", to run into the opposing team's half of the court, touch out as many of their players and return to their own half of the court, all without being tackled by the defenders in 30 seconds. Points are scored for each player tagged by the raider, while the opposing team earns a point for stopping the raider. Players are taken out of the game if they are touched or tackled, but are brought back in for each point scored by their team from a tag or a tackle.

Netball is a ball sport played on a court by two teams of seven players. It is among a rare number of sports which have been created exclusively for female competitors. The sport is played on indoor and outdoor netball courts and is specifically played in schools. Netball is most popularly played in Commonwealth nations.

Thumri is a vocal genre or style of Indian music. The term "thumri" is derived from the Hindi verb thumuknaa, which means "to walk with a dancing gait in such a way that the ankle-bells tinkle." The form is, thus, connected with dance, dramatic gestures, mild eroticism, evocative love poetry and folk songs, especially from Uttar Pradesh, though there are regional variations.

In ice hockey, a goal is scored when the puck entirely crosses the goal line between the two goal posts and below the goal crossbar. A goal awards one point to the team attacking the goal scored upon, regardless of which team the player who actually deflected the puck into the goal belongs to. Typically, a player on the team attempting to score shoots the puck with their stick towards the goal net opening, and a player on the opposing team called a goaltender tries to block the shot to prevent a goal from being scored against their team.
The Field Game is one of two codes of football devised and played at Eton College. The other is the Eton Wall Game. The game is like association football in some ways – the ball is round, but one size smaller than a standard football, and may not be handled – but the off-side rules – known as 'sneaking' – are more in keeping with rugby. There is also a small scrum or "Bully" of either six or seven a side. Goals can be scored much as in football, although there is no goalkeeper. But a team gains more points for scoring a 'rouge'. To score a rouge a player must kick the ball so that it deflects off one of the opposing players, or achieve a charge-down, and then goes beyond the opposition's end of the pitch. The ball is then 'rougeable' and must be touched – although not necessarily to the ground – by an attacking player to complete the rouge for five points. Rouges are similar to tries in that the scoring team then attempts to convert them for two points.

Tag is a playground game involving two or more players chasing other players in an attempt to "tag" and mark them out of play, usually by touching with a hand. There are many variations; most forms have no teams, scores, or equipment. Usually, when a person is tagged, the tagger says, "Tag, you're 'it'!" The last one tagged during tag is "it" for the next round. The game is known by other names in various parts of the world, including "running and catching" in India and "catch and cook" in the Middle East.

A corner kick is the method of restarting play in a game of association football when the ball goes out of play over the goal line, without a goal being scored and having last been touched by a member of the defending team. The kick is taken from the corner of the field of play nearest to the place where the ball crossed the goal line.

Awadhi, also known as Audhi (औधी), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in northern India and Nepal. It is primarily spoken in the Awadh region of present-day Uttar Pradesh, India. The name Awadh is connected to Ayodhya, the ancient city, which is regarded as the homeland of the Hindu god Rama. See also, the Oudh state which was settled in North India during the Mughal rule. It was, along with Braj Bhasha, used widely as a literary vehicle before being displaced by Hindustani in the 19th century.

Oină is a Romanian traditional sport, similar in many ways to baseball.
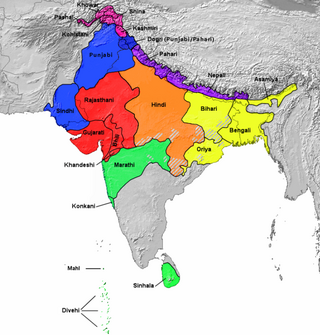
The Hindi Belt, also known as the Hindi Heartland, is a linguistic region encompassing parts of northern, central, eastern and western India where various Central Indo-Aryan languages subsumed under the term 'Hindi' are spoken. The Hindi belt is sometimes also used to refer to nine Indian states whose official language is Hindi, namely Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and the union territory of Chandigarh and the National Capital Territory of Delhi. It is also referred to as the Hindi–Urdu Belt or Hindustani Belt by some writers.

Kho kho or kho-kho is a traditional Indian sport that dates back to ancient India. It is the second-most popular traditional tag game in the Indian subcontinent after kabaddi. Kho kho is played on a rectangular court with a central lane connecting two poles which are at either end of the court. During the game, nine players from the chasing team are on the field, with eight of them sitting (crouched) in the central lane, while three runners from the defending team run around the court and try to avoid being touched. Each sitting player on the chasing team faces the opposite direction of their adjacent teammates.
Caribbean Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by Indo-Caribbeans and the Indo-Caribbean diaspora. It is mainly based on the Bhojpuri and Awadhi dialects. These Hindustani dialects were the most spoken dialects by the Indians who came as immigrants to the Caribbean from India as indentured laborers. It is closely related to Fiji Hindi and the Bhojpuri-Hindustani spoken in Mauritius and South Africa.
The Central Indo-Aryan languages or Hindi languages are a group of related language varieties Spoken across North India and Central India. These language varieties form the central part of the Indo-Aryan language family, itself a part of the Indo-European language family. They historically form a dialect continuum that descends from the Middle Prakrits. Located in the Hindi Belt, the Central Zone includes the Dehlavi (Delhi) dialect of the Hindustani language, The lingua franca of Northern India that is the basis of the Modern Standard Hindi and Modern Standard Urdu literary standards. In regards to the Indo-Aryan language family, the coherence of this language group depends on the classification being used; here only Eastern and Western Hindi will be considered.

Atya patya or atya-patya is a traditional Indian tag sport played by two sides of nine players. It is more popular in rural areas of India. It is more commonly played in Maharashtra, a western Indian state. Atya patya is described as a "game of feints". The playing area comprises nine trenches, coming out of either side of a central trench; a point is awarded to the attacking team's players for each trench they cross without being tagged out by the defensive players within the trenches. The game ends after 4 innings of 7 minutes each, with each team having two innings to score. It has been described as a game of "militant chase". The sport is played in a relatively small area and requires no equipment, similar to other games indigenous to India such as kabaddi, seven stones, kho kho, gillidanda and langdi.

Punjabis play a wide variety of sports and games, ranging from modern games such as hockey and cricket, to the more traditional games such as Kabaddi, Kushtian (wrestling) and Khuddo khoondi. There are over 100 traditional games and sports of Punjab.

India has several traditional games and sports, some of which have been played for thousands of years. Many of these games do not require much equipment or playing space. Some traditional Indian games are only played in certain regions of India, or may be known by different names and played under different rules in different regions of the country. Many Indian games are also similar to other traditional South Asian games.

Vidya Vindu Singh is an Indian author in Hindi and Awadhi languages. She is best known for her broad work in folk and children's literature. Singh has been awarded Padma Shri in 2022 by the Government of India for her contributions in the field of literature & education.


















